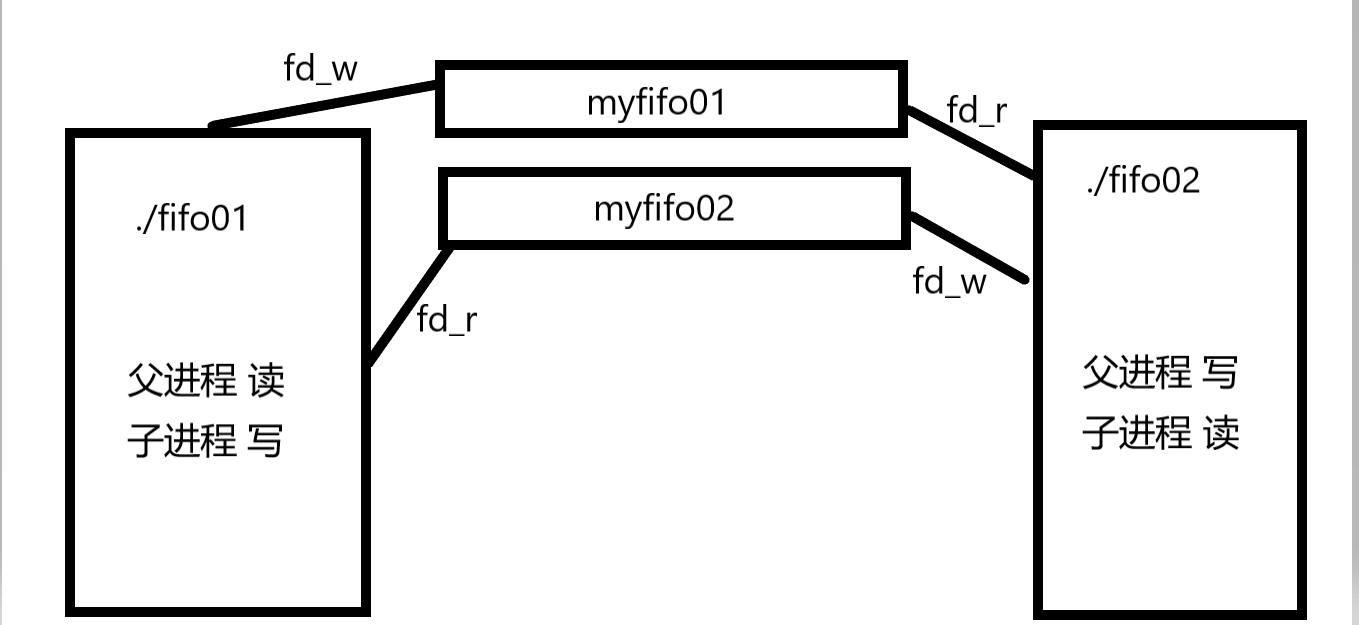
该案例是实现两个进程之间使用命名管道进行通信。
进程1:fifo01.c
1 #include<unistd.h> 2 #include<sys/types.h> 3 #include<sys/stat.h> 4 #include<stdio.h> 5 #include<stdlib.h> 6 #include<fcntl.h> 7 #include<string.h> 8 #include<errno.h> 9 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 10 { 11 if(mkfifo("myfifo1",0664) == -1) 12 { 13 if(errno != EEXIST) 14 { 15 perror("Fail to mkfifo1"); 16 exit(1); 17 } 18 } 19 if(mkfifo("myfifo2",0664) == -1) 20 { 21 if(errno != EEXIST) 22 { 23 perror("Fail to mkfifo1"); 24 exit(1); 25 } 26 } 27 int fd_w = open("myfifo1",O_WRONLY); 28 if(fd_w == -1) 29 { 30 perror("Fail to open myfifo1"); 31 exit(1); 32 } 33 int fd_r = open("myfifo2",O_RDONLY); 34 if(fd_r == -1) 35 { 36 perror("Fail to open myfifo2"); 37 exit(1); 38 } 39 pid_t pid; 40 pid = fork(); 41 if(pid < 0) 42 { 43 perror("fail to fork"); 44 exit(1); 45 } 46 else if(pid == 0) 47 { 48 while (1) 49 { 50 char buf[128] = ""; 51 fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin); 52 buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '�'; 53 if(write(fd_w,buf,strlen(buf)) == -1) 54 { 55 perror("Fail to write"); 56 exit(1); 57 } 58 } 59 60 } 61 else 62 { 63 while(1) 64 { 65 char buf[128] = ""; 66 if(read(fd_r,buf,sizeof(buf)) == -1) 67 { 68 perror("fail to read"); 69 exit(1); 70 } 71 printf("receive from fifo02:%s ",buf); 72 } 73 } 74 close(fd_r); 75 close(fd_w); 76 return 0; 77 }
进程2:fifo02
1 #include<unistd.h> 2 #include<sys/types.h> 3 #include<sys/stat.h> 4 #include<stdio.h> 5 #include<stdlib.h> 6 #include<fcntl.h> 7 #include<string.h> 8 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 9 { 10 int fd_r = open("myfifo1",O_RDONLY); 11 if(fd_r == -1) 12 { 13 perror("fail to open"); 14 exit(1); 15 } 16 int fd_w = open("myfifo2",O_WRONLY); 17 if(fd_w == -1) 18 { 19 perror("fail to write"); 20 exit(1); 21 } 22 pid_t pid; 23 pid = fork(); 24 if(pid == -1) 25 { 26 perror("fail to fork"); 27 exit(1); 28 } 29 else if(pid == 0) 30 { 31 while (1) 32 { 33 char buf[128] = ""; 34 if(read(fd_r,buf,sizeof(buf)) == -1) 35 { 36 perror("fail to read"); 37 exit(1); 38 } 39 printf("received from fifo01:%s ",buf); 40 } 41 42 } 43 else 44 { 45 while (1) 46 { 47 char buf[128] = ""; 48 fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin); 49 buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '�'; 50 if(write(fd_w,buf,strlen(buf)) == -1) 51 { 52 perror("fail to write"); 53 exit(1); 54 } 55 } 56 57 } 58 59 close(fd_w); 60 close(fd_r); 61 return 0; 62 }
运行结果:

原理如下: