Python学习系列(四)Python 入门语法规则2
2017-4-3 09:18:04
-
编码和解码
-
Unicode、gbk,utf8之间的关系
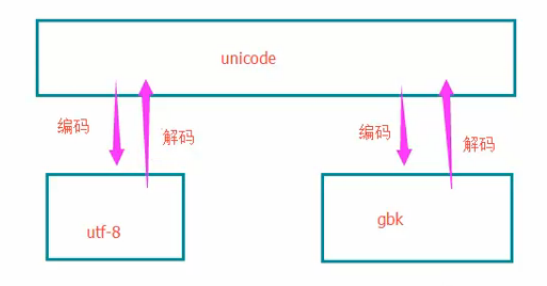
2、对于py2.7,
如果utf8>gbk,
utf8解码成Unicode,再将unicode编码成gbk
对于py3.5
如果utf8>gbk,
utf8 直接编码成gbk(中间那一步直接被优化了)
3、很多时候,这个可以直接跳过,只有当编码出下问题的时候,再考虑这个知识点
二、运算符
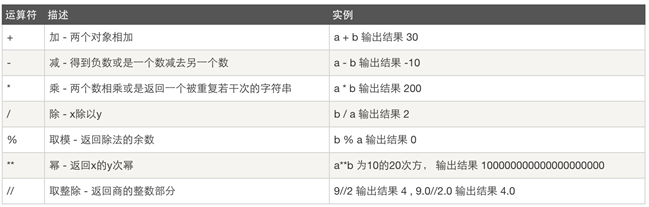
1、算数运算:
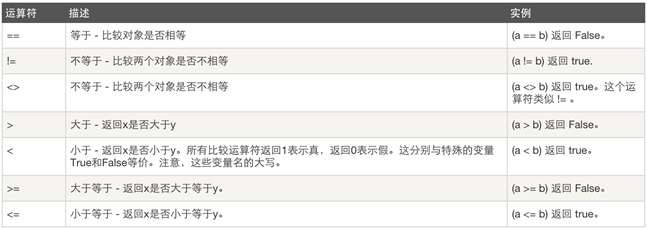
2、比较运算:
3、赋值运算:

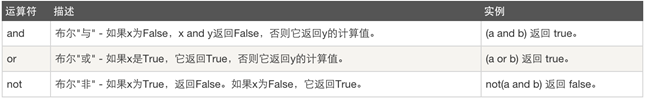
4、逻辑运算:
5、成员运算:
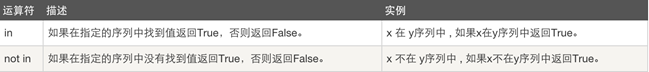
#example:1
r1="Bob is a boy"
r2= "boy" in r1
print(r2)
#example:1
classroom=["Bob","Lucy","Sb"]
r2= "Sb" in classroom
print(r2)
注意examp1和example2的区别
三、
四、基本数据类型
1、整型

a. n1=123 n2=345 print(n1+n2) print(n1.__add__(n2)) n1=123 b.获取二进制的最短位数 n=255 num=n.bit_length() print(num)
2、逻辑值(布尔值)
3、字符串
a.python的字符串内建函数

1 name='lucy' 2 3 n1=name.capitalize() 4 5 n2=name.center(20,'*') 6 7 name='lucy is a bbb lucy is a bbb' 8 9 n3=name.count('b',0,38) 10 11 n4=name.endswith('y',1,4) 12 13 name='lucy 999' 14 15 n5=name.expandtabs(tabsize=34) 16 17 name='lucy is a girl' 18 19 n6=name.find('ii') 20 21 s=['lucy','is','a','girl'] 22 23 n7='**'.join(s) 24 25 s=" lucy" 26 27 n8=s.lstrip() 28 29 s='lucy is a girl' 30 31 n9=s.partition('is') 32 33 n10=s.replace('cy', 'lu') 34 35 print(s) 36 37 print(n10) 38 39 40 41 b.字符串的常用功能 42 43 1)索引 44 45 s='lucy' 46 47 print(s[0]) 48 49 print(s[1]) 50 51 print(s[2]) 52 53 print(s[3]) 54 55 l=len(s) #获取长度 56 57 print(l) 58 59 2)切片 60 61 s='lucy' 62 63 l=s[0:4] 64 65 print(s[0:2]) 66 67 print(l) 68 69 70 71 s='lucy' 72 73 star=0 74 75 while star<len(s): 76 77 temp = s[star] 78 79 star+=1 80 81 print(temp) 82 83 84 85 86 87 #example:2 88 89 name='abcdefghijklmeopq' 90 91 print (name) 92 93 name_new=name.upper() 94 95 print(name_new) 96 97 print(type(name)) #通过type获取 类型
字符串方法是从python1.6到2.0慢慢加进来的——它们也被加到了Jython中。
这些方法实现了string模块的大部分方法,如下表所示列出了目前字符串内建支持的方法,所有的方法都包含了对Unicode的支持,有一些甚至是专门用于Unicode的。
|
方法 |
描述 |
|
把字符串的第一个字符大写 |
|
|
返回一个原字符串居中,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
|
|
返回 str 在 string 里面出现的次数,如果 beg 或者 end 指定则返回指定范围内 str 出现的次数 |
|
|
以 encoding 指定的编码格式解码 string,如果出错默认报一个 ValueError 的 异 常 , 除 非 errors 指 定 的 是 'ignore' 或 者'replace' |
|
|
以 encoding 指定的编码格式编码 string,如果出错默认报一个ValueError 的异常,除非 errors 指定的是'ignore'或者'replace' |
|
|
检查字符串是否以 obj 结束,如果beg 或者 end 指定则检查指定的范围内是否以 obj 结束,如果是,返回 True,否则返回 False. |
|
|
把字符串 string 中的 tab 符号转为空格,tab 符号默认的空格数是 8。 |
|
|
检测 str 是否包含在 string 中,如果 beg 和 end 指定范围,则检查是否包含在指定范围内,如果是返回开始的索引值,否则返回-1 |
|
|
跟find()方法一样,只不过如果str不在 string中会报一个异常. |
|
|
如果 string 至少有一个字符并且所有字符都是字母或数字则返 回 True,否则返回 False |
|
|
如果 string 至少有一个字符并且所有字符都是字母则返回 True, 否则返回 False |
|
|
如果 string 只包含十进制数字则返回 True 否则返回 False. |
|
|
如果 string 只包含数字则返回 True 否则返回 False. |
|
|
如果 string 中包含至少一个区分大小写的字符,并且所有这些(区分大小写的)字符都是小写,则返回 True,否则返回 False |
|
|
如果 string 中只包含数字字符,则返回 True,否则返回 False |
|
|
如果 string 中只包含空格,则返回 True,否则返回 False. |
|
|
如果 string 是标题化的(见 title())则返回 True,否则返回 False |
|
|
如果 string 中包含至少一个区分大小写的字符,并且所有这些(区分大小写的)字符都是大写,则返回 True,否则返回 False |
|
|
以 string 作为分隔符,将 seq 中所有的元素(的字符串表示)合并为一个新的字符串 |
|
|
返回一个原字符串左对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
|
|
转换 string 中所有大写字符为小写. |
|
|
截掉 string 左边的空格 |
|
|
maketrans() 方法用于创建字符映射的转换表,对于接受两个参数的最简单的调用方式,第一个参数是字符串,表示需要转换的字符,第二个参数也是字符串表示转换的目标。 |
|
|
返回字符串 str 中最大的字母。 |
|
|
返回字符串 str 中最小的字母。 |
|
|
有点像 find()和 split()的结合体,从 str 出现的第一个位置起,把 字 符 串 string 分 成 一 个 3 元 素 的 元 组 (string_pre_str,str,string_post_str),如果 string 中不包含str 则 string_pre_str == string. |
|
|
把 string 中的 str1 替换成 str2,如果 num 指定,则替换不超过 num 次. |
|
|
类似于 find()函数,不过是从右边开始查找. |
|
|
类似于 index(),不过是从右边开始. |
|
|
返回一个原字符串右对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
|
|
string.rpartition(str) |
类似于 partition()函数,不过是从右边开始查找. |
|
删除 string 字符串末尾的空格. |
|
|
以 str 为分隔符切片 string,如果 num有指定值,则仅分隔 num 个子字符串 |
|
|
按照行(' ', ' ', ')分隔,返回一个包含各行作为元素的列表,如果参数 keepends 为 False,不包含换行符,如果为 True,则保留换行符。 |
|
|
检查字符串是否是以 obj 开头,是则返回 True,否则返回 False。如果beg 和 end 指定值,则在指定范围内检查. |
|
|
在 string 上执行 lstrip()和 rstrip() |
|
|
翻转 string 中的大小写 |
|
|
返回"标题化"的 string,就是说所有单词都是以大写开始,其余字母均为小写(见 istitle()) |
|
|
根据 str 给出的表(包含 256 个字符)转换 string 的字符, 要过滤掉的字符放到 del 参数中 |
|
|
转换 string 中的小写字母为大写 |
|
|
返回长度为 width 的字符串,原字符串 string 右对齐,前面填充0 |
|
|
isdecimal()方法检查字符串是否只包含十进制字符。这种方法只存在于unicode对象。 |
4、列表
创建列表

1 name='lucy' 2 3 age=28 4 5 name_list=["bob",'jon','lucy'] 6 7 print(name_list) 8 9 print(name_list[0]) #索引 10 11 print(name_list[0:2])#切片 12 13 name_list.append('alex') #追加 14 15 name_list.append('smart') 16 17 name_list.append('smart') 18 19 n1=name_list.count('smart')#统计出现的次数 20 21 temp=[111,222,333] 22 23 name_list.extend(temp)#批量的添加数据 24 25 n2=name_list.index('jon') 26 27 print(n2)

1 python的列表内建函数 2 3 4 class list(object): 5 6 """ 7 8 list() -> new empty list 9 10 list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items 11 12 """ 13 14 def append(self, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 15 16 """ L.append(object) -- append object to end #追加""" 17 18 pass 19 20 21 22 def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 23 24 """ L.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value#统计出现的次数""" 25 26 return 0 27 28 29 30 def extend(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 31 32 """ L.extend(iterable) -- extend list by appending elements from the iterable #批量的添加数据""" 33 34 pass 35 36 37 38 def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 39 40 """ 41 42 L.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value. 43 44 Raises ValueError if the value is not present. 45 46 查找索引值 47 48 """ 49 50 return 0 51 52 53 54 def insert(self, index, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 55 56 """ L.insert(index, object) -- insert object before index 57 58 插入数据 59 60 """ 61 62 pass 63 64 65 66 def pop(self, index=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 67 68 """ 69 70 L.pop([index]) -> item -- remove and return item at index (default last). 71 72 Raises IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range. 73 74 移除列表里面的最后一个值,并可以赋值给返回值 75 76 """ 77 78 pass 79 80 81 82 def remove(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 83 84 """ 85 86 L.remove(value) -- remove first occurrence of value. 87 88 Raises ValueError if the value is not present. 89 90 移除指定值 91 92 """ 93 94 pass 95 96 97 98 def reverse(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 99 100 """ L.reverse() -- reverse *IN PLACE* 101 102 顺序翻转 103 104 """ 105 106 pass 107 108 109 110 def sort(self, cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 111 112 """ 113 114 L.sort(cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False) -- stable sort *IN PLACE*; 115 116 cmp(x, y) -> -1, 0, 1 117 118 简单的排序 119 120 """ 121 122 pass 123 124 125 126 def __add__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 127 128 """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ 129 130 pass 131 132 133 134 def __contains__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 135 136 """ x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """ 137 138 pass 139 140 141 142 def __delitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 143 144 """ x.__delitem__(y) <==> del x[y] """ 145 146 pass 147 148 149 150 def __delslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 151 152 """ 153 154 x.__delslice__(i, j) <==> del x[i:j] 155 156 157 158 Use of negative indices is not supported. 159 160 """ 161 162 pass 163 164 165 166 def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 167 168 """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """ 169 170 pass 171 172 173 174 def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 175 176 """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ 177 178 pass 179 180 181 182 def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 183 184 """ x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """ 185 186 pass 187 188 189 190 def __getslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 191 192 """ 193 194 x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j] 195 196 197 198 Use of negative indices is not supported. 199 200 """ 201 202 pass 203 204 205 206 def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 207 208 """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """ 209 210 pass 211 212 213 214 def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 215 216 """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """ 217 218 pass 219 220 221 222 def __iadd__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 223 224 """ x.__iadd__(y) <==> x+=y """ 225 226 pass 227 228 229 230 def __imul__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 231 232 """ x.__imul__(y) <==> x*=y """ 233 234 pass 235 236 237 238 def __init__(self, seq=()): # known special case of list.__init__ 239 240 """ 241 242 list() -> new empty list 243 244 list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items 245 246 # (copied from class doc) 247 248 """ 249 250 pass 251 252 253 254 def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 255 256 """ x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """ 257 258 pass 259 260 261 262 def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 263 264 """ x.__len__() <==> len(x) """ 265 266 pass 267 268 269 270 def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 271 272 """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """ 273 274 pass 275 276 277 278 def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 279 280 """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """ 281 282 pass 283 284 285 286 def __mul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 287 288 """ x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """ 289 290 pass 291 292 293 294 @staticmethod # known case of __new__ 295 296 def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 297 298 """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ 299 300 pass 301 302 303 304 def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 305 306 """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """ 307 308 pass 309 310 311 312 def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 313 314 """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ 315 316 pass 317 318 319 320 def __reversed__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 321 322 """ L.__reversed__() -- return a reverse iterator over the list """ 323 324 pass 325 326 327 328 def __rmul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 329 330 """ x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """ 331 332 pass 333 334 335 336 def __setitem__(self, i, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 337 338 """ x.__setitem__(i, y) <==> x[i]=y """ 339 340 pass 341 342 343 344 def __setslice__(self, i, j, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 345 346 """ 347 348 x.__setslice__(i, j, y) <==> x[i:j]=y 349 350 351 352 Use of negative indices is not supported. 353 354 """ 355 356 pass 357 358 359 360 def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 361 362 """ L.__sizeof__() -- size of L in memory, in bytes """ 363 364 pass 365 366 367 368 __hash__ = None 369 370 371 372 list
5、元祖(不能增,删,改)

1 lass tuple(object): 2 3 """ 4 5 tuple() -> empty tuple 6 7 tuple(iterable) -> tuple initialized from iterable's items 8 9 10 11 If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object. 12 13 """ 14 15 def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 16 17 """ T.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value 18 19 计算元素出现的个数 20 21 """ 22 23 return 0 24 25 26 27 def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 28 29 """ 30 31 T.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value. 32 33 Raises ValueError if the value is not present. 34 35 索引位置信息 36 37 """ 38 39 return 0 40 41 42 43 def __add__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 44 45 """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ 46 47 pass 48 49 50 51 def __contains__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 52 53 """ x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """ 54 55 pass 56 57 58 59 def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 60 61 """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """ 62 63 pass 64 65 66 67 def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 68 69 """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ 70 71 pass 72 73 74 75 def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 76 77 """ x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """ 78 79 pass 80 81 82 83 def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 84 85 pass 86 87 88 89 def __getslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 90 91 """ 92 93 x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j] 94 95 96 97 Use of negative indices is not supported. 98 99 """ 100 101 pass 102 103 104 105 def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 106 107 """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """ 108 109 pass 110 111 112 113 def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 114 115 """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """ 116 117 pass 118 119 120 121 def __hash__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 122 123 """ x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """ 124 125 pass 126 127 128 129 def __init__(self, seq=()): # known special case of tuple.__init__ 130 131 """ 132 133 tuple() -> empty tuple 134 135 tuple(iterable) -> tuple initialized from iterable's items 136 137 138 139 If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object. 140 141 # (copied from class doc) 142 143 """ 144 145 pass 146 147 148 149 def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 150 151 """ x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """ 152 153 pass 154 155 156 157 def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 158 159 """ x.__len__() <==> len(x) """ 160 161 pass 162 163 164 165 def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 166 167 """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """ 168 169 pass 170 171 172 173 def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 174 175 """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """ 176 177 pass 178 179 180 181 def __mul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 182 183 """ x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """ 184 185 pass 186 187 188 189 @staticmethod # known case of __new__ 190 191 def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 192 193 """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ 194 195 pass 196 197 198 199 def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 200 201 """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """ 202 203 pass 204 205 206 207 def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 208 209 """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ 210 211 pass 212 213 214 215 def __rmul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 216 217 """ x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """ 218 219 pass 220 221 222 223 def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 224 225 """ T.__sizeof__() -- size of T in memory, in bytes """ 226 227 pass 228 229 230 231 tuple
a.元祖和列表几乎一样
b.列表时刻可以修改的,元祖是不能修改的
c.元祖的创建
name_tuple=('lucy','bob')
#索引
print(name_tuple[0])
#len
print(name_tuple[len(name_tuple)-1])
#切片
print(name_tuple[0:1])
#for
for i in name_tuple:
print(i)
#删除 不支持
#del name_tuple[1]
print(name_tuple)
6、字典

1 class dict(object): 2 3 """ 4 5 dict() -> new empty dictionary 6 7 dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's 8 9 (key, value) pairs 10 11 dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via: 12 13 d = {} 14 15 for k, v in iterable: 16 17 d[k] = v 18 19 dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs 20 21 in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2) 22 23 """ 24 25 26 27 def clear(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 28 29 """ 清除内容 """ 30 31 """ D.clear() -> None. Remove all items from D. """ 32 33 pass 34 35 36 37 def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 38 39 """ 浅拷贝 """ 40 41 """ D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D """ 42 43 pass 44 45 46 47 @staticmethod # known case 48 49 def fromkeys(S, v=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 50 51 """ 52 53 dict.fromkeys(S[,v]) -> New dict with keys from S and values equal to v. 54 55 v defaults to None. 56 57 """ 58 59 pass 60 61 62 63 def get(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 64 65 """ 根据key获取值,如果key不存在,可以指定一个默认值,d是默认值 """ 66 67 """ D.get(k[,d]) -> D[k] if k in D, else d. d defaults to None. """ 68 69 pass 70 71 72 73 def has_key(self, k): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 74 75 """ 是否有key """ 76 77 """ D.has_key(k) -> True if D has a key k, else False """ 78 79 return False 80 81 82 83 def items(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 84 85 """ 所有项的列表形式 """ 86 87 """ D.items() -> list of D's (key, value) pairs, as 2-tuples """ 88 89 return [] 90 91 92 93 def iteritems(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 94 95 """ 项可迭代 """ 96 97 """ D.iteritems() -> an iterator over the (key, value) items of D """ 98 99 pass 100 101 102 103 def iterkeys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 104 105 """ key可迭代 """ 106 107 """ D.iterkeys() -> an iterator over the keys of D """ 108 109 pass 110 111 112 113 def itervalues(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 114 115 """ value可迭代 """ 116 117 """ D.itervalues() -> an iterator over the values of D """ 118 119 pass 120 121 122 123 def keys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 124 125 """ 所有的key列表 """ 126 127 """ D.keys() -> list of D's keys """ 128 129 return [] 130 131 132 133 def pop(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 134 135 """ 获取并在字典中移除 """ 136 137 """ 138 139 D.pop(k[,d]) -> v, remove specified key and return the corresponding value. 140 141 If key is not found, d is returned if given, otherwise KeyError is raised 142 143 """ 144 145 pass 146 147 148 149 def popitem(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 150 151 """ 获取并在字典中移除 """ 152 153 """ 154 155 D.popitem() -> (k, v), remove and return some (key, value) pair as a 156 157 2-tuple; but raise KeyError if D is empty. 158 159 """ 160 161 pass 162 163 164 165 def setdefault(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 166 167 """ 如果key不存在,则创建,如果存在,则返回已存在的值且不修改 """ 168 169 """ D.setdefault(k[,d]) -> D.get(k,d), also set D[k]=d if k not in D """ 170 171 pass 172 173 174 175 def update(self, E=None, **F): # known special case of dict.update 176 177 """ 更新 178 179 {'name':'alex', 'age': 18000} 180 181 [('name','sbsbsb'),] 182 183 """ 184 185 """ 186 187 D.update([E, ]**F) -> None. Update D from dict/iterable E and F. 188 189 If E present and has a .keys() method, does: for k in E: D[k] = E[k] 190 191 If E present and lacks .keys() method, does: for (k, v) in E: D[k] = v 192 193 In either case, this is followed by: for k in F: D[k] = F[k] 194 195 """ 196 197 pass 198 199 200 201 def values(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 202 203 """ 所有的值 """ 204 205 """ D.values() -> list of D's values """ 206 207 return [] 208 209 210 211 def viewitems(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 212 213 """ 所有项,只是将内容保存至view对象中 """ 214 215 """ D.viewitems() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's items """ 216 217 pass 218 219 220 221 def viewkeys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 222 223 """ D.viewkeys() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's keys """ 224 225 pass 226 227 228 229 def viewvalues(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 230 231 """ D.viewvalues() -> an object providing a view on D's values """ 232 233 pass 234 235 236 237 def __cmp__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 238 239 """ x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """ 240 241 pass 242 243 244 245 def __contains__(self, k): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 246 247 """ D.__contains__(k) -> True if D has a key k, else False """ 248 249 return False 250 251 252 253 def __delitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 254 255 """ x.__delitem__(y) <==> del x[y] """ 256 257 pass 258 259 260 261 def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 262 263 """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """ 264 265 pass 266 267 268 269 def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 270 271 """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ 272 273 pass 274 275 276 277 def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 278 279 """ x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """ 280 281 pass 282 283 284 285 def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 286 287 """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """ 288 289 pass 290 291 292 293 def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 294 295 """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """ 296 297 pass 298 299 300 301 def __init__(self, seq=None, **kwargs): # known special case of dict.__init__ 302 303 """ 304 305 dict() -> new empty dictionary 306 307 dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's 308 309 (key, value) pairs 310 311 dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via: 312 313 d = {} 314 315 for k, v in iterable: 316 317 d[k] = v 318 319 dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs 320 321 in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2) 322 323 # (copied from class doc) 324 325 """ 326 327 pass 328 329 330 331 def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 332 333 """ x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """ 334 335 pass 336 337 338 339 def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 340 341 """ x.__len__() <==> len(x) """ 342 343 pass 344 345 346 347 def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 348 349 """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """ 350 351 pass 352 353 354 355 def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 356 357 """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """ 358 359 pass 360 361 362 363 @staticmethod # known case of __new__ 364 365 def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 366 367 """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ 368 369 pass 370 371 372 373 def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 374 375 """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """ 376 377 pass 378 379 380 381 def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 382 383 """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ 384 385 pass 386 387 388 389 def __setitem__(self, i, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 390 391 """ x.__setitem__(i, y) <==> x[i]=y """ 392 393 pass 394 395 396 397 def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 398 399 """ D.__sizeof__() -> size of D in memory, in bytes """ 400 401 pass 402 403 404 405 __hash__ = None 406 407 408 409 dict
a.字典的每一个元素,都是一个键值对
'''
user_info={
1:"lucy",
2:73,
3:'M'
}
#索引
print(user_info[2])
user_info={
'name':"lucy",
"age":73,
"gender":'M'
}
#索引
print(user_info['name'])
#不能进行
#循环,默认值输出key
for i in user_info:
print(i)
print(user_info.keys())#获取所有的键
print(user_info.values())#获取所有的值
print(user_info.items())#获取所有的键值对
for i in user_info.values():
print(i)
for i,j in user_info.items():
print(i)
print(j)
#get,注意get和索引之间的差别
val=user_info.get('age')#根据key获取值,如果key不存在,可以指定一个默认值,d是默认值
print(val)
val=user_info.get('age11',123)
print(val)
#update更新
test={
'name':'yaun',
"age":24,
'adress':'hb',
'tel':18272163806
}
user_info.update(test)
print(user_info)
#删除
del user_info['name']
print(user_info)
#note:查看对象的类,或对象所具备的的功能
方法一:
temp="lucy"
t=type(tenp)
print(t)
#str,ctr+鼠标左,找到str类,内部所有的方法
方法二:
temp="lucy"
b = dir(temp)
方法三:
help(str)
五、内容补充

内容补充: 一、运算符 二、基本的数据类型 1、int n1 = 456 # 根据int类,创建了一个对象 n2 = 456 # 根据int类,创建了一个对象 特有的功能表现在: int类 功能1 功能2 功能3 _int_ #(初始化) 2、str str() str类 _init_ #(初始化) a、创建方式 #无参数,创建空字符串 #一个参数,创建普通字符串 #两个参数,int(字节),编码===》。 n='LUCY' n1='lucy' n2=str('lucy') n3=str() b、特有功能 n.strip() #两端去除空格 n.startswith()#以。。。开头 n.find()#找到子序列 n.replace(old, new)#将字符串中的某子序列替换成指定值 n.upper()#变大写 n.isalpha()#是,,,吗 c、公共功能 索引:只能取一个元素 切片:可以取多个元素 len: name='湖北' len(name)=2 for: 编码:3.5循环的时候,循环的每一个元素是“字符” d、bytes和str的转换 name="湖北" #将字符串转换成字节 b1=bytes(name,encoding='utf-8') print(b1) b2=bytes(name,encoding='gbk') print(b2) #将字节转换成字符串 n1=str(b1,encoding='utf-8') print(n1) n2=str(b2,encoding='gbk') print(n2) #======= n=str() #创建字符串 #转换成字符串,字节,编码 m=bytes() #创建字节 #转换成字节,字符串,要变成什么编码字节的类型字节 3、list 元素的‘集合’,列表 list() list类 _init_ #(初始化) ---------- str—>创建字符串,或者将其他的准换成字符串 ---------- list—>创建列表,将其他元素转换成列表 a、创建和转换 1、创建 list=[11,22,33,44,55] list=list() list=list([11,22,33,44,55]) 2、转换(字符串,元祖、字典都可以转换成列表) s1='湖北' l1=list(s1) #for循环,将循环的每一个元素,当做了列表的元素 #print(l1) ['湖', '北'] t2=('lucy','bob','earth') l2=list(t2) #print(l2) ['lucy', 'bob', 'earth'] dic={'k1':'lucy','k2':'earth'} l3=list(dic.keys()) l4=list(dic.items()) print(l3) b、列表特有的功能 li=list() new_list=list.append(object)#追加字符串(改变自身) new_list=list.clear()#清除 new_list=list.extend(iterable)#批量增加,用另外一个可以迭代的 对象扩展到自己的内部 new_list=list.reverse()#翻转,自己内部元素翻转 new_list=list.insert(index, object)#向指定的位置插入一个元素 c、公共功能: 索引: 切片: 4、元组(tuple) a、创建和转换 t=(11,22,33) t=tuple(t) t=tuple([])#字符串,列表,字典都可以 b、特有的方法 count index c、嵌套(元素不可修改) t= (11,22,33) t= (11,22,['lucy',{'k1':'v1'}]) t[2][1][k1] e、元祖的特性,(元祖的元素)不可修改, 儿子不能变,孙子可以(可能)变,,,, #'k2':'123' t=(11,22,["lucy",{'k1':'v1'}]) #t2=t[2].append('&*&*&') #None #t[2].append('&*&*&') #(11, 22, ['lucy', {'k1': 'v1'}, '&*&*&']) t2=t[2][1].update({'k2':'123'}) t2=t[2][1]['k3']='987' #(11, 22, ['lucy', {'k1': 'v1', 'k2': '123', 'k3': '987'}]) 整理: 一般字符串,执行一个功能,生成一个新内容,原来内容不变 list,tuple,dict,执行一个功能,自身发生变化 5、字典 a、创建和转换 a={'k1':'467'} #{'k1': '467'} a=dict(k1=4324,k2='yuan') #{'k2': 'yuan', 'k1': 4324} li=['lucy','bob','earth'] new_dict=dict(enumerate(li)) #自动为列表添加key #{0: 'lucy', 1: 'bob', 2: 'earth'} b、字典的内部功能
六、新加元素
1、for循环
2、enumrate
'''enumrate 为可迭代的对象添加序号,
自动生成1列,从0开始,自增1,默认值可以更改
'''
list=['电脑','手机','家具','课本']
for key,item in enumerate(list,1):
print(key,item)
temp=int(input('请选择一个'))-1
print(list[temp])
3、range和xrange
python2.7 range,用获取指定范围内的数 range(0,10000)
xrange,只有在循环的时候才会使用,循环一次,+一次,
python3.0 只有range,等同于xrange
'''
#
print(range(1,10))
for i in range(20,1,-3):
print(i)
六、exercise
1、
有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90...],将所有大于 66 的值保存至字典的第一个key中,将小于 66 的值保存至第二个key的值中。
即: {'k1': 大于66的所有值, 'k2': 小于66的所有值}
2、
查找列表中元素,移除每个元素的空格,并查找以 a或A开头并且以 c 结尾的所有元素。
li = ["alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain"]
tu = ("alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain")
dic = {'k1': "alex", 'k2': ' aric', "k3": "Alex", "k4": "Tony"}
3、输出商品列表,用户输入序号,显示用户选中的商品
商品 li = ["手机", "电脑", '鼠标垫', '游艇']
4、购物车
功能要求:
-
要求用户输入总资产,例如:2000
-
显示商品列表,让用户根据序号选择商品,加入购物车
-
购买,如果商品总额大于总资产,提示账户余额不足,否则,购买成功。
-
附加:可充值、某商品移除购物车
5、用户交互,显示省市县三级联动的选择
