1.函数
def sayHello(name="Levi") puts "hello #{name}." end sayHello
结果如下
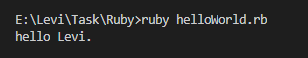
2.类
class Player def initialize(name="levi")#构造函数 @name=name end def show() puts "player:#{@name}" end end levi=Player.new() levi.show() curry=Player.new("curry") curry.show() harden=Player.new("harden") harden.show()
结果如下:
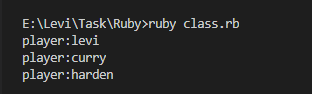
3.类的instance_methods()方法,ture表示输出他的实例方法,false输出所有的方法
对象的respond_to?() 方法,表示对象是否含有这个参数签名的方法
对象的send()方法,表示执行这个方法
class Game def initialize(title="怪物猎人",price=200) @title=title @price=price end def show() puts "标题:#{@title}" puts "价格:#{@price}" end def show2() end def show3() end end puts Game.instance_methods(false) mario=Game.new("超级马里奥",360); if mario.respond_to?("show") mario.send("show") end
4.类的属性:
class Game attr_accessor:price ,:title def initialize(title="怪物猎人设计",price=200) @title=title @price=price end def show() puts "标题: #{@title}" puts "价格: #{@price}" end end mygame=Game.new() mygame.show() puts "title is "+mygame.respond_to?("title").to_s puts "price is"+mygame.respond_to?("price").to_s mygame.price=150 mygame.show()
输出如下

5.数组
games=["绝地逃生","怪物猎人世界","LOL"] games.each do |game| puts "我爱<<#{game}>>" end games.each_with_index do |game,i| puts "#{i}.#{game}" end puts games.join(",") if games.respond_to?("each")##respond_to用来判断是不是有each这个方法 end
输出如下:
