题目描述
飞飞国是一个传说中的国度,国家的居民叫做飞飞侠。飞飞国是一个N×M 的矩形方阵,每个格子代表一个街区。
然而飞飞国是没有交通工具的。飞飞侠完全靠地面的弹射装置来移动。
每个街区都装有弹射装置。使用弹射装置是需要支付一定费用的。而且每个弹射装置都有自己的弹射能力。
我们设第 i 行第 j 列的弹射装置有 A_{i,j} 的费用和 B_{i,j}
的弹射能力。并规定有相邻边的格子间距离是 1。那么,任何飞飞侠都只需要在 (i,j)支付 A_{i,j}
的费用就可以任意选择弹到距离不超过 B_{i,j}的位置了。如下图
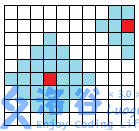
(从红色街区交费以后可以跳到周围的任意蓝色街区。)
现在的问题很简单。有三个飞飞侠,分别叫做 X, Y, Z现在它们决定聚在一起玩,于是想往其中一人的位置集合。告诉你 3 个飞飞侠的坐标,求往哪里集合大家需要花的费用总和最低。(费用相同时优先 X,次优先 Y)
输入格式
输入的第一行包含两个整数 N 和 M,分别表示行数和列数。
接下来是 22 个N×M 的自然数矩阵,为 B_{i,j}和 A_{i,j}
最后一行六个数,分别代表 X, Y, Z所在地的行号和列号。
输出格式
第一行输出一个字符 X, Y或者 Z。表示最优集合地点。
第二行输出一个整数,表示最小费用。
如果无法集合,只输出一行 NO。
输入输出样例
输入
4 4
0 0 0 0
1 2 2 0
0 2 2 1
0 0 0 0
5 5 5 5
5 5 5 5
5 5 5 5
5 5 5 5
2 1 3 4 2 2
输出
Z
15
说明/提示
对于 100% 的数据,(1leq N, Mleq 150 quad 0leq B_{i, j}leq 10^9 quad 0leq A_{i, j}leq 1000)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
namespace FastIO {
char buf[1 << 21], buf2[1 << 21], a[20], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf, hh = '
';
int p, p3 = -1;
void read() {}
void print() {}
inline int getc() {
return p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 1 << 21, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++;
}
inline void flush() {
fwrite(buf2, 1, p3 + 1, stdout), p3 = -1;
}
template<typename T, typename... T2>
inline void read(T &x, T2 &... oth) {
int f = 0;
x = 0;
char ch = getc();
while (!isdigit(ch)) {
if (ch == '-')
f = 1;
ch = getc();
}
while (isdigit(ch)) {
x = x * 10 + ch - 48;
ch = getc();
}
x = f ? -x : x;
read(oth...);
}
template<typename T, typename... T2>
inline void print(T x, T2... oth) {
if (p3 > 1 << 20)
flush();
if (x < 0)
buf2[++p3] = 45, x = -x;
do {
a[++p] = x % 10 + 48;
} while (x /= 10);
do {
buf2[++p3] = a[p];
} while (--p);
buf2[++p3] = hh;
print(oth...);
}
} // namespace FastIO
#define read FastIO::read
#define print FastIO::print
//======================================
using namespace std;
const int maxn=3e5+10;
const int mod=31011;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> PII ;
int n,m,ans=inf;
char ansch;
int a[160][160],b[160][160];
int d[160][160][320],vis[160][160][320];
int dx[]={0,1,-1,0,0};
int dy[]={0,0,0,1,-1};
struct node {
int x, y, sheng, cost;
bool operator<(const node &oth) const {
return cost > oth.cost;
}
};
int x1,yy,x2,y2,y3,x3;
void Dijkstra(int x,int y) {
priority_queue<node> q;
memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d));
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
vis[x][y][0] = 1;
d[x][y][b[x][y]] = a[x][y];
q.push(node{x, y, b[x][y], a[x][y]});
while (!q.empty()) {
if (vis[x1][yy][0] && vis[x2][y2][0] && vis[x3][y3][0]) break;
node p = q.top();
q.pop();
x=p.x;y=p.y;
int sheng = p.sheng;
if (vis[x][y][sheng]) continue;
vis[x][y][sheng] = 1;
if (sheng > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int nowx = x + dx[i];
int nowy = y + dy[i];
if (nowx >= 1 && nowx <= n && nowy >= 1 && nowy <= m) {
if (d[nowx][nowy][sheng - 1] > d[x][y][sheng]) {
d[nowx][nowy][sheng - 1] = d[x][y][sheng];
q.push(node{nowx, nowy, sheng - 1, d[nowx][nowy][sheng - 1]});
}
}
}
} else {
int t = b[x][y];
if (d[x][y][t] > d[x][y][0] + a[x][y]) {
d[x][y][t] = d[x][y][0] + a[x][y];
q.push(node{x, y, b[x][y], d[x][y][t]});
}
}
}
}
int main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin);
//freopen("2.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
//======================================
read(n, m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
read(b[i][j]);
b[i][j] = min(b[i][j], max(i + j - 2, n - i + m - j));
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
read(a[i][j]);
}
}
read(x1, yy, x2, y2, x3, y3);
Dijkstra(x1, yy);
int a1 = d[x2][y2][0], a2 = d[x3][y3][0];
Dijkstra(x2, y2);
int b1 = d[x1][yy][0], b2 = d[x3][y3][0];
Dijkstra(x3, y3);
int c1 = d[x1][yy][0], c2 = d[x2][y2][0];
if (ans > b1 + c1) {
ans = b1 + c1;
ansch = 'X';
}
if (ans > a1 + c2) {
ans = a1 + c2;
ansch = 'Y';
}
if (ans > a2 + b2) {
ans = a2 + b2;
ansch = 'Z';
}
if (ans == inf) puts("NO");
else {
printf("%c
%d
", ansch, ans);
}
//======================================
FastIO::flush();
return 0;
}