2017-2018-1 20155220实验四——外设驱动程序设计
任务一
要求
- 学习资源中全课中的“hqyj.嵌入式Linux应用程序开发标准教程.pdf”中的第十一章
- 提交康奈尔笔记的照片
步骤
使用印象笔记中的康奈尔笔记模板
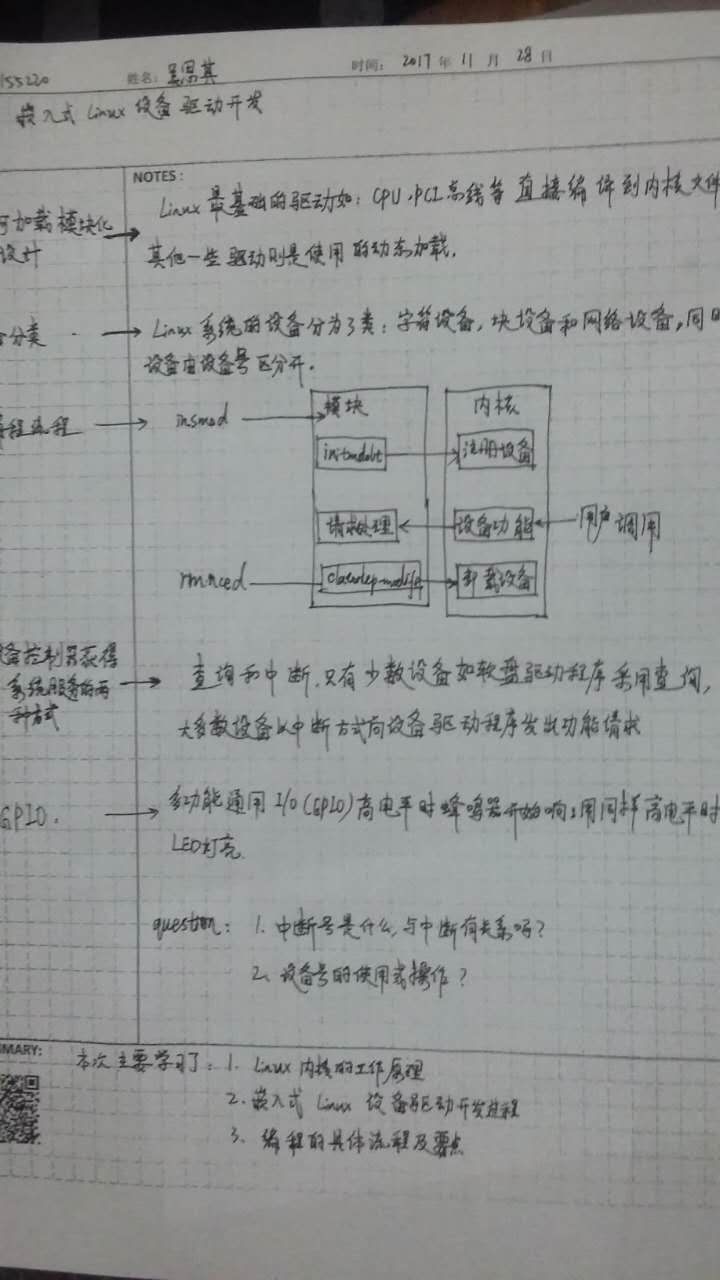
任务二
要求
- 在Ubuntu完成资源中全课中的“hqyj.嵌入式Linux应用程序开发标准教程.pdf”中的第十一章的test试验
- 提交编译,加载模块,卸载模块,测试运行的截图(要多张,全屏,体现学号信息)
编写代码
- 驱动程序
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#define TEST_DEVICE_NAME "test_dev"
#define BUFF_SZ 1024
/*全局变量*/
static struct cdev test_dev;
unsigned int major =0;
static char *data = NULL;
/*读函数*/
static ssize_t test_read(struct file *file,char *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{
int len;
if (count < 0 )
{
return -EINVAL;
}
len = strlen(data);
count = (len > count)?count:len;
if (copy_to_user(buf, data, count)) /* 将内核缓冲的数据拷贝到用户空间*/ {
return -EFAULT;
}
return count;
}
/*写函数*/
static ssize_t test_write(struct file *file, const char *buffer,size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{
if(count < 0)
{
return -EINVAL;
}
memset(data, 0, BUFF_SZ);
count = (BUFF_SZ > count)?count:BUFF_SZ;
if (copy_from_user(data, buffer, count)) /* 将用户缓冲的数据复制到内核空间*/ {
return -EFAULT;
}
return count;
}
/*打开函数*/
static int test_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {
printk("This is open operation
"); /* 分配并初始化缓冲区*/
data = (char*)kmalloc(sizeof(char) * BUFF_SZ, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!data){
return -ENOMEM;
}
memset(data, 0, BUFF_SZ);
return 0;
}
/*关闭函数*/
static int test_release(struct inode *inode,struct file *file) {
printk("This is release operation
");
if (data)
{
kfree(data); /* 释放缓冲区*/
data = NULL; /* 防止出现野指针 */ }
return 0;
}
/* 创建、初始化字符设备,并且注册到系统*/
static void test_setup_cdev(struct cdev *dev, int minor,struct file_operations *fops)
{
int err, devno = MKDEV(major, minor);
cdev_init(dev, fops);
dev->owner = THIS_MODULE;
dev->ops = fops;
err = cdev_add (dev, devno, 1);
if (err)
{
printk (KERN_NOTICE "Error %d adding test %d", err, minor);
}
}
/* 虚拟设备的 file_operations 结构 */
static struct file_operations test_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = test_read,
.write = test_write,
.open = test_open,
.release = test_release,
};
/*模块注册入口*/
int init_module(void) {
int result;
dev_t dev = MKDEV(major, 0);
if (major)
{/* 静态注册一个设备,设备号先前指定好,并设定设备名,用 cat /proc/devices 来查看 */
result = register_chrdev_region(dev, 1, TEST_DEVICE_NAME); }
else {
result = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev, 0, 1, TEST_DEVICE_NAME); }
if (result < 0)
{
printk(KERN_WARNING "Test device: unable to get major %d
", major);
return result;
}
test_setup_cdev(&test_dev, 0, &test_fops);
printk("The major of the test device is %d
", major);
return 0;
}
/*卸载模块*/
void cleanup_module(void) {
cdev_del(&test_dev);
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major, 0), 1);
printk("Test device uninstalled
");
}
- Makefile文件
ifeq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
KERNELDIR ?= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
PWD := $(shell pwd)
modules:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
modules_install:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules_install
clean:
rm -rf *.o *~ core .depend .*.cmd *.ko *.mod.c .tmp_versions
.PHONY: modules modules_install clean
else
obj-m := test_drv.o
endif
- 加载模块脚本
#!/bin/sh
# 驱动模块名称
module="test_drv"
# 设备名称。在/proc/devices 中出现
device="test_dev"
# 设备文件的属性
mode="664"
group="root"
# 删除已存在的设备节点
rm -f /dev/${device}
# 加载驱动模块
#/sbin/insmod ./$module.ko $* || exit 1
# 查到创建设备的主设备号
major=`cat /proc/devices | awk "\$2=="$device" {print \$1}"`
# 创建设备文件节点
mknod /dev/${device} c $major 0
# 设置设备文件属性
chgrp $group /dev/${device}
chmod $mode /dev/${device}
- 编译test.c并执行
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define TEST_DEVICE_FILENAME "/dev/test_dev" /* 设备文件名*/
#define BUFF_SZ 1024
int main() {
int fd, nwrite, nread;
char buff[BUFF_SZ];
fd = open(TEST_DEVICE_FILENAME, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
do {
printf("Input some words to kernel(enter 'quit' to exit):");
memset(buff, 0, BUFF_SZ);
if (fgets(buff, BUFF_SZ, stdin) == NULL)
{
perror("fgets");
break; }
buff[strlen(buff) - 1] = '�';
if (write(fd, buff, strlen(buff)) < 0) /* 向设备写入数据 */ {
perror("write");
break; }
if (read(fd, buff, BUFF_SZ) < 0) {
perror("read");
break; }
else {
printf("The read string is from kernel:%s
", buff);
}
} while(strncmp(buff, "quit", 4));
close(fd);
exit(0);
}
- 卸载模块
#!/bin/sh
module="test_drv"
device="test_dev"
# 卸载驱动模块
/sbin/rmmod $module $* || exit 1
# 删除设备文件
rm -f /dev/${device}
exit 0
实验过程:
make clean
make
./test_drv_load
gcc -o test test.c
./test_drv_unload
实验截图:
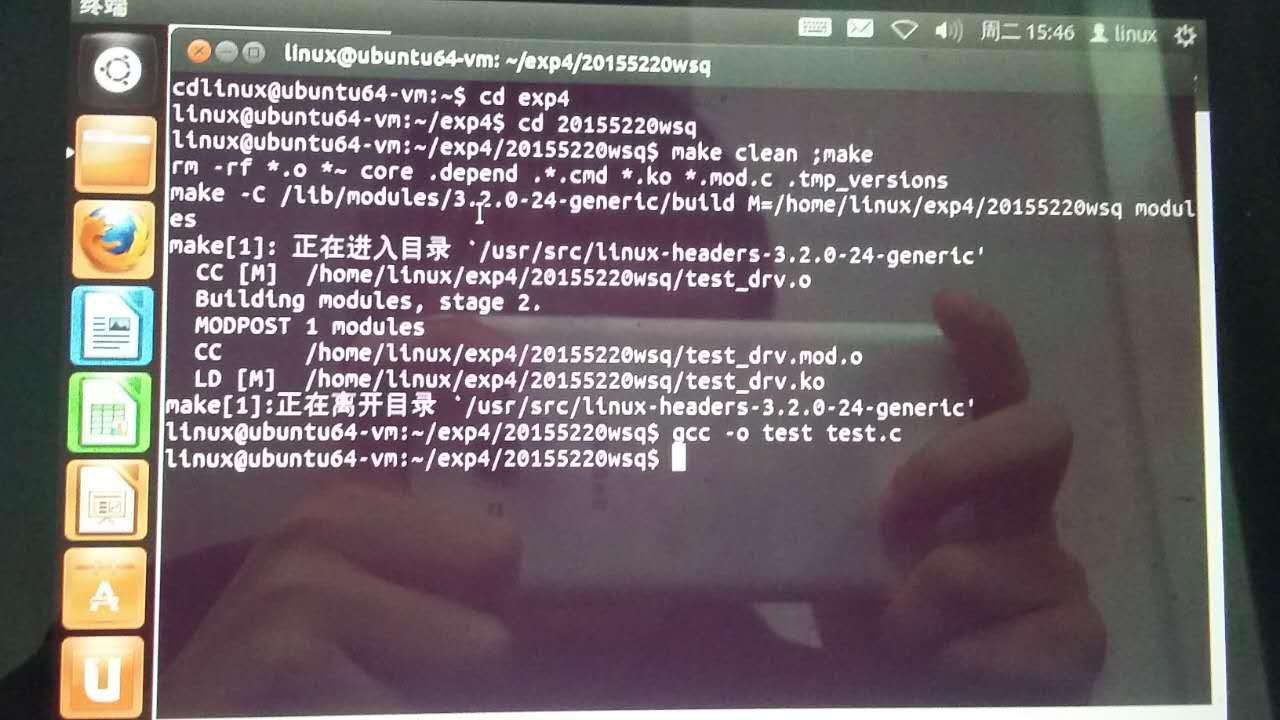
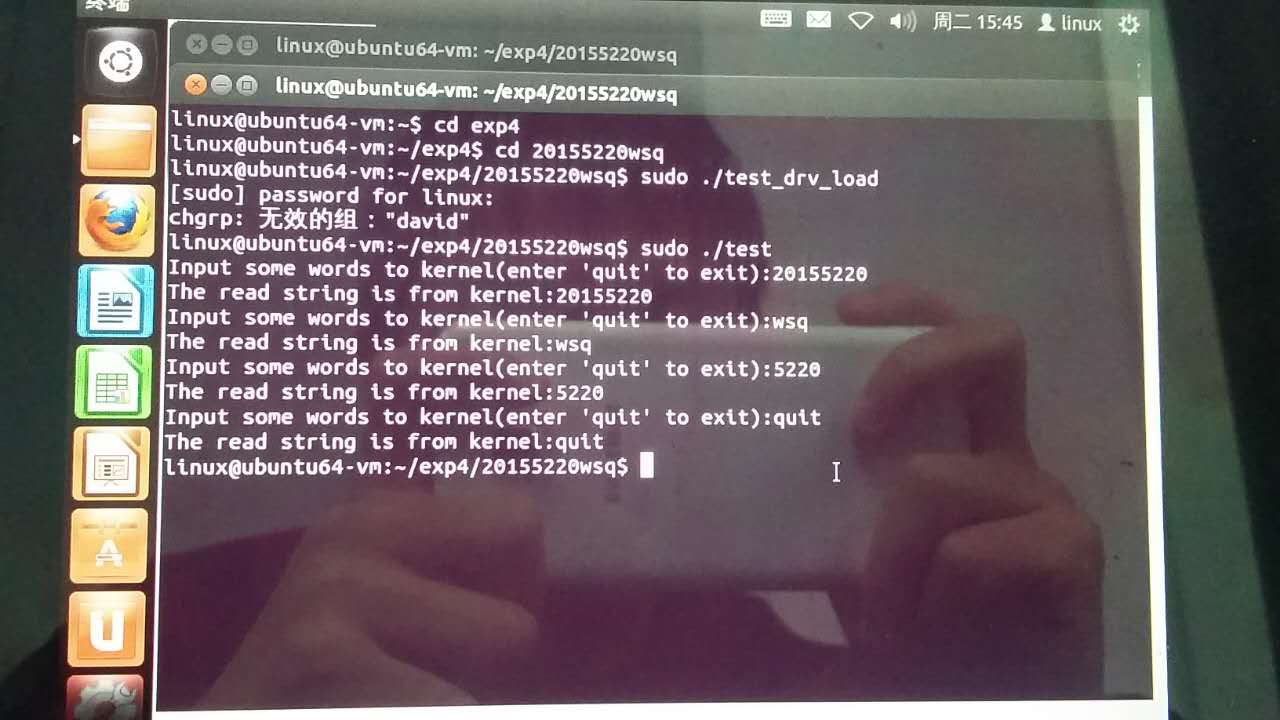
实验感想:
本次实验自学了嵌入式Linux设备驱动的开发相关知识,为之后的实验做了铺垫,但从中学习到了 有关linux系统许多知识。