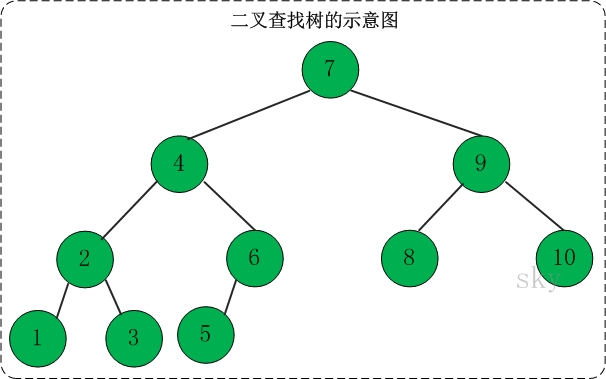
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),又被称为二叉搜索树。
它是特殊的二叉树:对于二叉树,假设x为二叉树中的任意一个结点,x节点包含关键字key,节点x的key值记为key[x]。如果y是x的左子树中的一个结点,则key[y] <= key[x];如果y是x的右子树的一个结点,则key[y] >= key[x]。那么,这棵树就是二叉查找树。如下图所示:
在二叉查找树中:
(01) 若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
(02) 任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
(03) 任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树。
(04) 没有键值相等的节点(no duplicate nodes)。
查找节点:
若二叉查找树为空,则查找失败
若该树非空且查找数据x等于根节点的值,则查找成功,返回根节点
若该树非空且查找数据x小于根节点的值,则查找左子树,直到值相等,并返回节点
若该树非空且查找数据x大于根节点的值,则查找右子树,直到值相等,并返回节点
插入节点:
若二叉查找树为空,则将结点作为根节点插入
若所插入节点关键字值等于根节点的值,则插入失败,并返回
若所插入节点关键字值小于根节点的值,则把节点插入到左子树中
若所插入节点关键字值大于根节点的值,则把节点插入到右子树中
删除节点:
若p结点为叶子结点,则删去该叶子结点,修改其双亲结点的指针即可。
若p结点只有左子树PL或右子树PR,此时只要令PL或PR直接成为其双亲结点的左子树(当p是左子树)或右子树(当p是右子树)。
若p结点的左子树和右子树均不空。找出节点p的后继节点y(一定在节点p的右子树中),以右子树中的最小数作为后继节点。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#define LENGTH 11
struct BinSearNode
{
int key;
struct BinSearNode *left_child;
struct BinSearNode *right_child;
struct BinSearNode *parent;
}Node;
typedef struct BinSearNode *PNode;
/*Search the node of the tree*/
PNode Search_Tree(PNode root, int key)
{
PNode x = root;
//the tree is not empty and the key is not equal
while (NULL != x && x->key != key)
{
if (x->key<key)
x = x->right_child;//along the right child of tree,until it is empty
else
x = x->left_child;//along the left child of tree,until it is empty
}
return x;//return the node
}
/*the minimum key of node in the tree*/
PNode Minimum_Tree(PNode root)
{
PNode x = root;
while (NULL != x->left_child)
{
x = x->left_child;
}
return x;
}
/*the maxmum key of node in the tree*/
PNode Maxmum_Tree(PNode root)
{
PNode x = root;
while (NULL != x->right_child)
{
x = x->right_child;
}
return x;
}
/*the successor node of the x,后继节点可以这么理解,将查找树从小到大排序,比他大的值
如果有右孩子,那么应该是右子树当中的最小值
如果没有右孩子,那么应该向上追溯,直至一个分支节点是其父节点的左孩子,返回父节点
可以用于operate++*/
PNode Successor_Tree(PNode x)
{
PNode y = NULL;
//case 1:the right subtree of node x is not empty
if (NULL != x->right_child)
{
y = Minimum_Tree(x->right_child);
}
//case 2:the right subtree of node x is empty
//and the node of x has a successor node y
else
{
y = x->parent;
while (NULL != y && x == y->right_child)
{
x = y;
y = y->parent;
}
}
return y;
}
/*the predecessor node of the x,前任节点
如果节点有左孩子,那么找到左孩子的最大值
如果没有左孩子,那么向上追溯直至一个分支当前节点是对应父节点的右孩子,返回父节点的值
*/
PNode Predecessor_Tree(PNode x)
{
PNode y = NULL;
//case 1:the left subtree of node x is not empty
if (NULL != x->left_child)
{
y = Maxmum_Tree(x->left_child);
}
//case 2:the left subtree of node x is empty
//and the node of x has a predecessor node y
else
{
y = x->parent;
while (NULL != y && x == y->left_child)
{
x = y;
y = y->parent;
}
}
return y;
}
/*insert a new node into the BST*/
void Insert_Tree(PNode *root, int key)
{
PNode x = *root;
PNode y = NULL;
PNode z = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));//<开辟一个节点的空间
if (NULL == z)
{
printf("malloc the z is failed.");
exit(1);
}
//initial the node of z
z->key = key;
z->left_child = z->right_child = z->parent = NULL;
//Find the location node of y to insert the node of z
while (NULL != x)
{
y = x; //<找到当前树满足条件的叶子节点了,表示为y,之后在y节点后面进行插入操作
if (z->key<x->key)
x = x->left_child;
else
x = x->right_child;
}
//insert the node of z
z->parent = y;
if (NULL == y)
*root = z;//tree was empty
else
{
if (z->key<y->key)
y->left_child = z;
else
y->right_child = z;
}
}
void Transplant(PNode *root, PNode u, PNode v)
{
if (NULL == u->parent)
*root = v;
else
{
if (u == u->parent->left_child)
u->parent->left_child = v;
else
u->parent->right_child = v;
}
if (NULL != v)
v->parent = u->parent;
}
/*delete a node in the binary search tree*/
void Delete_Tree(PNode *root, int key) //<删除节点
{
//Find the node you want to delete
PNode p = Search_Tree(*root, key);
if (NULL == p->left_child)
Transplant(root, p, p->right_child);
else
{
if (NULL == p->right_child)
Transplant(root, p, p->left_child);
else
{
PNode y = Successor_Tree(*root);
if (y->parent != p)
{
Transplant(root, y, y->right_child);
y->right_child = p->right_child;
y->right_child->parent = y;
}
Transplant(root, p, y);
y->left_child = p->left_child;
y->left_child->parent = y;
}
}
}
/*print the key of binary search tree*/
void ioder_Tree(PNode root)
{
if (NULL != root)
{
ioder_Tree(root->left_child);
printf(" %d", root->key);
ioder_Tree(root->right_child);
}
}
int main()
{
int i;
int Arr[LENGTH] = { 16, 6, 20, 2, 7, 19, 22, 1, 4, 11, 8 };
PNode root = NULL;
PNode p = NULL;
for (i = 0; i<LENGTH; i++)
{
Insert_Tree(&root, Arr[i]);
}
ioder_Tree(root);
printf("
");
//printf("Hello world!
");
Delete_Tree(&root, 11);
ioder_Tree(root);
printf("
");
p = Maxmum_Tree(root);
printf("The Maxmum of node is:%d
", p->key);
p = Minimum_Tree(root);
printf("The Minimum of node is:%d
", p->key);
getchar();
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
///声明(int为键 , const char* 为值)
map <int, const char*> m;
///插入元素
m.insert(make_pair(1, "ONE"));
m.insert(make_pair(10, "TEN"));
m[100] = "HUNDRED";///其他写法
///查找元素
map<int, const char*>::iterator ite;
ite = m.find(1);
puts(ite->second);
ite = m.find(2);
if (ite == m.end())
puts("no found");
else
puts(ite->second);
puts(m[10]);///其他写法
///删除元素
m.erase(10);
for (ite = m.begin(); ite != m.end(); ++ite)
{
printf("%d: %s
", ite->first, ite->second);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}