使用pydoc可以很方便的查看类和方法结构,可以在命令行里打开,也可以在浏览器里。
网页界面好可爱的说。。。极大地提高了我查看源码的兴趣啊。。。
命令行版像这样。。。回车就能查看更多。
PS C:pythonlearnPy3Hardway> python -m pydoc os Help on module os: NAME os - OS routines for NT or Posix depending on what system we're on. DESCRIPTION This exports: - all functions from posix or nt, e.g. unlink, stat, etc. - os.path is either posixpath or ntpath - os.name is either 'posix' or 'nt' - os.curdir is a string representing the current directory (always '.') - os.pardir is a string representing the parent directory (always '..') - os.sep is the (or a most common) pathname separator ('/' or '\') - os.extsep is the extension separator (always '.') - os.altsep is the alternate pathname separator (None or '/') - os.pathsep is the component separator used in $PATH etc - os.linesep is the line separator in text files (' ' or ' ' or ' ') - os.defpath is the default search path for executables - os.devnull is the file path of the null device ('/dev/null', etc.) Programs that import and use 'os' stand a better chance of being portable between different platforms. Of course, they must then only use functions that are defined by all platforms (e.g., unlink and opendir), and leave all pathname manipulation to os.path (e.g., split and join). CLASSES builtins.Exception(builtins.BaseException) builtins.OSError builtins.object nt.DirEntry builtins.tuple(builtins.object) nt.times_result -- More --
浏览器版:(在8080端口打开)
PS C:pythonlearnPy3Hardway> python -m pydoc -p 8080 Server ready at http://localhost:8080/ Server commands: [b]rowser, [q]uit server> b
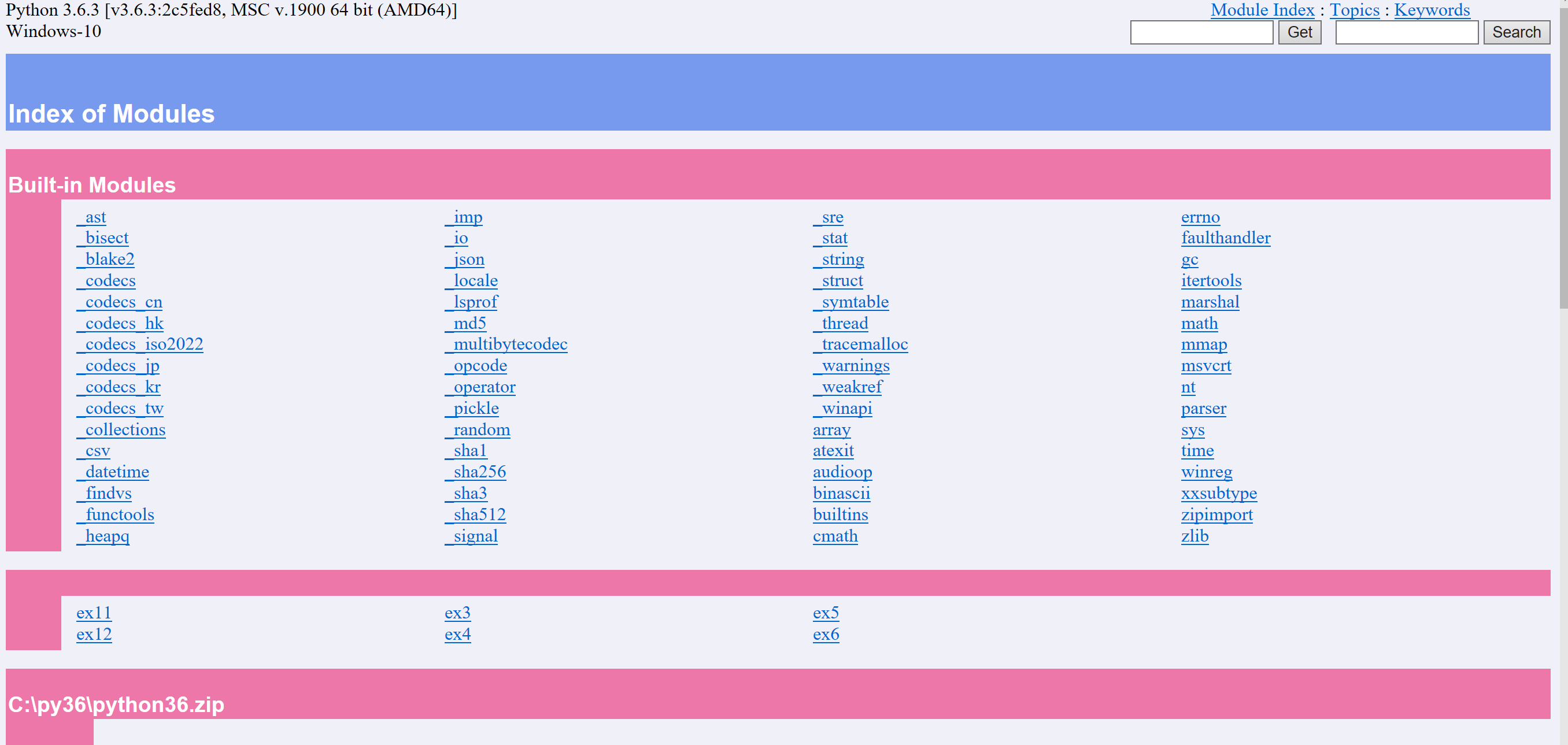
我最喜欢的少女粉呐!!!