知识点梳理
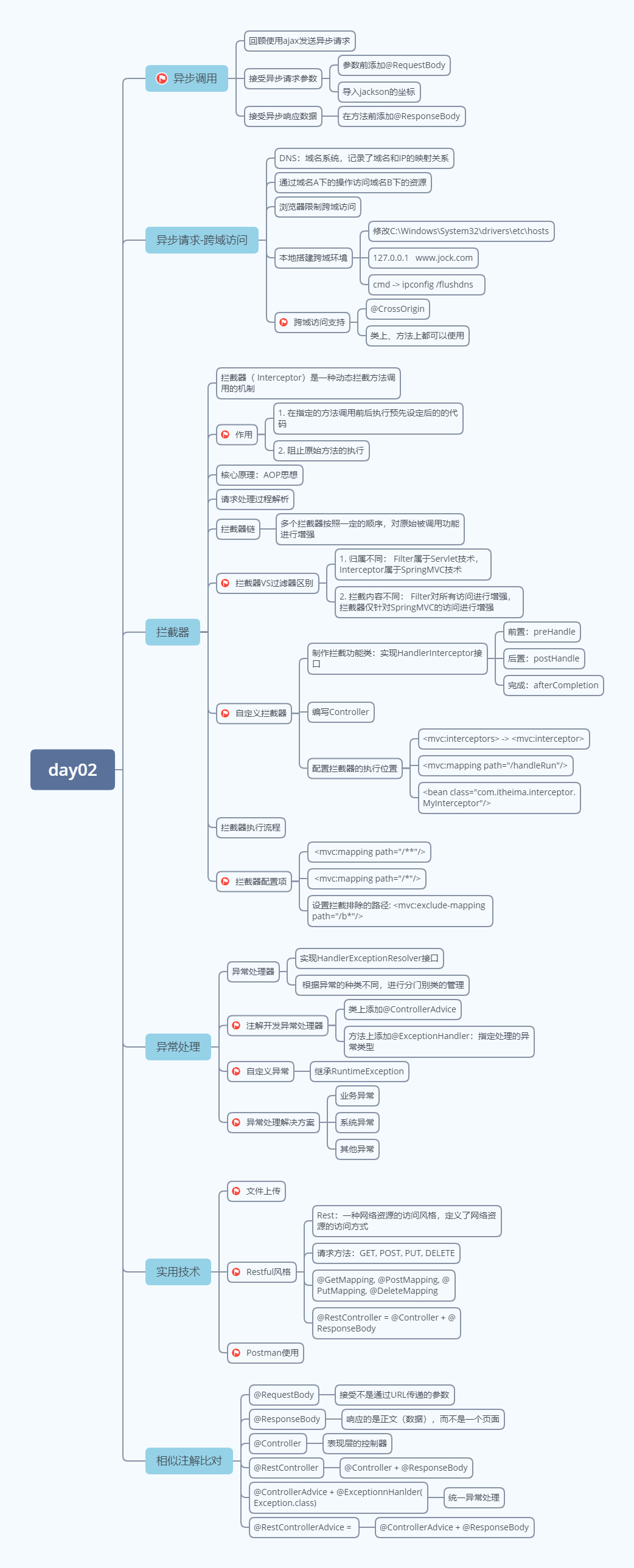
课堂讲义
学习目标
-
-
能够运用@RequestBody和@ResponseBody实现异步交互开发
-
能够阐述@RestController和@RestControllerAdvice注解的作用
-
能够叙述跨域访问的概念
-
能够总结跨域访问产生的问题
-
能够运用@CrossOrigin注解解决跨域访问的问题
-
能够描述REST风格URL的特性和运用的四种请求方式
-
能够描述@PathVariable注解的作用
-
能够使用Postman工具对SpringMVC基于REST风格URL的工程的测试
1 异步调用(重点)
1.1 发送异步请求(回顾)
使用jQuery的ajax方法发送异步请求:
<a href="javascript:void(0);" id="testAjax">访问controller</a> <script type="text/javascript" src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/js/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> $(function(){ $("#testAjax").click(function(){ //为id="testAjax"的组件绑定点击事件 $.ajax({ //发送异步调用 type:"POST", //请求方式: POST请求 url:"ajaxController", //请求url data:'ajax message', //请求参数(也就是请求内容) dataType:"text", //响应正文类型 contentType:"application/text", //请求正文的MIME类型 }); }); }); </script>
1.2 接受异步请求参数(重点)
名称: @RequestBody 类型: 形参注解 位置:处理器类中的方法形参前方 作用:将异步提交数据组织成标准请求参数格式,并赋值给形参 范例:
@RequestMapping("/ajaxController")
public String ajaxController(@RequestBody String message){
System.out.println(message);
return "page.jsp";
}
检查pom.xml是否导入jackson的坐标
<!--json相关坐标3个--> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId> <version>2.9.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.9.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId> <version>2.9.0</version> </dependency>
-
通过JavaScript传递JSON格式数据到服务器
注意:请求数据格式与POJO中的属性对应
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
//添加get,set方法
}
{"name":"Jock","age":39}
//为id="testAjaxPojo"的组件绑定点击事件
$("#testAjaxPojo").click(function(){
$.ajax({
type:"POST",
url:"ajaxPojoToController",
data:'{"name":"Jock","age":39}',
dataType:"text",
contentType:"application/json",
});
});
将@RequestBody注解添加到Pojo参数前方
{"name":"Jock","age":39}
@RequestMapping("/ajaxPojoToController")
//如果处理参数是POJO,且页面发送的请求数据格式与POJO中的属性对应,@RequestBody注解可以自动映射对应请求数据到POJO中
public String ajaxPojoToController(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println("controller pojo :"+user);
return "page.jsp";
}
-
注解添加到集合参数前方时,封装的异步提交数据按照集合的存储结构进行关系映射 注意:页面发送的数据是JSON格式的对象数组
[{"name":"Jock","age":39},{"name":"Jockme","age":40}]//为id="testAjaxList"的组件绑定点击事件$("#testAjaxList").click(function(){ $.ajax({ type:"POST", url:"ajaxListToController", data:'[{"name":"Jock","age":39},{"name":"Jockme","age":40}]', dataType:"text", contentType:"application/json", }); });@RequestMapping("/ajaxListToController") //如果处理参数是List集合且封装了POJO,且页面发送的数据是JSON格式的,数据将自动映射到集合参数中 public String ajaxListToController(@RequestBody List<User> userList){ System.out.println("controller list :"+userList); return "page.jsp"; }
1.3 响应异步请求(复习)
方法返回值为Pojo时,自动封装数据成json对象数据
@RequestMapping("/ajaxReturnJson")
@ResponseBody
public User ajaxReturnJson(){
System.out.println("controller return json pojo...");
User user = new User();
user.setName("Jockme");
user.setAge(40);
return user;
}
方法返回值为List时,自动封装数据成json对象数组数据
@RequestMapping("/ajaxReturnJsonList")
@ResponseBody
//基于jackon技术,使用@ResponseBody注解可以将返回的保存POJO对象的集合转成json数组格式数据
public List ajaxReturnJsonList(){
System.out.println("controller return json list...");
User user1 = new User();
user1.setName("Tom");
user1.setAge(3);
User user2 = new User();
user2.setName("Jerry");
user2.setAge(5);
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.add(user1);
al.add(user2);
return al;
}
//为id="testAjaxReturnJson"的组件绑定点击事件
$("#testAjaxReturnJson").click(function(){
//发送异步调用
$.ajax({
type:"POST",
url:"ajaxReturnJson",
//回调函数
success:function(data){
console.log(data);
alert(JSON.stringify(data));
// alert(data['name']+" , "+data['age']);
}
});
});
2 异步请求-跨域访问
2.1 跨域访问介绍-视频03
-
DNS:域名系统,记录了域名和IP的映射关系
-
在淘宝网站上使用JS访问京东网站
-
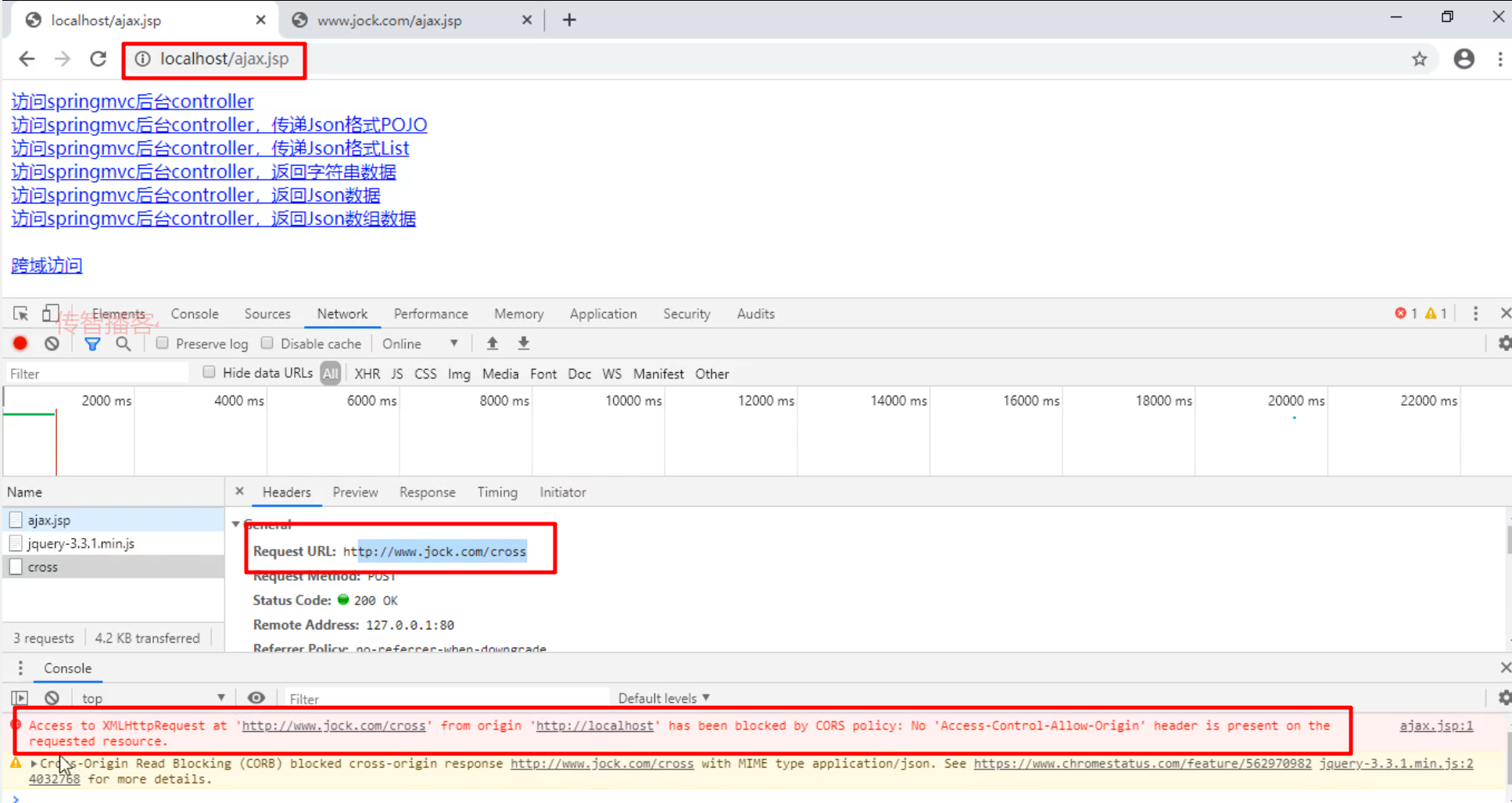
跨域访问:通过域名A下的操作访问域名B下的资源时

-
跨域访问时,会出现无法访问的现象
2.2 跨域环境搭建
-
为当前主机添加备用域名:C:WindowsSystem32driversetc
-
修改windows安装目录中的hosts文件:欺骗浏览器将www.jock.com映射到127.0.0.1
127.0.0.1 www.jock.com -
格式: ip 域名
-
-
动态刷新DNS
-
命令: ipconfig /displaydns
-
命令: ipconfig /flushdns
-
2.3 跨域访问支持
发送跨域请求:
//为id="testCross"的组件绑定点击事件
$("#testCross").click(function(){
//发送异步调用
$.ajax({
type:"POST",
// url:"cross",
url:"http://www.jock.com/cross",
// url:"http://localhost/cross",
//回调函数
success:function(data){
alert("跨域调用信息反馈:"+data['name']+" , "+data['age']);
}
});
});
名称: @CrossOrigin 类型: 方法注解 、 类注解 位置:处理器类中的方法上方 或 类上方 作用:设置当前处理器方法/处理器类中所有方法支持跨域访问 范例:
@RequestMapping("/cross")
@ResponseBody
//使用@CrossOrigin开启跨域访问
//标注在处理器方法上方表示该方法支持跨域访问
//标注在处理器类上方表示该处理器类中的所有处理器方法均支持跨域访问
@CrossOrigin
public User cross(HttpServletRequest request){
System.out.println("controller cross..."+request.getRequestURL());
User user = new User();
user.setName("Jockme");
user.setAge(39);
return user;
}
3 拦截器
3.1 拦截器概念-视频04
拦截器( Interceptor)是一种动态拦截方法调用的机制。
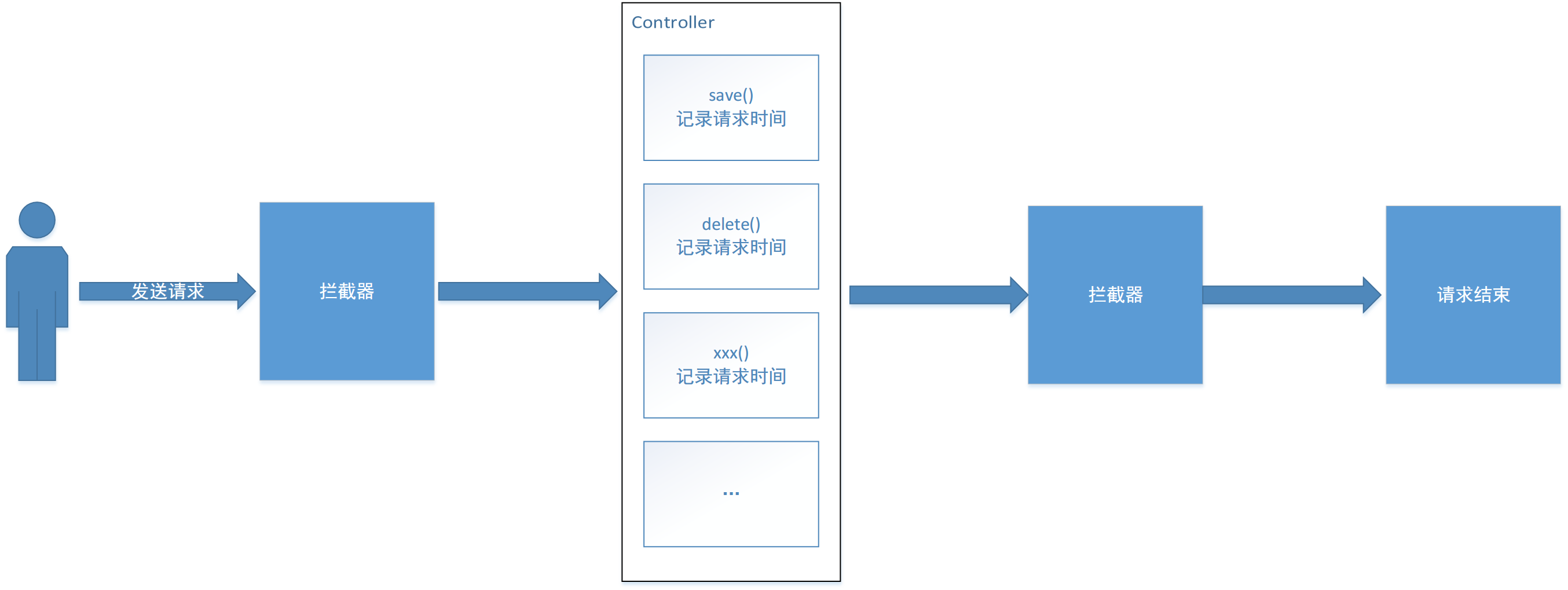
作用:
-
在指定的方法调用前后执行预先设定后的的代码
-
阻止原始方法的调用
核心原理:AOP思想
请求处理过程解析
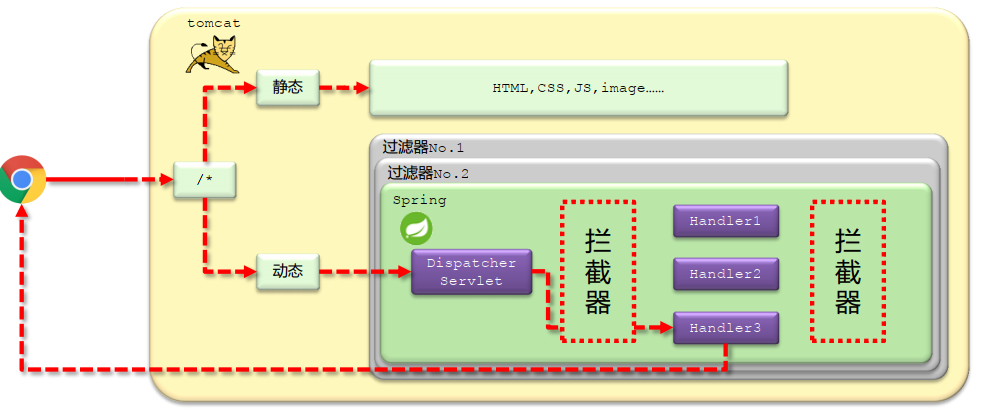
拦截器链:多个拦截器按照一定的顺序,对原始被调用功能进行增强
拦截器VS过滤器区别
-
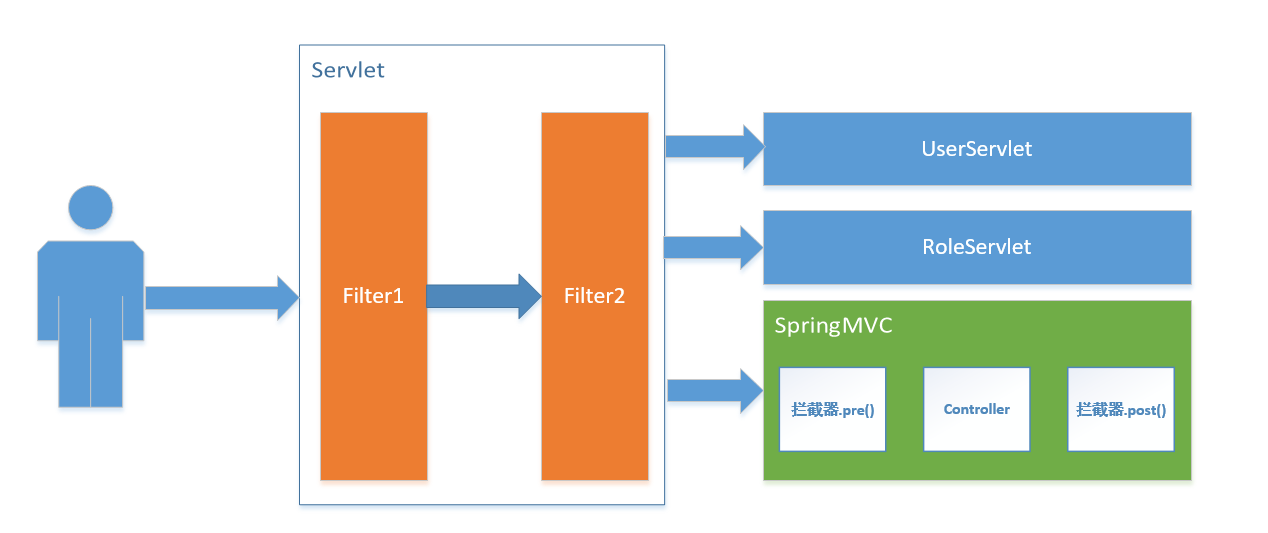
归属不同: Filter属于Servlet技术, Interceptor属于SpringMVC技术
-
拦截内容不同: Filter对所有访问进行增强, 拦截器仅针对SpringMVC的访问进行增强
3.2 自定义拦截器-视频05
-
制作拦截功能类(通知):实现HandlerInterceptor接口
//自定义拦截器需要实现HandleInterceptor接口 public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { //处理器运行之前执行 @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("前置运行----a1"); //返回值为false将拦截原始处理器的运行 //如果配置多拦截器,返回值为false将终止当前拦截器后面配置的拦截器的运行 return true; } //处理器运行之后执行 @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("后置运行----b1"); } //所有拦截器的后置执行全部结束后,执行该操作 @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("完成运行----c1"); } //三个方法的运行顺序为 preHandle -> postHandle -> afterCompletion //如果preHandle返回值为false,三个方法仅运行preHandle }
-
编写Controller
@Controller public class InterceptorController { @RequestMapping("/handleRun") public String handleRun() { System.out.println("业务处理器运行------------main"); return "page.jsp"; } }
-
配置拦截器的执行位置(类似切入点)
<!--开启拦截器使用--> <mvc:interceptors> <!--开启具体的拦截器的使用,可以配置多个--> <mvc:interceptor> <!--设置拦截器的拦截路径--> <mvc:mapping path="/handleRun"/> <!--指定具体的拦截器类--> <bean class="com.itheima.interceptor.MyInterceptor"/> </mvc:interceptor> </mvc:interceptors>
注意:配置顺序为先配置执行位置,后配置执行类
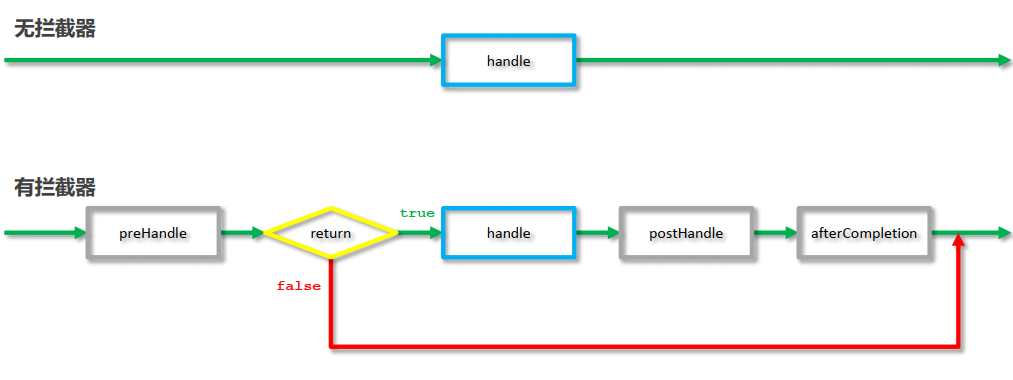
3.3 拦截器执行流程
-
三个方法的运行顺序为 preHandle -> postHandle -> afterCompletion
-
如果preHandle返回值为false,三个方法仅运行preHandle
3.4 详解方法参数-视频06
3.4.1 前置处理方法
原始方法之前运行
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("preHandle"); return true; }
-
参数 request:请求对象 response:响应对象 handler:被调用的处理器对象,本质上是一个方法对象,对反射中的Method对象进行了再包装
-
返回值
返回值为false,被拦截的处理器将不执行
3.4.2 后置处理方法
原始方法运行后运行,如果原始方法被拦截,则不执行
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("postHandle"); System.out.println(modelAndView.getViewName()); modelAndView.setViewName("page2.jsp"); }
-
参数 modelAndView:如果处理器执行完成具有返回结果,可以读取到对应数据与页面信息,并进行调整
3.4.3 完成处理方法
拦截器最后执行的方法,无论原始方法是否执行
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("afterCompletion"); }
-
参数 ex:如果处理器执行过程中出现异常对象,可以针对异常情况进行单独处理
3.5 拦截器配置项
<mvc:interceptor> <!--设置拦截器的拦截路径,支持*通配--> <!--/* 表示拦截所有/开头的映射--> <!--匹配/user,但不能匹配/user/add、/user/del--> <!--/** 表示拦截所有映射--> <!--匹配/user、/user/add、/user/del--> <!--/user/* 表示拦截所有/user/开头的映射--> <!--/user/add* 表示拦截所有/user/开头,且具体映射名称以add开头的映射--> <!--/user/*All 表示拦截所有/user/开头,且具体映射名称以All结尾的映射--> <mvc:mapping path="/**"/> <!--设置拦截排除的路径--> <mvc:exclude-mapping path="/b*"/> <!--指定具体的拦截器类--> <bean class="com.itheima.interceptor.MyInterceptor"/> </mvc:interceptor>
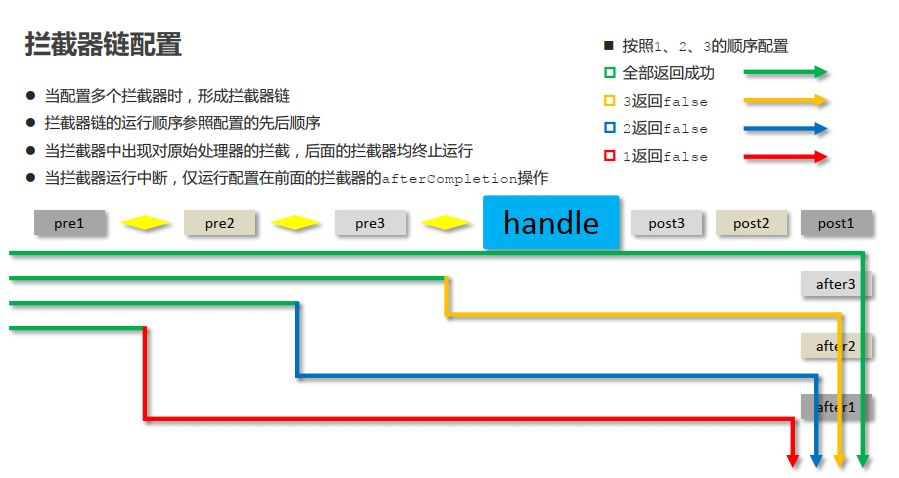
拦截器完整执行过程如下所示:

3.6 多拦截器配置-视频07
多拦截配置使用多个mvc:interceptor
<mvc:interceptors> <mvc:interceptor> <mvc:exclude-mapping path="/*"/> <!--指定具体的拦截器类--> <bean class="com.itheima.interceptor.MyInterceptor1"/> </mvc:interceptor> <!--配置多个拦截器,配置顺序即为最终运行顺序--> <mvc:interceptor> <mvc:mapping path="/*"/> <bean class="com.itheima.interceptor.MyInterceptor2"/> </mvc:interceptor> <mvc:interceptor> <mvc:mapping path="/*"/> <bean class="com.itheima.interceptor.MyInterceptor3"/> </mvc:interceptor> </mvc:interceptors>
拦截器链:多个拦截器按照一定的顺序,对原始被调用功能进行增强
责任链模式 责任链模式是一种行为模式 特征:沿着一条预先设定的任务链顺序执行,每个节点具有独立的工作任务 优势: 独立性:只关注当前节点的任务,对其他任务直接放行到下一节点 隔离性:具备链式传递特征,无需知晓整体链路结构,只需等待请求到达后进行处理即可 灵活性:可以任意修改链路结构动态新增或删减整体链路责任 解耦:将动态任务与原始任务解耦
弊端: 链路过长时,处理效率低下 如果节点对象存在循环引用时,会造成死循环,导致系统崩溃
4 异常处理
4.1 异常处理器-视频08
1.实现HandlerExceptionResolver接口(异常处理器)
@Component
public class ExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler,
Exception ex) {
System.out.println("异常处理器正在执行中");
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
//定义异常现象出现后,反馈给用户查看的信息
modelAndView.addObject("msg","出错啦! ");
//定义异常现象出现后,反馈给用户查看的页面
modelAndView.setViewName("error.jsp");
return modelAndView;
}
}
2.根据异常的种类不同,进行分门别类的管理,返回不同的信息
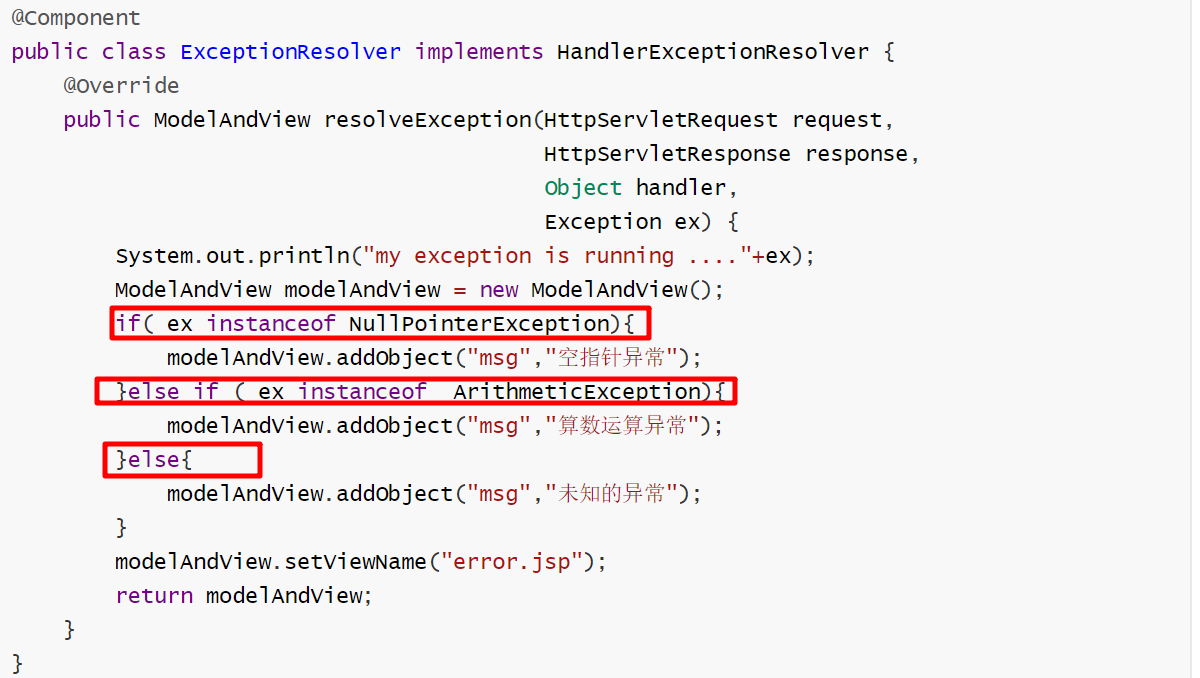
@Component public class ExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver { @Override public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) { System.out.println("my exception is running ...."+ex); ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); if( ex instanceof NullPointerException){ modelAndView.addObject("msg","空指针异常"); }else if ( ex instanceof ArithmeticException){ modelAndView.addObject("msg","算数运算异常"); }else{ modelAndView.addObject("msg","未知的异常"); } modelAndView.setViewName("error.jsp"); return modelAndView; } }
3.在Controller中模拟不同的异常进行测试
//http://localhost/save @RequestMapping("/save") @ResponseBody public String save() throws Exception { System.out.println("user controller save is running ..."); //模拟业务层发起调用产生了异常 //除0算术异常 //int i = 1/0; //空指针异常 //String str = null; //str.length(); return ""; }
4.2 注解开发异常处理器(重点)-视频09
上述异常处理器中包含太多if else逻辑判断,需要进行优化:
-
使用注解实现异常分类管理 名称: @ControllerAdvice 类型: 类注解 位置:异常处理器类上方 作用:设置当前类为异常处理器类 范例:
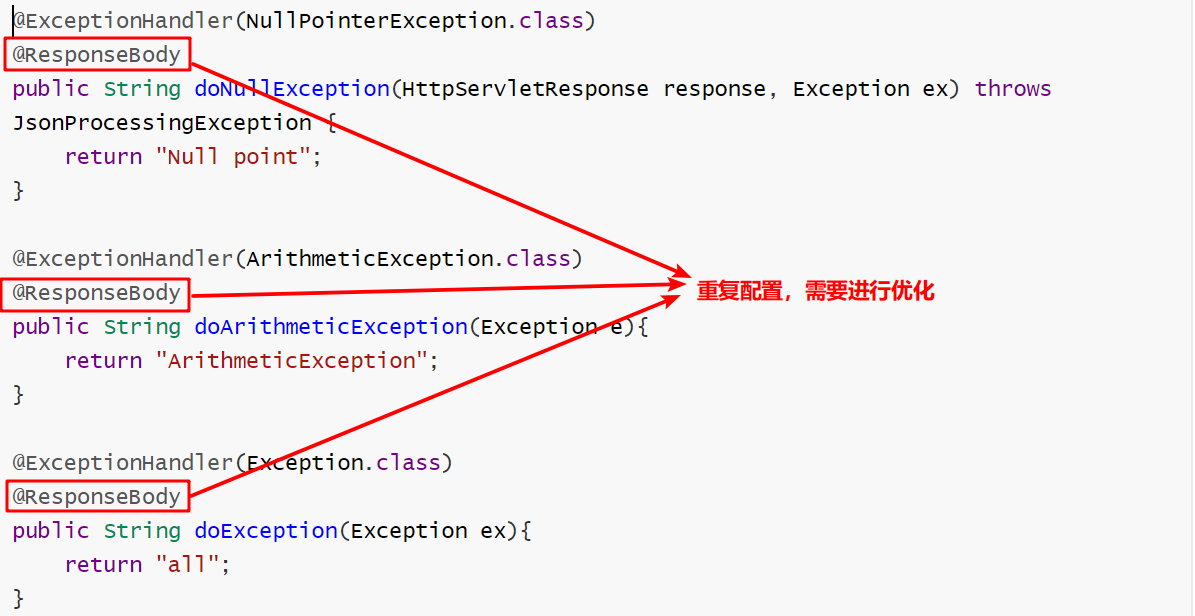
@ControllerAdvice public class ExceptionAdvice { } 使用注解实现异常分类管理 名称: @ExceptionHandler 类型: 方法注解 位置:异常处理器类中针对指定异常进行处理的方法上方 作用:设置指定异常的处理方式 说明:处理器方法可以设定多个 范例: @ExceptionHandler(NullPointerException.class) @ResponseBody public String doNullException(HttpServletResponse response, Exception ex) throws JsonProcessingException { return "Null point"; } @ExceptionHandler(ArithmeticException.class) @ResponseBody public String doArithmeticException(Exception e){ return "ArithmeticException"; } @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) @ResponseBody public String doException(Exception ex){ return "all"; }
扩展知识
1.如果标记了@ControllerAdvice类中的每个方法都使用了@ResponseBody,可以采用如下的简写方式:
//@ResponseBody //@ControllerAdvice @RestControllerAdvice //= @ControllerAdvice + @ResponseBody public class ExceptionAdvice { }
@RestControllerAdvice = @ControllerAdvice + @ResponseBody
2.@ResponseBody返回中文字符串乱码,在spring-mvc.xml配置转换器编码:
<mvc:annotation-driven> <mvc:message-converters> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter"> <constructor-arg value="UTF-8" /> </bean> </mvc:message-converters> </mvc:annotation-driven>
4.3 项目异常处理方案(理解)-视频10
-
异常处理方案
-
业务异常: 发送对应消息传递给用户,提醒规范操作
-
系统异常: 发送固定消息传递给用户,安抚用户 发送特定消息给运维人员,提醒维护 记录日志
-
其他异常: 发送固定消息传递给用户,安抚用户 发送特定消息给编程人员,提醒维护
-
纳入预期范围内
记录日志
-
-
4.4 自定义异常
-
自定义BusinessException
//自定义异常继承RuntimeException,覆盖父类所有的构造方法 public class BusinessException extends RuntimeException { public BusinessException() { } public BusinessException(String message) { super(message); } public BusinessException(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } public BusinessException(Throwable cause) { super(cause); } public BusinessException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) { super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace); } }
-
自定义SystemException
//自定义异常继承RuntimeException,覆盖父类所有的构造方法 public class SystemException extends RuntimeException { public SystemException() { } public SystemException(String message) { super(message); } public SystemException(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } public SystemException(Throwable cause) { super(cause); } public SystemException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) { super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace); } }
4.5 项目异常处理实现
-
在UserControll中模拟触发异常
//http://localhost/ajax.jsp @RequestMapping("/save") @ResponseBody public String save(@RequestBody User user) throws Exception { System.out.println("user controller save is running ..."); //对用户的非法操作进行判定,并包装成异常对象进行处理,便于统一管理 if(user.getName().trim().length() < 8){ throw new BusinessException("对不起,用户名长度不满足要求,请重新输入!"); } if(user.getAge() < 0){ throw new BusinessException("对不起,年龄必须是0到100之间的数字!"); } if (user.getAge() > 100) { throw new SystemException("我是系统异常,不能给用户看!"); } if (true) { throw new RuntimeException("test"); } }
-
通过自定义异常将所有的异常现象进行分类管理,以统一的格式对外呈现异常消息
@RestControllerAdvice //= @ControllerAdvice + @ResponseBody public class ProjectExceptionAdvice { @ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class) public String doBusinessException(Exception ex){ //业务异常出现的消息要发送给用户查看 return ex.getMessage(); } @ExceptionHandler(SystemException.class) public String doSystemException(Exception ex){ System.out.println(ex.getMessage()); //系统异常出现的消息不要发送给用户查看,发送统一的信息给用户看 return "服务器出现问题,请联系管理员!"; //实际的问题现象应该传递给redis服务器,运维人员通过后台系统查看 //redisTemplate.opsForvalue.set("msg", ex.getMessage()); } @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) public String doException(Exception ex){ //将ex堆栈信息保存起来 ex.printStackTrace(); return "太热情,请稍候……"; }
5 实用技术
5.1 文件上传-视频11
-
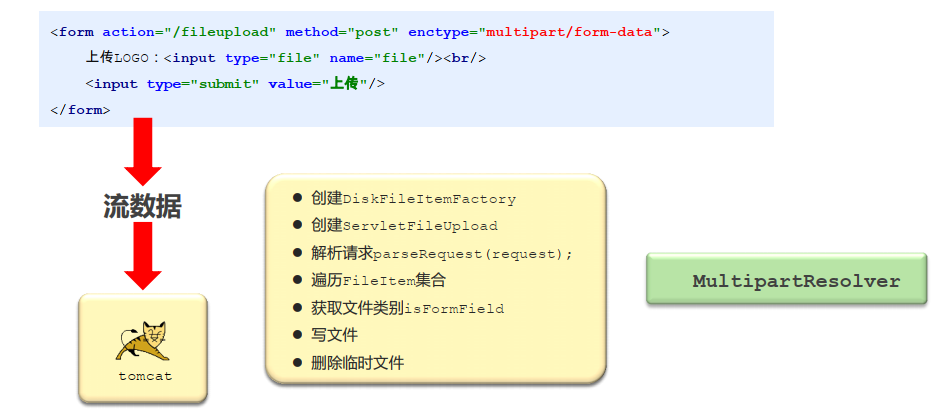
上传文件过程分析
-
MultipartResolver接口
-
MultipartResolver接口定义了文件上传过程中的相关操作,并对通用性操作进行了封装
-
MultipartResolver接口底层实现类CommonsMultipartResovler
-
CommonsMultipartResovler并未自主实现文件上传下载对应的功能,而是调用了apache的文件上传下载组件
-
第一步:引入commons-fileupload坐标
<dependency> <groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId> <artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId> <version>1.4</version> </dependency>
-
第二步:编写页面表单
<form action="/fileupload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> 上传LOGO: <input type="file" name="file"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="上传"/> </form> -
第三步:SpringMVC配置 CommonsMultipartResolver
<!--配置文件上传处理器--> <bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver"> <property name="maxUploadSize" value="1024000000"/> </bean>
-
第四步:在Controller中保存上传的文件
@RequestMapping(value = "/fileupload") public String fileupload(MultipartFile file) throws IOException { file.transferTo(new File("file.png")); return "page.jsp"; }
-
5.2 文件上传注意事项-视频12
-
文件命名问题, 获取上传文件名,并解析文件名与扩展名
file.getOriginalFilename();
-
文件名过长问题
-
重名问题
//使用uuid做为文件名 String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "").toUpperCase(); //获取文件后缀名 String suffix = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf(".")); //以uuid+文件后缀名保存文件 file.transferTo(new File(realPath, uuid + suffix));
-
文件保存路径
ServletContext context = request.getServletContext(); String basePath = context.getRealPath("/images"); File file = new File(basePath+"/"); if(!file.exists()) file.mkdirs();
同时上传多个文件:
<form action="/fileupload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <%--文件上传表单的name属性值一定要与controller处理器中方法的参数对应,否则无法实现文件上传--%> 上传LOGO:<input type="file" name="file"/><br/> 上传照片:<input type="file" name="file1"/><br/> 上传任意文件:<input type="file" name="file2"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="上传"/> </form>
完整代码:
@RequestMapping(value = "/fileupload") //参数中定义MultipartFile参数,用于接收页面提交的type=file类型的表单,要求表单名称与参数名相同 public String fileupload(MultipartFile file,MultipartFile file1,MultipartFile file2, HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException { System.out.println("file upload is running ..."+file); //MultipartFile参数中封装了上传的文件的相关信息 //首先判断是否是空文件,也就是存储空间占用为0的文件 if(!file.isEmpty()){ //如果大小在范围要求内正常处理,否则抛出自定义异常告知用户(未实现) //获取原始上传的文件名,可以作为当前文件的真实名称保存到数据库中备用 String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename(); //设置保存的路径 String realPath = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/images"); //保存文件的方法,指定保存的位置和文件名即可,通常文件名使用随机生成策略产生,避免文件名冲突问题 file.transferTo(new File(realPath,file.getOriginalFilename())); } //测试一次性上传多个文件 if(!file1.isEmpty()){ String fileName = file1.getOriginalFilename(); //可以根据需要,对不同种类的文件做不同的存储路径的区分,修改对应的保存位置即可 String realPath = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/images"); file1.transferTo(new File(realPath,file1.getOriginalFilename())); } if(!file2.isEmpty()){ String fileName = file2.getOriginalFilename(); String realPath = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/images"); file2.transferTo(new File(realPath,file2.getOriginalFilename())); } return "page.jsp"; }
5.4 RESTful开发风格(重点)
5.4.1 Rest-视频13
-
Rest( REpresentational State Transfer) 一种网络资源的访问风格,定义了网络资源的访问方式
-
传统风格访问路径 http://localhost/user/get?id=1
-
Rest风格访问路径 GET: http://localhost/user/1
DELETE: http://localhost/user/1
UPDATE: http://localhost/user/1
-
-
Restful是按照Rest风格访问网络资源
-
优点
隐藏资源的访问行为,通过地址无法得知做的是何种操作
简化书写
5.4.2 HTTP请求的四种方式
GET(查询) http://localhost/user/1 GET POST(保存) http://localhost/user POST PUT(更新) http://localhost/user/1 PUT DELETE(删除) http://localhost/user/1 DELETE
注意:上述行为是约定方式,约定不是规范,可以打破,所以称Rest风格,而不是Rest规范
查询id=100的用户信息两种实现方式:
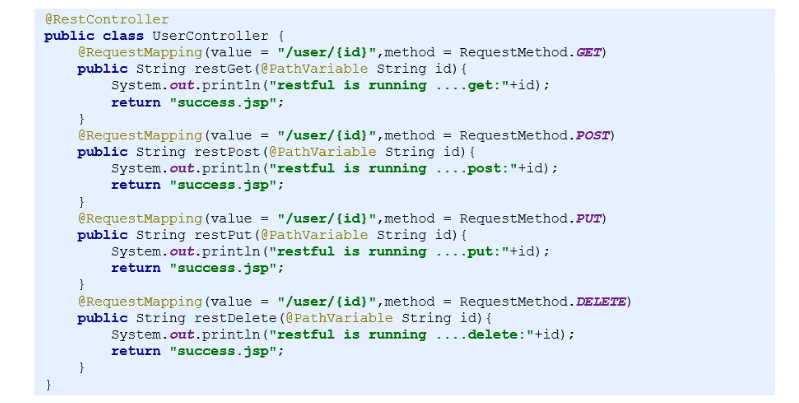
//@Controller //@ResponseBody //设置rest风格的控制器 @RestController //= @Controller + @ResponseBody //设置公共访问路径,配合方法上的访问路径使用 @RequestMapping("/user") public class UserController { //第一种获取请求参数:?id=xx&age= //http://localhost/user/getUser?id=100 @RequestMapping("/getUser") public String get(int id) { System.out.println("running ....get:"+id); return "success"; } //第二种获取请求参数:/user/100 //查询 http://localhost/user/100 @GetMapping("/{id}") public String restGet(@PathVariable int id) { System.out.println("restful is running ....get:"+id); return "success.jsp"; } }
5.4.3 Restful开发入门-视频14
四种请求方式:GET, POST, PUT, DELETE
发送PUT, DELETE请求的两种方式:
第一种方式:使用页面form表单提交PUT与DELETE请求
-
开启SpringMVC对RESTful风格的访问支持过滤器
<!--配置拦截器,解析请求中的参数_method,否则无法发起PUT请求与DELETE请求,配合页面表单使用--> <filter> <filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name> <servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name> </filter-mapping>
-
页面表单使用隐藏域提交请求类型,参数名称固定为_method,必须配合提交类型method=post使用
<form action="/user/1" method="post"> <input type="hidden" name="_method" value="PUT"/> <input type="submit"/> </form>
扩展知识
第二种方式:使用ajax发送PUT, DELETE请求(常用)
<%@page pageEncoding="UTF-8" language="java" contentType="text/html;UTF-8" %> <a href="javascript:void(0);" id="testPut">测试PUT提交</a><br/> <a href="javascript:void(0);" id="testDelete">测试DELETE提交</a><br/> <script type="text/javascript" src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/js/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> $(function () { $("#testPut").click(function(){ $.ajax({ type:"PUT", url:"/user/1", success:function(data){ window.location = data; } }); }); $("#testDelete").click(function(){ $.ajax({ type:"DELETE", url:"/user/2", success:function(data){ window.location = data; } }); }); }); </script>
第三种方式:使用Postman发送PUT, DELETE请求
5.4.4 Restful开发简写方式
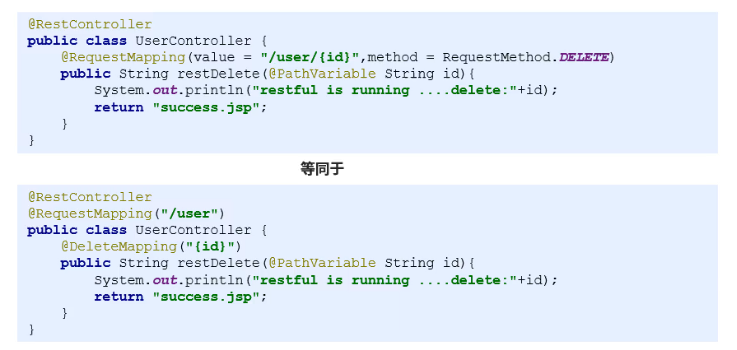
-
Restful请求路径简化配置方式 : @RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody
-
完整的简化后代码,@RestController = @Controller + @Response
//设置rest风格的控制器 @RestController //设置公共访问路径,配合下方访问路径使用 @RequestMapping("/user") public class UserController { //接收GET请求简化配置方式 @GetMapping("/{id}") public String get(@PathVariable Integer id){ System.out.println("restful is running ....get:"+id); return "success.jsp"; } //接收POST请求简化配置方式 @PostMapping("/{id}") public String post(@PathVariable Integer id){ System.out.println("restful is running ....post:"+id); return "success.jsp"; } //接收PUT请求简化配置方式 @PutMapping("/{id}") public String put(@PathVariable Integer id){ System.out.println("restful is running ....put:"+id); return "success.jsp"; } //接收DELETE请求简化配置方式 @DeleteMapping("/{id}") public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id){ System.out.println("restful is running ....delete:"+id); return "success.jsp"; } }
5.5 Postman安装与使用
postman 是一款可以发送Restful风格请求 的工具,方便开发调试
