VFS-目录项对象(dentry)
- 每个文件除了有一个索引节点 inode 数据结构外,还有一个目录项 dentry 数据结构
-
dentry 结构代表的是逻辑意义上的文件,描述的是文件逻辑上的属性,目录项对象在磁盘上并没有对应的映像
-
inode 结构代表的是物理意义上的文件,记录的是物理上的属性 对于一个具体的文件,系统 其 inode 结构在磁盘上就有对应的映像
- 一个索引节点对象可能对应多个目录项对象
VFS-文件对象(file)
- 进程是通过文件描述符来访问文件的
By convention, UNIX System shells associate file descriptor 0 with the standard
input of a process, file descriptor 1 with the standard output, and file descriptor 2 with
the standard error. This convention is used by the shells and many applications; it is
not a feature of the UNIX kernel. Nevertheless, many applications would break if these
associations weren’t followed.
Although their values are standardized by POSIX.1, the magic numbers 0, 1, and 2
should be replaced in POSIX-compliant applications with the symbolic constants
STDIN_FILENO, STDOUT_FILENO, and STDERR_FILENO to improve readability.
These constants are defined in the <unistd.h> header.
File descriptors range from 0 through OPEN_MAX−1. (Recall Figure 2.11.) Early
historical implementations of the UNIX System had an upper limit of 19, allowing a
maximum of 20 open files per process, but many systems subsequently increased this
limit to 63.
- Linux 中专门用了一个 file 文件对象来保存打开文件的文件位置,这个对象称为打开的文件描述 open file description
- 文件描述符是用来描述打开的文件的 。 每个进程用一个 files_struct 结构来记录文件描述符的使用情况,这个 files_struct 结构称为用户打开文件表, 它是进程的私有数据
- file 结构中主要保存了文件位置,还把指向该文件索引节点的指针也放在其中 。file 结构形成一个双链表,称为系统打开文件表 。


-
超级块是对一个文件系统的描述
查看超级块的命令:DUMPE2FS (dumpe2fs - dump ext2/ext3/ext4 filesystem information)
DUMPE2FS(8) System Manager's Manual DUMPE2FS(8)
NAME
dumpe2fs - dump ext2/ext3/ext4 filesystem information
SYNOPSIS
dumpe2fs [ -bfghixV ] [ -o superblock=superblock ] [ -o blocksize=blocksize ] device
DESCRIPTION
dumpe2fs prints the super block and blocks group information for the filesystem present on
device.
Note: When used with a mounted filesystem, the printed information may be old or inconsis‐
tent.
OPTIONS
-b print the blocks which are reserved as bad in the filesystem.
-o superblock=superblock
use the block superblock when examining the filesystem. This option is not usually
needed except by a filesystem wizard who is examining the remains of a very badly
corrupted filesystem.
-o blocksize=blocksize
use blocks of blocksize bytes when examining the filesystem. This option is not usu‐
ally needed except by a filesystem wizard who is examining the remains of a very
badly corrupted filesystem.
##################################################################################################
至于DUMPE2FS(8), 8是什么意思呢?
The table below shows the section numbers of the manual followed by the types of pages they
contain.
1 Executable programs or shell commands
2 System calls (functions provided by the kernel)
3 Library calls (functions within program libraries)
4 Special files (usually found in /dev)
5 File formats and conventions eg /etc/passwd
6 Games
7 Miscellaneous (including macro packages and conventions), e.g. man(7), groff(7)
8 System administration commands (usually only for root)(系统管理命令)
9 Kernel routines [Non standard]
~$ df -Th # 只可以查看已经挂载的分区和文件系统类型。 Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on udev devtmpfs 888M 0 888M 0% /dev tmpfs tmpfs 184M 6.0M 178M 4% /run /dev/vda1 ext4 50G 4.5G 43G 10% / tmpfs tmpfs 917M 24K 917M 1% /dev/shm tmpfs tmpfs 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock tmpfs tmpfs 917M 0 917M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup tmpfs tmpfs 184M 0 184M 0% /run/user/500
#dumpe2fs /dev/loop0 【-h不打印Group信息】 dumpe2fs 1.42.9 (网上示例仅供参照) Filesystem volume name: <none> Last mounted on: <not available> 最后挂载目录 Filesystem UUID: cef5f647-058f-49bd-88c6-baf3ce2338a0 Filesystem magic number: 0xEF53 ext4文件系统标志 Filesystem revision #: 1 (dynamic) Filesystem features: has_journal ext_attr resize_inode dir_index filetype needs_recovery extent 64bit flex_bg sparse_super huge_file uninit_bg dir_nlink extra_isize Filesystem flags: signed_directory_hash Default mount options: user_xattr acl Filesystem state: clean Errors behavior: Continue Filesystem OS type: Linux Inode count: 25688 文件系统inode号总数,由系统决定但可以指定比例 Block count: 102400 文件系统block总数,==容量/默认的1KB Reserved block count: 5120 保留的block总数,默认比例为5% Free blocks: 93504 空闲的block总数, Free inodes: 25677 空闲的inode总数 First block: 1 第一个block号 Block size: 1024 block大小 Fragment size: 1024 Group descriptor size: 64 块组描述大小 Reserved GDT blocks: 256 预留块组描述block数量 Blocks per group: 8192 块组中block数量 Fragments per group: 8192 Inodes per group: 1976 块组中inode数量==25688/13 Inode blocks per group: 247 块组中inode占用block总数 Flex block group size: 16 inode表大小? Filesystem created: Tue Nov 27 13:26:27 2018 Last mount time: Tue Nov 27 13:28:39 2018 Last write time: Tue Nov 27 13:28:39 2018 Mount count: 1 挂载次数 Maximum mount count: -1 Last checked: Tue Nov 27 13:26:27 2018 Check interval: 0 (<none>) Lifetime writes: 4447 kB Reserved blocks uid: 0 (user root) Reserved blocks gid: 0 (group root) First inode: 11 文件系统的第一个inode号 Inode size: 128 inode大小 Journal inode: 8 日志文件inode号 Default directory hash: half_md4 Directory Hash Seed: 45d2f9d4-714a-4ccf-9c9d-308d12552317 Journal backup: inode blocks Journal features: journal_64bit 日志大小: 4096k Journal length: 4096 Journal sequence: 0x00000002 Journal start: 1 Group 0: (Blocks 1-8192) [ITABLE_ZEROED] Checksum 0x0229, unused inodes 1965 主 superblock at 1, Group descriptors at 2-2 保留的GDT块位于 3-258 Block bitmap at 259 (+258), Inode bitmap at 275 (+274) Inode表位于 291-537 (+290) 4683 free blocks, 1965 free inodes, 2 directories, 1965个未使用的inodes 可用块数: 3510-8192 可用inode数: 12-1976
- 索引节点是对一个文件物理属性的描述
索引节点(Inode)查看命令: stat <file>
- 目录项是对一个文件逻辑属性的描述
-
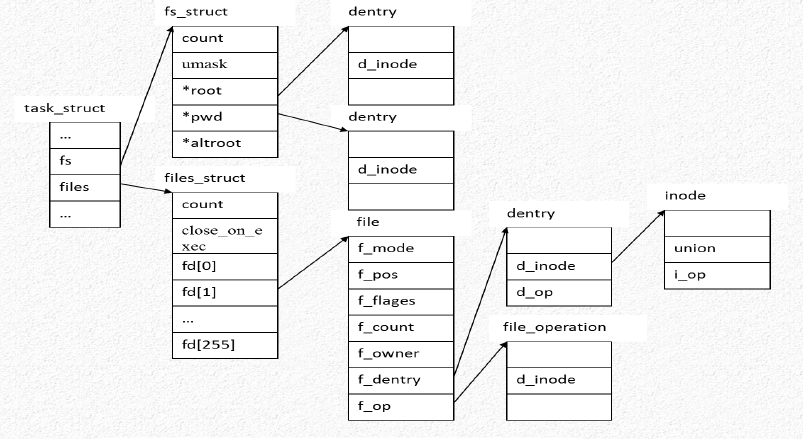
一个进程所处的位置是由 fs_struct 来描述的,而一个进程 或用户 打开的文件是由
files_struct 来描述的,而整个系统所打开的文件是由 file 结构来描述 - VFS-数据结构之间的关系
文件系统的注册和注销
- 当内核被编译时 就已经确定了可以支持哪些文件系统,这些文件系统在系统引导时在 VFS 中进行注册 。
- VFS 的初始化函数用来向 VFS 注册,即填写文件注册表 file_system_type 数据结构
- 注册调用 register_filesystem 函数
- 注销即删除一个 file_system_type 结构,需调用 unregister_filesystem() 函数
文件系统的安装
- 安装一个文件系统实际上是安装一个物理设备
-
自己( 一般是超级用户 )安装文件系统时 需要指定三种信息:文件系统的名称 、 包含
文件系统的物理块设备 、 文件系统在已有文件系统中的安装点 。 -
mount -t iso9660 /dev/hdc /mnt/cdrom 其中 iso9660 是光驱文件系统的名称,
/dev/hdc 是包含文件系统的物理块设备 ,/mnt/cdrom 就是将要安装到的目录,即安装点 。 -
在用户程序中要安装一个文件系统则可以调用 mount 系统调用 。 安装过程主要工作
是创建安装点对象,将其挂接到根文件系统的指定安装点下,然后初始化超级块对象,从而
获得文件系统基本信息和相关的操作 。
文件系统的安装
- 如果文件系统中的文件当前正在使用 该文件系统是不能被卸载的
-
否则,查看对应的 VFS 超级块,如果该文件系统的 VFS 超级块标志为 脏,则必须将超级块信息写回磁盘
-
之后,对应的 VFS 超级块被释放,vfsmount 数据结构将从 vfsmntlist 链表中断开并被释放
- 具体的实现代码为 fs/super.c 中的 sys_umount 函数