1、在pom.xml中引入依赖
<!--引入swagger2的jar包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--引入接口文档页面UI-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
2、新建config文件夹,编写配置文件SwaggerConfig.java
package com.gxa.config;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration //依赖Spring注解
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean //依赖Spring注解
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) //使用2.0版本
.enable(true) // 是否禁用swagger,可以控制全局
.useDefaultResponseMessages(false) //是否使用默认响应消息的方式
.apiInfo(apiInfo()) //创建api的基本信息,如:标题、描述、版本等
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withClassAnnotation(Api.class))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("swagger API文档")
.description("测试接口文档")
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
3、在SpringMVC配置文件中配置扫描
<!-- 扫描com.gxa.config -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.gxa.config"/>
4、swagger使用
4.1、@Api 修饰整个类,描述Controller的作用
@Controller
@Api(value = "用户数据test",tags = "用户数据接口API") //value:代表代码级描述 tags:代表页面级描述
public class Swagger2Controller {
// code..
}
在http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html地址中查看下面的效果
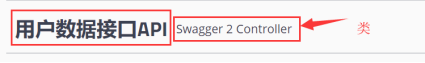
4.2、@ApiOperation 修饰一个方法,代表此方法为一个接口,通常配合Spring MVC RequestMapping注解一起放置在方法上
@RequestMapping(value = "/think_login",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ApiOperation(value = "用户登录接口",notes = "验证用户的用户名和密码",httpMethod = "post", response = String.class) //value:代表页面级接口描述 notes:代表完整接口说明 httpMethod:可选参数,代表调用的请求方式,但是swagger标示的spring mvc的请求方式,所以即使像上面那样,定义为了post,但是Spring MVC是get请求,在接口文档中还是呈现get方式。 response:可选参数,代表返回类型
public String login() {
return "login";
}

4.3、@ApiImplicitParam 代表一个请求参数的定义,通常与Spring MVC的RequestParam注解一起使用。
@RequestMapping(value = "/think_login",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ApiOperation(value = "用户登录接口",notes = "验证用户的用户名和密码",httpMethod = "post", response = String.class)
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "username",value = "用户名",required = true,dataType = "String",paramType = "query")
/**
* name:代表页面级描述参数名
* value:代表页面级描述参数说明
* required:代表页面级展示是否一定要输入
* dataType:代表页面级描述参数类型
* paramType:
* path 以地址的形式提交数据
* query 直接跟参数完成自动映射赋值
* body 以流的形式提交 仅支持POST
* header 参数在request headers 里边提交
* form 以form表单的形式提交 仅支持POST
* 被这个paramType坑过,当发POST请求的时候,当时接受的整个参数,不论用body还是query,后台都会报Body Missing错误;这个参数和SpringMvc中的@RequestBody冲突,去掉paramType对接口测试并没有影响。
*/
public String login(@RequestParam(name = "username") String username) {
return username;
}

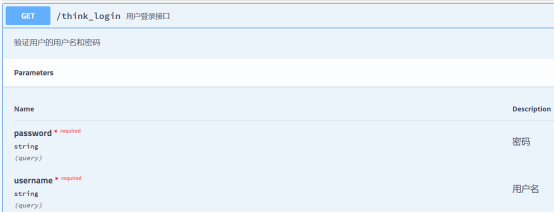
4.4、@ApiImplicitParams 代表多个形式参数的表达形式,内部是数组形态,可以包含多个@ApiImplicitParam注解标记
@RequestMapping(value = "/think_login",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ApiOperation(value = "用户登录接口",notes = "验证用户的用户名和密码",httpMethod = "post", response = String.class)
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "username",value = "用户名",paramType = "query",dataType = "String",required = true),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "password",value = "密码",paramType = "query",dataType = "String",required = true)
})
public String login(@RequestParam(name = "username") String username,
@RequestParam(name = "password") String password) {
return username + password;
}
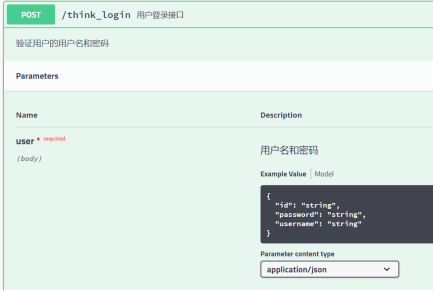
4.5、@ApiParam Json参数的定义,通常与Spring MVC的@RequestBody配合使用,特别注意的是,因为是json参数请求,所以接收方式必须是post,如果使用的get可能会出现错误
@RequestMapping(value = "/think_login",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
@ApiOperation(value = "用户登录接口",notes = "验证用户的用户名和密码",httpMethod = "post", response = String.class)
public User login(@RequestBody @ApiParam(name = "user",value = "用户名和密码",required = true) User user) { //name:页面级描述形式参数的名字 value:页面级形参的说明 required:页面级标注是否一定需要输入
return user;
}
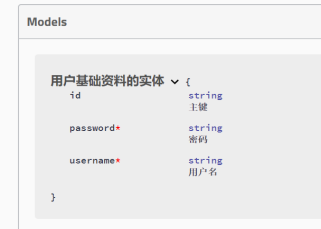
4.6、@ApiModel和@ApiProperty @ApiModel和@ApiModelProperty两个注解的作用是在接口文档中显示出entity的完整信息,@ApiModel定义在entity类名上,@ApiModelProperty定义在entity的属性上
@ApiModel(value = "用户基础资料的实体")
public class ThinkUser {
@ApiModelProperty(name = "id",notes = "主键",dataType = "String",required = false) //name:页面级字段名展示 notes:页面级字段名描述 dataType:页面级字段类型说明 required:页面级标注字段是否必输
private String id;
@ApiModelProperty(name = "username",notes = "用户名",dataType = "String",required = true)
private String username;
@ApiModelProperty(name = "password",notes = "密码",dataType = "String",required = true)
private String password;
// set、get方法...
}
4.7、@ApiResponses和@ApiResponse @ApiResponses包含多个响应结果模板,在此注解中加入@ApiResponse代表每一种响应格式
@RequestMapping(value = "/think_login",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
@ApiOperation(value = "用户登录接口",notes = "验证用户的用户名和密码",httpMethod = "post", response = String.class)
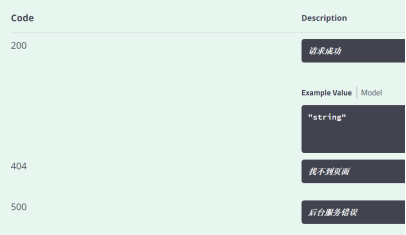
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code=200,message="请求成功"), //code:代表状态码 message:代表说明信息
@ApiResponse(code=404,message="找不到页面"),
@ApiResponse(code=500,message="后台服务错误")
})
public ThinkUser login(@RequestBody @ApiParam(name = "thinkUser",value = "用户名和密码",required = true) ThinkUser thinkUser) {
return thinkUser;
}
4.8、@ApiIgnore 定义在类上,代表此类会swagger忽略,定义在方法上,代表此方法被swagger忽略
5、禁用Swagger 禁用处理最直接的方式,就是剥离掉所有的swagger注解
第一步,修改enable属性为false,这样处理以后再次访问swagger-ui.html页面会发现,页面中的信息不会暴露了,但是还会有对应的响应存在,这样会让外部人员知道此系统使用了swagger技术,如下效果:

@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.enable(false) // 是否禁用swagger
.useDefaultResponseMessages(false)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withClassAnnotation(Api.class))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
第二步,增加一个controller,管理/swagger-ui路径,如下:
@RequestMapping("/swagger-ui")
public String getUserInfo() {
return "error";
}
这样的方式,是利用了spring mvc优先查找requestMapping的功能,这样相当于拦截了这个页面路径的请求,这时候访问swagger-ui.html当出现错误提示,可以根据业务需要修改为任意的跳转地址。
