1小组成员及任务分配
| 班级 | 姓名 | 任务 |
|---|---|---|
| 网络1911 | 陈浩 | 前期调查与功能设计,博客总结,面向对象设计 |
| 网络1911 | 陈毅隆 | (主要)面向对象设计 ,功能调试 |
| 网络1911 | 许少 | (主要)面向对象设计 ,功能调试 |
| 网络1911 | 尤志峰 | 编码规范,UML制作,面向对象设计 |
2前期调查(以淘宝网为例)
2.1商品信息
2.1.1主页面

观察结果:商品罗列有分类,使购买者更有目的性。
2.1.1商品展示
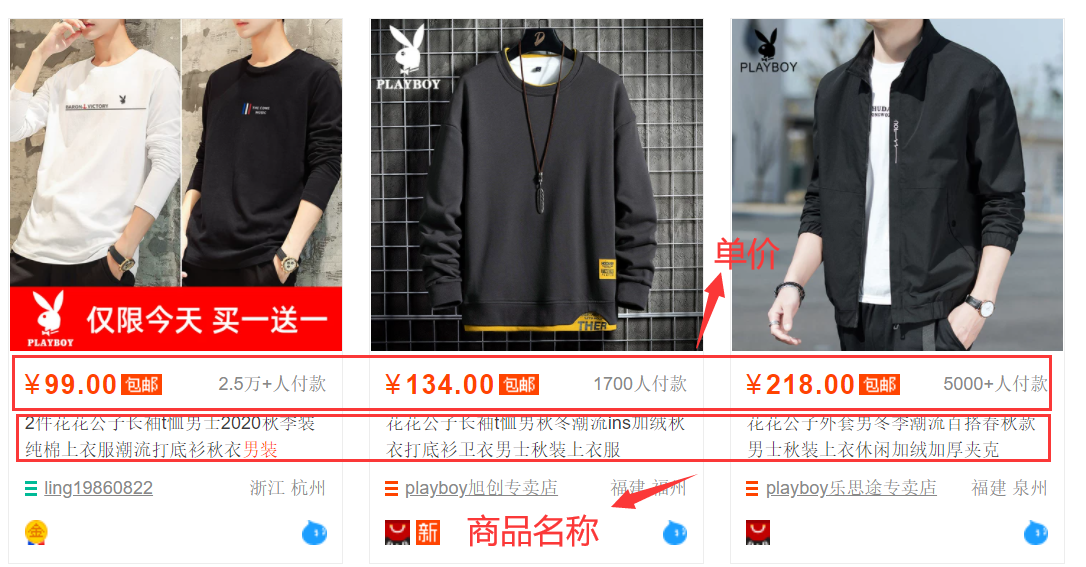
观察结果:商品展示时主要信息含商品的名称描述和单价
2.2购物车界面
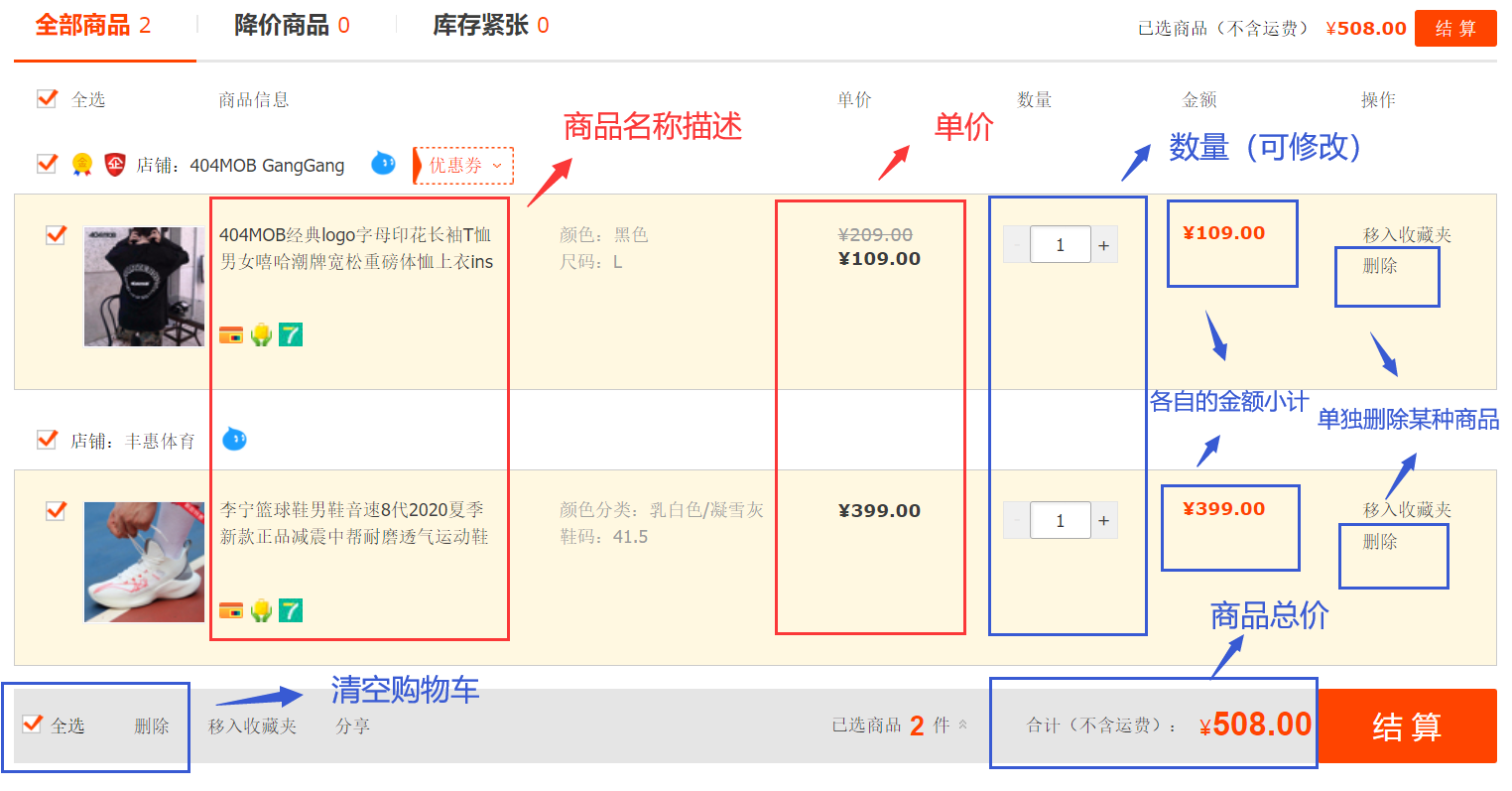
观察结果:
- 购物车显示的信息有:商品名称和单价,每种商品的预购数量和金额小计,所有商品的总金额。
- 购物车的功能操作按键有:增加或者减少某种商品的预购数量,删除某种商品,清空购物车。
3功能设计结构图与功能展示
3.1功能结构图

3.2功能实现截图
主菜单

查看商品罗列

增添商品
- 先增加编号为2的商品5个

- 在此基础上再增加编号为2的商品3个

- 增添编号为3的商品5个(购物车里原本没有的)

完全删除某个商品
-
删除购物车里面有的

-
删除购物车里面没有的

减少某个商品数量
-
减少购物车里面有的

-
减少购物车里面没有的

清空购物车
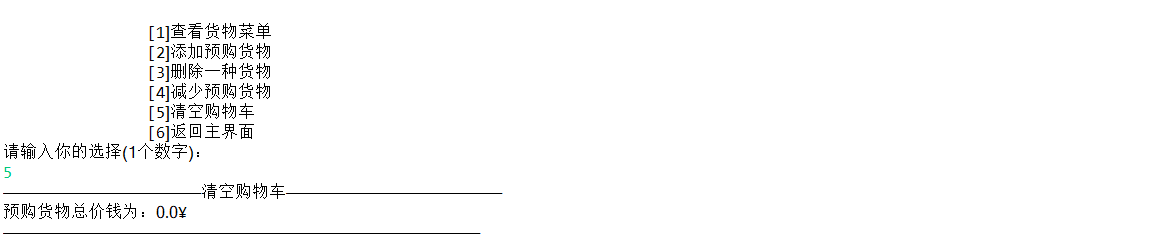
4类的设计与UML图
4.1UML图

4.2类的设计(主要的类)
商品类Commodity(是一个父类,子类有服饰、电子、食品、书籍,为继承关系)
class Commodity {
private Integer id;//商品编号
private String name;//名字
private Double price;//商品价格
private String category;//商品类别
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getCategory() {
return category;
}
public void setCategory(String category) {
this.category = category;
}
public Commodity()
{
}
public Commodity(Integer id, String name, Double price) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Commodity other = (Commodity) obj;
if (id == null) {
if (other.id != null)
return false;
} else if (!id.equals(other.id))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Commodity [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", price=" + price + ", category=" + category + "]";
}
}
菜单类Menu(购物车的功能实现都通过其方法)
class Menu {//菜单类
private static Map<Integer, Commodity> map = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, Commodity>();
static{//类别// 货物编号// 货物名称// 单价//属性
Food good1 = new Food(1, "可食用野生奥特曼", 3.0,"20200815","180"); //此处只展示一个商品的赋值代码,其他省略
map.put(good1.getId(), good1); //此处只展示将一个商品加入map集合,其他省略
}
public static void showMenu() {
System.out.println();
System.out.println(" [1]查看货物菜单 ");
System.out.println(" [2]添加预购货物 ");
System.out.println(" [3]删除一种货物 ");
System.out.println(" [4]减少预购货物 ");
System.out.println(" [5]清空购物车 ");
System.out.println(" [6]返回主界面 ");
}
public static void ShowCategory() {
System.out.println("[1]食品类");
System.out.println("[2]电子类");
System.out.println("[3]服饰类");
System.out.println("[4]书籍类");
System.out.println("请选择商品类型:");
}
public static void showOption() {
ShowCategory();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = sc.nextInt();
switch(choice) {
case 1:{
System.out.println("编号1:可食用野生奥特曼,单价为:3¥"); //此处每一类商品只展示其中一个的代码
}
break;
case 2:{
System.out.println("编号4:联想Y7000,单价为:6400¥");
}break;
case 3:{
System.out.println("编号7:AK男装冬季军事复古,单价为:888¥");
}break;
case 4:{
System.out.println("编号10:《断舍离》,单价为:39¥");
}break;
default :break;
}
}
public static void inputOption(ShoppingCart cart) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你要添加的货物编号及个数:");
if (sc.hasNextLine()) {
String s = sc.nextLine();
String[] strings = s.split(" ");
int id = Integer.parseInt(strings[0]);
int count = Integer.parseInt(strings[1]);
Commodity p = map.get(id);
cart.addGood(p, count);
}
System.out.println("——————————————————————用户总预购货物——————————————————————");
cart.showAll();
System.out.println("货物总价钱为:" + cart.totalAllMoney()+"¥");
System.out.println("—————————————————————————————————————————————————————");
}
public static void deleteOption(ShoppingCart cart) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你想要删除的货物编号:");
if (sc.hasNextLine()) {
String s = sc.nextLine();
int id = Integer.parseInt(s);
boolean flag = cart.deleteGood(id);
if (flag) {
System.out.println("货物编号:" + id + "的货物删除成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("货物编号" + id + "删除失败,购物车没有该货物!!!");
}
}
System.out.println("——————————————————————用户总预购货物——————————————————————");
cart.showAll();
System.out.println("货物总价钱为:" + cart.totalAllMoney()+"¥");
System.out.println("—————————————————————————————————————————————————————");
}
public static void reduceOption(ShoppingCart cart) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你想要减少的货物编号及个数:");
if (sc.hasNextLine()) {
String s = sc.nextLine();
String[] strings = s.split(" ");
int id = Integer.parseInt(strings[0]);
int count = Integer.parseInt(strings[1]);
boolean flag = cart.reduceGood(id,count);
if (flag) {
System.out.println("货物编号:" + id + "的货物减少"+count+"个!");
} else {
System.out.println("减少失败!");
}
}
System.out.println("——————————————————————用户总预购货物——————————————————————");
cart.showAll();
System.out.println("货物总价钱为:" + cart.totalAllMoney()+"¥");
System.out.println("—————————————————————————————————————————————————————");
}
public static void clearOption(ShoppingCart cart) {
cart.clearCart();
System.out.println("——————————————————————清空购物车————————————————————————");
cart.showAll();
System.out.println("预购货物总价钱为:" + cart.totalAllMoney()+"¥");
System.out.println("—————————————————————————————————————————————————————");
}
}
购物车类
class ShoppingCart {// 购物车类
private Map<Integer, GoodItem> map = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, GoodItem>();
// 集合
public void addGood(Commodity p, int count) {// 添加货物
int goodID = p.getId();
if (map.containsKey(goodID)) {// 如果购物车已经存在同样的货物,则的数量增加
GoodItem goodItem = map.get(goodID);
goodItem.setCount(goodItem.getCount() + count);
} else {
map.put(goodID, new GoodItem(p, count));// 如果没有,则新建一个商品信息
}
}
public void showAll() {// 查看购物车所有信息
Collection<GoodItem> GoodItems = map.values();
Iterator<GoodItem> iterator = GoodItems.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
GoodItem GoodItem = iterator.next();
Commodity Good = GoodItem.getGood();
System.out.println("货物编号" + ":" + Good.getId() + ", 货物名称:" + Good.getName() + ", 单价:"
+ Good.getPrice() + "¥, 数量:" + GoodItem.getCount() + ", 小计:" + GoodItem.totalMoney()+"¥");
}
}
public boolean deleteGood(int goodID) {// 删除货物
if (map.containsKey(goodID)) {
map.remove(goodID);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean reduceGood(int goodId,int count) {// 减少货物
GoodItem goodItem = map.get(goodId);
if (map.containsKey(goodId)) {
if(count>goodItem.getCount()) {
System.out.println("不能把货物数量减少成负数哦");
return false;
}else if (count < goodItem.getCount()) {
goodItem.setCount(goodItem.getCount()-count);//数量设置成原数量-count
return true;
} else if (count == goodItem.getCount()) {// 删除该商品,数量减到0
deleteGood(goodId);
return true;
}
}
else System.out.println("购物车中没有该货物");
return false;
}
public void clearCart() {// 清空购物车
map.clear();
}
public double totalAllMoney() {// 货物总价格
double total = 0;
Collection<GoodItem> GoodItems = map.values();
Iterator<GoodItem> iterator = GoodItems.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
GoodItem GoodItem = iterator.next();
double money = GoodItem.totalMoney();
total += money;
}
return total;
}
public Map<Integer, GoodItem> getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map<Integer, GoodItem> map) {
this.map = map;
}
}
商品信息类(属性为某个商品的信息和数量)
class GoodItem {//货物信息类
private Commodity Good;// 购买的货物(包含货物编号,名称,单价)
private int count;// 货物数量
public double totalMoney() {// 小计
double price = Good.getPrice();// 获取货物单价
return price * count; // 获取这个货物的总的价格
}
public GoodItem(Commodity Good, Integer count) {
this.Good = Good;
this.count = count;
}
public Commodity getGood() {
return Good;
}
public void setGood(Commodity Good) {
this.Good = Good;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
}
6关键代码及其说明
商品与编号的map映射
class Menu {//菜单类
private static Map<Integer, Commodity> map = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, Commodity>();
static{//类别// 货物编号// 货物名称// 单价//属性
Food good1 = new Food(1, "可食用野生奥特曼", 3.0,"20200815","180");
Food good2 = new Food(2, "菠萝", 7.0,"20201031","20");
Electronic good3 = new Electronic(3, "MP4" , 99.0,"15V","5000mA");
Electronic good4 = new Electronic(4, "联想Y7000", 6400.0,"220V","60000mA");
Electronic good5 = new Electronic(5, "华为手机", 2998.0,"30V","20000mA");
Electronic good6 = new Electronic(6, "松下洗衣机", 2478.0,"220V","0mA");
Clothes good7 = new Clothes(7, "AK男装冬季军事复古", 888.0,42,"Green");
Clothes good8 = new Clothes(8, "耐克低帮板鞋", 399.0,41,"Blue");
Clothes good9 = new Clothes(9, "一次性手套", 1.0,0,"Write");
Book good10=new Book(10,"断舍离",39.0,"山下英子","湖南文艺出版社");
Book good11=new Book(11,"时间简史",43.2,"史蒂芬·霍金","湖南科学技术出版社");
Book good12=new Book(12,"围城",38.2,"钱钟书","人民文学出版社");
map.put(good1.getId(), good1);
map.put(good2.getId(), good2);
map.put(good3.getId(), good3);
map.put(good4.getId(), good4);
map.put(good5.getId(), good5);
map.put(good6.getId(), good6);
map.put(good7.getId(), good7);
map.put(good8.getId(), good8);
map.put(good9.getId(), good9);
map.put(good10.getId(), good10);
map.put(good11.getId(), good11);
map.put(good12.getId(), good12);
}
}
- 说明:将商品的名称和有序编号映射,便于后续的函数调用的参数设计
增加商品时对商品信息类对象的赋值并且将其加入map集合
public void addGood(Commodity p, int count) {// 添加货物
int goodID = p.getId();
if (map.containsKey(goodID)) {// 如果购物车已经存在同样的货物,则的数量增加
GoodItem goodItem = map.get(goodID); //商品信息类赋值
goodItem.setCount(goodItem.getCount() + count);
} else {
map.put(goodID, new GoodItem(p, count));// 如果没有,则新建一个商品信息加入map集合
}
}
- 说明:新增或者删除某个商品时,都用类似的方法加入map集合或者从map集合中移除。
7总结
- 完成一个较大内容的系统设计时,前期调查,类与对象的设计,代码结构设计都很重要:前期充分的调查保证了系统功能的完整性,功能的完整性依赖于合理的类与对象设计,代码结构梳理好了会使编写代码时目的性和条理性更强,编写效率更高。
- 编写代码时一定要注意变量名,函数名,类名的定义,也要注意方法的规范格式,总的来说就是重视代码的规范性,这将使得后期调试运行时发现问题更容易解决,也会使得代码可读性更强。
- 由于小组几个人都比较懒,任务开始的比较晚,也就是时间不够充足,所以有很多功能没有进行编写,如用户登陆,界面设计,用户增加新商品等。并且函数的有些地方输入错误提示也没有弄完整,我们会在后面陆陆续续补上。