1. 首先在src目录下新建beans.xml文件,该文件名可更改。
2. 编辑xml文件如下,这里需要注意的是beans的表头中信息需要根据不同的版本对应的内容不同,本例中使用的spring的版本为4.0.4。
在做单元测试时一直提示错误“找不到元素 'beans' 的声明”,最后找到原因是网上找的头部内容与我使用的spring的版本不一致导致的。
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" default-autowire="byName"> <context:annotation-config/> <bean id="date" class="java.util.Date"></bean> <bean id="person" class="com.model.Person"> <property name="user" ref="user"></property> </bean> <bean id="user" class="com.model.User"></bean> </beans>
3. 新建个测试类BeanTest.java如下, 这里是通过类加载的方式来生成Person的对象。
@Test public void beanTest(){ //ApplicationContext为Spring容器最常用的接口 //ClassPathXmlApplicationContext为ApplicationContext的实现类 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); Person p = ctx.getBean("person",Person.class); p.useUser(); }
4. Person类如下:
package com.model; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.GenerationType; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Table; @Entity @Table(name="t_person") public class Person { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Integer id; private String name; private String sex; private User user; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } public User getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(User user) { this.user = user; } //持有其他类的方法 public void useUser(){ System.out.println("准备使用user"); user.getName(); } }
5. User.java类如下
package com.model; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.GenerationType; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Table; @Entity @Table(name="t_user") public class User extends BaseModel { /** * */ private static final long serialVersionUID = -8640311439809984837L; @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY) private int id; private String name; private String lastName; private String password; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { System.out.println("pring getName:" + name); return name; } public void setName(String name) { System.out.println("pring setName:" + name); this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } public User() { super(); } }
6.执行3中的测试类,结果如下
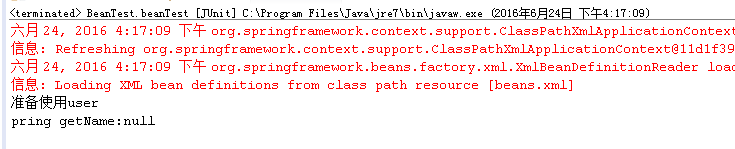
7. 由此可以得出,通过ApplicationContext的实现类ClassPathXmlApplicationContext可以拿到Person类的bean的实例。
然后通过该实例中方法,访问到User对象中的方法。