最近本人接到一个需求,需要从文件读取数据,然后经过业务处理之后存储到数据库中。这个需求,说实话不是很难,本人很快完成了第一个版本。
内存读取
第一个版本,本人采用内存读取的方式,所有的数据首先读读取到内存中,程序代码如下:
Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.createStarted(); // 将全部行数读取的内存中 List<String> lines = FileUtils.readLines(new File("temp/test.txt"), Charset.defaultCharset()); for (String line : lines) { // pass } stopwatch.stop(); System.out.println("read all lines spend " + stopwatch.elapsed(TimeUnit.SECONDS) + " s"); // 计算内存占用 logMemory();
logMemory方法如下:
MemoryMXBean memoryMXBean = ManagementFactory.getMemoryMXBean(); //堆内存使用情况 MemoryUsage memoryUsage = memoryMXBean.getHeapMemoryUsage(); //初始的总内存 long totalMemorySize = memoryUsage.getInit(); //已使用的内存 long usedMemorySize = memoryUsage.getUsed(); System.out.println("Total Memory: " + totalMemorySize / (1024 * 1024) + " Mb"); System.out.println("Free Memory: " + usedMemorySize / (1024 * 1024) + " Mb");
上述程序中,本人使用 Apache Common-Io 开源第三方库,FileUtils#readLines将会把文件中所有内容,全部读取到内存中。
这个程序简单测试并没有什么问题,但是等拿到真正的数据文件,运行程序,很快程序发生了 OOM。
之所以会发生 OOM,主要原因是因为这个数据文件太大。假设上面测试文件 test.txt总共有 200W 行数据,文件大小为:740MB。
通过上述程序读取到内存之后,在我的电脑上内存占用情况如下:
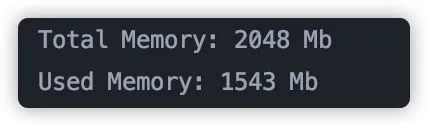
可以看到一个实际大小为 700 多 M 的文件,读到内存中占用内存量为 1.5G 之多。而我之前的程序,虚拟机设置内存大小只有 1G,所以程序发生了 OOM。
当然这里最简单的办法就是加内存呗,将虚拟机内存设置到 2G,甚至更多。不过机器内存始终有限,如果文件更大,还是没有办法全部都加载到内存。
不过仔细一想真的需要将全部数据一次性加载到内存中?
很显然,不需要!
在上述的场景中,我们将数据到加载内存中,最后不还是一条条处理数据。
所以下面我们将读取方式修改成逐行读取。
逐行读取
逐行读取的方式比较多,这里本人主要介绍两种方式:
-
BufferReader
-
Apache Commons IO
-
Java8 stream
BufferReader
我们可以使用 BufferReader#readLine 逐行读取数据。
try (BufferedReader fileBufferReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("temp/test.txt"))) { String fileLineContent; while ((fileLineContent = fileBufferReader.readLine()) != null) { // process the line. } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
Apache Commons IO
Common-IO 中有一个方法 FileUtils#lineIterator可以实现逐行读取方式,使用代码如下:
Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.createStarted(); LineIterator fileContents = FileUtils.lineIterator(new File("temp/test.txt"), StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name()); while (fileContents.hasNext()) { fileContents.nextLine(); // pass } logMemory(); fileContents.close(); stopwatch.stop(); System.out.println("read all lines spend " + stopwatch.elapsed(TimeUnit.SECONDS) + " s");
这个方法返回一个迭代器,每次我们都可以获取的一行数据。
其实我们查看代码,其实可以发现 FileUtils#lineIterator,其实用的就是 BufferReader,感兴趣的同学可以自己查看一下源码。
Java8 stream
Java8 Files 类新增了一个 lines,可以返回 Stream我们可以逐行处理数据。
Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.createStarted(); // lines(Path path, Charset cs) try (Stream<String> inputStream = Files.lines(Paths.get("temp/test.txt"), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) { inputStream .filter(str -> str.length() > 5)// 过滤数据 .forEach(o -> { // pass do sample logic }); } logMemory(); stopwatch.stop(); System.out.println("read all lines spend " + stopwatch.elapsed(TimeUnit.SECONDS) + " s");
使用这个方法有个好处在于,我们可以方便使用 Stream 链式操作,做一些过滤操作。
注意:这里我们使用 try-with-resources 方式,可以安全的确保读取结束,流可以被安全的关闭。
并发读取
逐行的读取的方式,解决我们 OOM 的问题。不过如果数据很多,我们这样一行行处理,需要花费很多时间。
上述的方式,只有一个线程在处理数据,那其实我们可以多来几个线程,增加并行度。
下面在上面的基础上,本人就抛砖引玉,介绍下本人自己比较常用两种并行处理方式。
逐行批次打包
第一种方式,先逐行读取数据,加载到内存中,等到积累一定数据之后,然后再交给线程池异步处理。
@SneakyThrows public static void readInApacheIOWithThreadPool() { // 创建一个 最大线程数为 10,队列最大数为 100 的线程池 ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10, 60l, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(100)); // 使用 Apache 的方式逐行读取数据 LineIterator fileContents = FileUtils.lineIterator(new File("temp/test.txt"), StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name()); List<String> lines = Lists.newArrayList(); while (fileContents.hasNext()) { String nextLine = fileContents.nextLine(); lines.add(nextLine); // 读取到十万的时候 if (lines.size() == 100000) { // 拆分成两个 50000 ,交给异步线程处理 List<List<String>> partition = Lists.partition(lines, 50000); List<Future> futureList = Lists.newArrayList(); for (List<String> strings : partition) { Future<?> future = threadPoolExecutor.submit(() -> { processTask(strings); }); futureList.add(future); } // 等待两个线程将任务执行结束之后,再次读取数据。这样的目的防止,任务过多,加载的数据过多,导致 OOM for (Future future : futureList) { // 等待执行结束 future.get(); } // 清除内容 lines.clear(); } } // lines 若还有剩余,继续执行结束 if (!lines.isEmpty()) { // 继续执行 processTask(lines); } threadPoolExecutor.shutdown(); } private static void processTask(List<String> strings) { for (String line : strings) { // 模拟业务执行 try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
上述方法,等到内存的数据到达 10000 的时候,拆封两个任务交给异步线程执行,每个任务分别处理 50000 行数据。
后续使用 future#get(),等待异步线程执行完成之后,主线程才能继续读取数据。
之所以这么做,主要原因是因为,线程池的任务过多,再次导致 OOM 的问题。
大文件拆分成小文件
第二种方式,首先我们将一个大文件拆分成几个小文件,然后使用多个异步线程分别逐行处理数据。
public static void splitFileAndRead() throws Exception { // 先将大文件拆分成小文件 List<File> fileList = splitLargeFile("temp/test.txt"); // 创建一个 最大线程数为 10,队列最大数为 100 的线程池 ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10, 60l, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(100)); List<Future> futureList = Lists.newArrayList(); for (File file : fileList) { Future<?> future = threadPoolExecutor.submit(() -> { try (Stream inputStream = Files.lines(file.toPath(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) { inputStream.forEach(o -> { // 模拟执行业务 try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); futureList.add(future); } for (Future future : futureList) { // 等待所有任务执行结束 future.get(); } threadPoolExecutor.shutdown(); } private static List<File> splitLargeFile(String largeFileName) throws IOException { LineIterator fileContents = FileUtils.lineIterator(new File(largeFileName), StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name()); List<String> lines = Lists.newArrayList(); // 文件序号 int num = 1; List<File> files = Lists.newArrayList(); while (fileContents.hasNext()) { String nextLine = fileContents.nextLine(); lines.add(nextLine); // 每个文件 10w 行数据 if (lines.size() == 100000) { createSmallFile(lines, num, files); num++; } } // lines 若还有剩余,继续执行结束 if (!lines.isEmpty()) { // 继续执行 createSmallFile(lines, num, files); } return files; }
上述方法,首先将一个大文件拆分成多个保存 10W 行的数据的小文件,然后再将小文件交给线程池异步处理。
由于这里的异步线程每次都是逐行从小文件的读取数据,所以这种方式不用像上面方法一样担心 OOM 的问题。
另外,上述我们使用 Java 代码,将大文件拆分成小文件。这里本人还有一个简单的办法,我们可以直接使用下述命令,直接将大文件拆分成小文件:
# 将大文件拆分成 100000 的小文件 split -l 100000 test.txt
后续 Java 代码只需要直接读取小文件即可。
总结
当我们从文件读取数据时,如果文件不是很大,我们可以考虑一次性读取到内存中,然后快速处理。
如果文件过大,我们就没办法一次性加载到内存中,所以我们需要考虑逐行读取,然后处理数据。但是单线程处理数据毕竟有限,所以我们考虑使用多线程,加快处理数据。
本篇文章我们只是简单介绍了下,数据从文件读取几种方式。数据读取之后,我们肯定还需要处理,然后最后会存储到数据库中或者输出到另一个文件中。
这个过程,说实话比较麻烦,因为我们的数据源文件,可能是 txt,也可能是 excel,这样我们就需要增加多种读取方法。同样的,当数据处理完成之后,也有同样的问题。
以下贴出所有源码:
package com.just.samples; import com.google.common.base.Joiner; import com.google.common.base.Stopwatch; import com.google.common.collect.Lists; import lombok.SneakyThrows; import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; import org.apache.commons.io.LineIterator; import java.io.*; import java.lang.management.ManagementFactory; import java.lang.management.MemoryMXBean; import java.lang.management.MemoryUsage; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.nio.file.Files; import java.nio.file.Paths; import java.util.List; import java.util.UUID; import java.util.concurrent.Future; import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.stream.Stream; /** * @author andyXu xu9529@gmail.com * @date 2020/6/9 * 读取超大文件 */ public class ReadLargeFileExample { @SneakyThrows public static void main(String[] args) { readInMemory(); } /** * 全部读进内存 */ @SneakyThrows public static void readInMemory() { Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.createStarted(); List<String> lines = FileUtils.readLines(new File("temp/test.txt"), Charset.defaultCharset()); for (String line : lines) { // pass } stopwatch.stop(); System.out.println("read all lines spend " + stopwatch.elapsed(TimeUnit.SECONDS) + " s"); logMemory(); } public static void readInBuffer() { try (BufferedReader fileBufferReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("temp/test.txt"))) { String fileLineContent; while ((fileLineContent = fileBufferReader.readLine()) != null) { // process the line. } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @SneakyThrows public static void readInApacheIO() { Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.createStarted(); LineIterator fileContents = FileUtils.lineIterator(new File("temp/test.txt"), StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name()); while (fileContents.hasNext()) { fileContents.nextLine(); // pass } logMemory(); fileContents.close(); stopwatch.stop(); System.out.println("read all lines spend " + stopwatch.elapsed(TimeUnit.SECONDS) + " s"); } @SneakyThrows public static void readInStream() { Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.createStarted(); // lines(Path path, Charset cs) try (Stream<String> inputStream = Files.lines(Paths.get("temp/test.txt"), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) { inputStream .filter(str -> str.length() > 5)// 过滤数据 .forEach(o -> { // pass do sample logic }); } logMemory(); stopwatch.stop(); System.out.println("read all lines spend " + stopwatch.elapsed(TimeUnit.SECONDS) + " s"); } @SneakyThrows public static void readInApacheIOWithThreadPool() { // 创建一个 最大线程数为 10,队列最大数为 100 的线程池 ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10, 60l, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(100)); // 使用 Apache 的方式逐行读取数据 LineIterator fileContents = FileUtils.lineIterator(new File("temp/test.txt"), StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name()); List<String> lines = Lists.newArrayList(); while (fileContents.hasNext()) { String nextLine = fileContents.nextLine(); lines.add(nextLine); // 读取到十万的时候 if (lines.size() == 100000) { // 拆分成两个 50000 ,交给异步线程处理 List<List<String>> partition = Lists.partition(lines, 50000); List<Future> futureList = Lists.newArrayList(); for (List<String> strings : partition) { Future<?> future = threadPoolExecutor.submit(() -> { processTask(strings); }); futureList.add(future); } // 等待两个线程将任务执行结束之后,再次读取数据。这样的目的防止,任务过多,加载的数据过多,导致 OOM for (Future future : futureList) { // 等待执行结束 future.get(); } // 清除内容 lines.clear(); } } // lines 若还有剩余,继续执行结束 if (!lines.isEmpty()) { // 继续执行 processTask(lines); } } public static void splitFileAndRead() throws Exception { // 先将大文件拆分成小文件 List<File> fileList = splitLargeFile("temp/test.txt"); // 创建一个 最大线程数为 10,队列最大数为 100 的线程池 ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10, 60l, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(100)); List<Future> futureList = Lists.newArrayList(); for (File file : fileList) { Future<?> future = threadPoolExecutor.submit(() -> { try (Stream inputStream = Files.lines(file.toPath(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) { inputStream.forEach(o -> { // 模拟执行业务 try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); futureList.add(future); } for (Future future : futureList) { // 等待所有任务执行结束 future.get(); } threadPoolExecutor.shutdown(); } private static List<File> splitLargeFile(String largeFileName) throws IOException { LineIterator fileContents = FileUtils.lineIterator(new File(largeFileName), StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name()); List<String> lines = Lists.newArrayList(); // 文件序号 int num = 1; List<File> files = Lists.newArrayList(); while (fileContents.hasNext()) { String nextLine = fileContents.nextLine(); lines.add(nextLine); // 每个文件 10w 行数据 if (lines.size() == 100000) { createSmallFile(lines, num, files); num++; } } // lines 若还有剩余,继续执行结束 if (!lines.isEmpty()) { // 继续执行 createSmallFile(lines, num, files); } return files; } public static void createSmallFile(List<String> lines, int num, List<File> files) throws IOException { File file = new File("temp/small_file_" + num + ".txt"); FileUtils.writeLines(file, lines); files.add(file); lines.clear(); } private static void processTask(List<String> strings) { for (String line : strings) { // 模拟业务执行 try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } private static void logMemory() { MemoryMXBean memoryMXBean = ManagementFactory.getMemoryMXBean(); //椎内存使用情况 MemoryUsage memoryUsage = memoryMXBean.getHeapMemoryUsage(); //初始的总内存 long totalMemorySize = memoryUsage.getInit(); //已使用的内存 long usedMemorySize = memoryUsage.getUsed(); System.out.println("Total Memory: " + totalMemorySize / (1024 * 1024) + " Mb"); System.out.println("Used Memory: " + usedMemorySize / (1024 * 1024) + " Mb"); } /** * 创建一个超大的文件 */ @SneakyThrows public static void createLargeFile() { List<String> fields = Lists.newArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { fields.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); } String line = Joiner.on(",").join(fields); List<String> lines = Lists.newArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i < 200 * 10000; i++) { lines.add(line); // 防止 OOM,批量输出 if (lines.size() == 100000) { FileUtils.writeLines(new File("temp/test.txt"), lines, true); lines.clear(); } } } }
POM.XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <parent> <groupId>com.just.do</groupId> <artifactId>java-samples</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <artifactId>learn-java-io</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>learn-java-io</name> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-io</groupId> <artifactId>commons-io</artifactId> <version>2.6</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.google.guava/guava --> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> <artifactId>guava</artifactId> <version>29.0-jre</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>