练习目标-在类中使用List作为模拟集合操作: 在本练习中,将用List实现银行与客户间的多重关系。
任务
对银行来说,可添加Bank类。 Bank 对象跟踪自身与其客户间的关系。用Customer对象的List实现这个集合化的关系。还要保持一个整数属性来跟踪银行当前有多少客户。
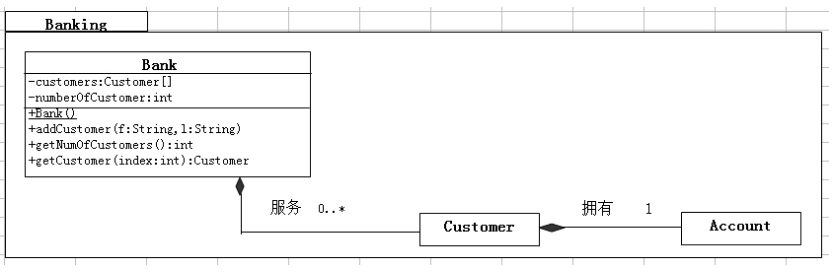
- 创建 Bank 类
- 为Bank类增加两个属性:customers(Customer对象的List)和numberOfCustomers(整数, 当前Customer对象的数量)
- 添加公有构造器,初始化customersList。
- 添加addCustomer方法。该方法必须依照参数(姓,名)构造一个新的Customer对象然后把它放到customerList中。
- 添加getNumOfCustomers 访问方法,它返回numberofCustomers属性值。
- 添加getCustomer方法。它返回与给出的index参数相关的客户。
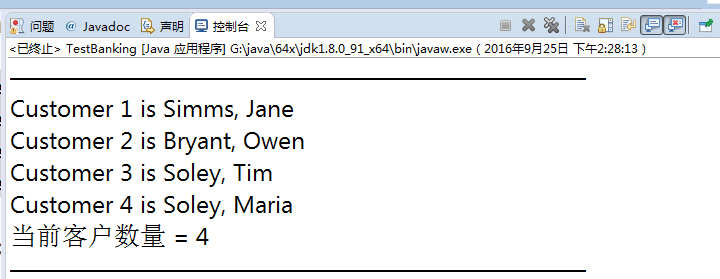
- 编译并运行TestBanking程序。可以看到下列输出结果:
Customer 1 is Simms,Jane
Customer 2 is Bryant,Owen
Customer 3 is Soley,Tim
Customer 4 is Soley,Maria
当前客户数量 = 4
package banking; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Bank1 { private List<Customer> customers ; private int numberOfCustomers = 1 ; public Bank1( ) { customers =new ArrayList<>() ; } public void addCustomer(String firstName ,String lastName) { customers.add(new Customer(firstName,lastName)); } public int getNumberOfCustomers() { numberOfCustomers=customers.size(); return numberOfCustomers; } public Customer getCustomer(int index) { Customer s=new Customer(); s=customers.get(index); return s; } }
package banking; import java.util.List; public class Customer extends Account { //成员属性 private String firstName ; private String lastName ; private double account ; //构造方法 public Customer() { } //构造方法 public Customer(String f , String l) { this.firstName = f ; this.lastName = l ; } //get set public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } public double getAccount() { return account; } public void setAccount(double account) { this.account = account; } public String toString() { return firstName + ", " + lastName ; } }
package banking; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; public class TestBanking { public static void main(String[] args) { //实例化账户 Account at = new Account(500) ; System.out.println("Creating an account with a "+at.getBalance( ) +" balance") ; System.out.println("Withdraw "+(at.getBalance( ) -at.withdraw(150) )); double x=at.getBalance( ); System.out.println("Deposit "+(at.deposit(22.5)-x)) ; System.out.println("Withdraw "+(at.getBalance( ) -at.withdraw(47.62) )); System.out.println("The account has a balance of "+at.getBalance()) ; System.out.println("————————————————————————"); //实例化顾客 Customer cr = new Customer( ) ; cr.setFirstName("Jane"); cr.setLastName("Smith"); cr.setBalance(500); System.out.println("Creating the customer "+cr.getFirstName() +" "+cr.getLastName()); System.out.println("Creating her account with a " +cr.getBalance()+" balance"); System.out.println("Withdraw "+(cr.getBalance()-cr.withdraw(150)) ); double x1 = cr.getBalance( ) ; System.out.println("Deposit "+(cr.deposit(22.5)-x1)); System.out.println("Withdraw "+(cr.getBalance()-cr.withdraw(47.62))); System.out.println("Customer "+cr.getLastName()+" "+cr.getFirstName()+ " has a balance of "+cr.getBalance()); System.out.println("————————————————————————"); Customer cr1 = new Customer( ) ; cr1.setFirstName("Jane"); cr1.setLastName("Smith"); cr1.setBalance(500); System.out.println("Creating the customer "+cr1.getFirstName() +" "+cr1.getLastName()); System.out.println("Creating her account with a " +cr1.getBalance()+" balance"); System.out.println(cr1.withdraw1(150) ); System.out.println(cr1.deposit1(22.5)); System.out.println(cr1.withdraw1(47.62)); System.out.println(cr1.withdraw1(400)); System.out.println("Customer "+cr1.getLastName()+" "+cr1.getFirstName()+ " has a balance of "+cr1.getBalance()); System.out.println("————————————————————————"); Bank bk =new Bank( ) ; bk.addCustomer( "Simms" , "Jane" ); bk.addCustomer( "Bryant" , "Owen" ); bk.addCustomer( "Soley" , "Tim" ); bk.addCustomer( "Soley" , "Maria" ); System.out.println("————————————————————————"); // Bank1 bk1 = new Bank1(){}; bk1.addCustomer("Simms", "Jane"); bk1.addCustomer("Bryant", "Owen"); bk1.addCustomer("Soley","Tim"); bk1.addCustomer("Soley","Maria"); for(int i=0 ;i <bk1.getNumberOfCustomers();i++) { System.out.println("Customer "+(i+1)+" is"+" "+bk1.getCustomer(i)); } System.out.println("当前客户数量 = "+bk1.getNumberOfCustomers()); System.out.println("————————————————————————"); } }