2018-2019-120189224 《庖丁解牛Iinux内核分析》第三周学习总结
MenuOS的构造
下载内核源代码编译内核
cd ~/LinuxKernel/
wget https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v3.x/linux-3.18.6.tar.xz
xz -d linux-3.18.6.tar.xz
tar -xvf linux-3.18.6.tar
cd linux-3.18.6
make i386_defconfig
make #
制作根文件系统
cd ~/LinuxKernel/
mkdir rootfs
git clone https://github.com/mengning/menu.git
cd menu
gcc -o init linktable.c menu.c test.c -m32 -static –lpthread
cd ../rootfs
cp ../menu/init ./
find . | cpio -o -Hnewc |gzip -9 > ../rootfs.img
启动MenuOS系统
cd ~/LinuxKernel/
qemu -kernel linux-3.18.6/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.img
跟踪调试Linux内核的启动过程
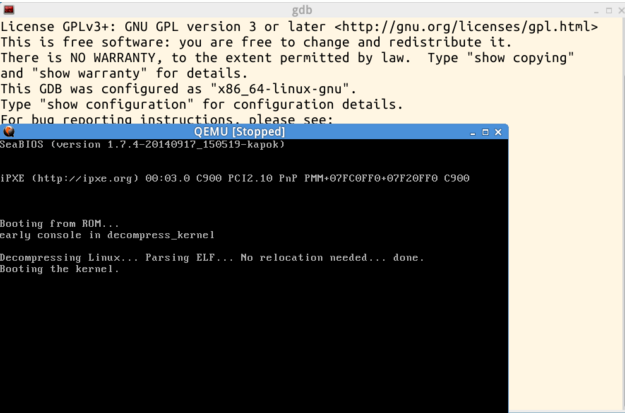
1.构建一个简单的Linux内核,在实验楼虚拟机中:cd LinuxKernel/ qemu -kernel linux-3.18.6/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.img通过这两个简单的命令把Linux系统和一个简单的文件系统运行起来,结果如下图

2.qemu -kernel linux-3.18.6/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.img -S -s
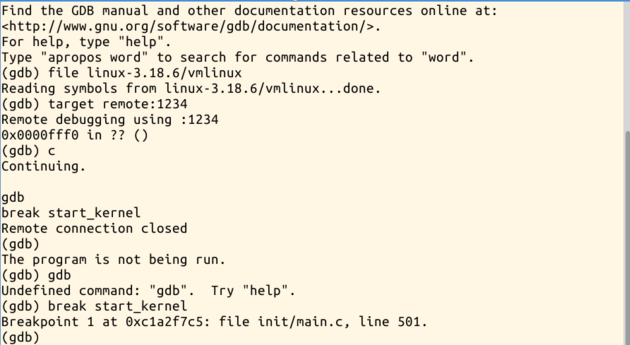
3.打开一个新的命令窗口,启动gdb,加载内核建立连接cd LinuxKernel/ gdb file linux-3.18.6/vmlinux target remote:1234
按c内核继续运行

4.在start_kernel处设置断点break start_kernel
5.按c继续运行,运行到断点停止
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
- 问题1:找不到vmlinux
- 问题1解决方案:调试前要进入LinuxKernel目录下
- 问题2:调试过程中虚拟机桌面没有反应
- 问题2解决方案:Ctrl+Alt切换鼠标控制
内核启动过程分析
Linux内核启动相关的代码基本在init目录下,init/main.c是内核的启动起点。
start_kernel函数相当于普通C程序中的main函数,搭建环境,启动内核。
调用sched_init()函数来初始化调度程序
调用build_all_zonelists()函数俩初始化内存管理
调用page_alloc_init()函数来初始化伙伴系统分配程序
调用trap_init()函数和init_IRQ()函数以初始化IDT
调用softing_init()函数初始化TASKLET_SOFTIRQ和HI_SOFTIRQ(软中断)
调用time_init()初始化系统日期时间
调用kmem_cache_init()函数初始化slab分配器(普通和高速缓存)
调用calibrate_delay()函数用于确定CPU时钟(延迟函数)
调用kernel_thread()函数为进程1创建内个线程,这个内核线程又会创建其他的内核线程并执行/sbin/init程序
start_kernel()
asmlinkage __visible void __init start_kernel(void)
{
char *command_line;
char *after_dashes;
/*
* Need to run as early as possible, to initialize the
* lockdep hash:
*/
lockdep_init();
set_task_stack_end_magic(&init_task);
smp_setup_processor_id();
debug_objects_early_init();
/*
* Set up the the initial canary ASAP:
*/
boot_init_stack_canary();
cgroup_init_early();
local_irq_disable();
early_boot_irqs_disabled = true;
init_task()
static noinline void __init_refok rest_init(void)
394{
395 int pid;
396
397 rcu_scheduler_starting();
398 /*
399 * We need to spawn init first so that it obtains pid 1, however
400 * the init task will end up wanting to create kthreads, which, if
401 * we schedule it before we create kthreadd, will OOPS.
402 */
403 kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS);
404 numa_default_policy();
405 pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES);
406 rcu_read_lock();
407 kthreadd_task = find_task_by_pid_ns(pid, &init_pid_ns);
408 rcu_read_unlock();
409 complete(&kthreadd_done);
410
411 /*
412 * The boot idle thread must execute schedule()
413 * at least once to get things moving:
414 */
415 init_idle_bootup_task(current);
416 schedule_preempt_disabled();
417 /* Call into cpu_idle with preempt disabled */
418 cpu_startup_entry(CPUHP_ONLINE);
419}
420
421/* Check for early params. *
rest_init()
static noinline void __init_refok rest_init(void)
394{
395 int pid;
396
397 rcu_scheduler_starting();
398 /*
399 * We need to spawn init first so that it obtains pid 1, however
400 * the init task will end up wanting to create kthreads, which, if
401 * we schedule it before we create kthreadd, will OOPS.
402 */
403 kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS);
404 numa_default_policy();
405 pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES);//调用kernel_thread执行kthreadd,创建PID为2的内核线程
406 rcu_read_lock();
407 kthreadd_task = find_task_by_pid_ns(pid, &init_pid_ns);
408 rcu_read_unlock();
409 complete(&kthreadd_done);
410
411 /*
412 * The boot idle thread must execute schedule()
413 * at least once to get things moving:
414 */
415 init_idle_bootup_task(current);
416 schedule_preempt_disabled();
417 /* Call into cpu_idle with preempt disabled */
418 cpu_startup_entry(CPUHP_ONLINE);
419}
420
421/* Check for early params. */