TreeMap和HashMap实现了同样的接口Map,因此,用法基本么有区别,但是hashMap的效率高于TreeMap,在需要排序的Map才选用TreeMap。TreeMap是红黑二叉树实现的,打开源码会看到核心代码:
private transient Entry<K,V> root;
root用来存储整个树的根结点。root是Entry<k,v>类型,接下来看看Entry。
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { K key; V value; Entry<K,V> left; Entry<K,V> right; Entry<K,V> parent; boolean color = BLACK; Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) { this.key = key; this.value = value; this.parent = parent; }
Entry是TreeMap的内部类,可以看到里面存储的本身数据,左右结点,父节点以及节点的颜色。
public class TestTreeMap {
public staticvoid main(String[] args) {
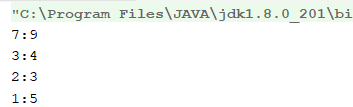
TreeMap<Integer,Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
treeMap.put(2,3);
treeMap.put(3,4);
treeMap.put(1,5);
treeMap.put(7,9);
for (Integer key:treeMap.keySet()
) {
System.out.println(key+":"+treeMap.get(key));
}
}
}

由代码发现treeMap,是按照key自增的方式排列。
如果想要上面的数据实现从大到小的顺序排列:

当key为自定义的类型时,便需要实现Comparable接口,实现ComparaTo方法。有三个返回值,分别是负数,零,正数。
例如下面的例子对学生Student类进行score属性进行从小到大的顺序进行排序。
import java.util.TreeMap; public class TestTreeMap { public static void main(String[] args) { TreeMap<Integer, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>(); treeMap.put(2, 3); treeMap.put(3, 4); treeMap.put(1, 5); treeMap.put(7, 9); for (Integer key : treeMap.keySet() ) { System.out.println(key + ":" + treeMap.get(key)); } TreeMap<Student, Integer> treeMap1 = new TreeMap<>(); treeMap1.put(new Student(1001,18,95),1001); treeMap1.put(new Student(1002,18,87),1002); treeMap1.put(new Student(1003,18,85),1003); treeMap1.put(new Student(1004,18,97),1004); for (Student key : treeMap1.keySet() ) { System.out.println(key + ":" + treeMap1.get(key)); } } } class Student implements Comparable<Student>{ private int age; private int id; private int score; public Student(int id, int age, int score) { this.age = age; this.id = id; this.score = score; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "age=" + age + ", id=" + id + ", score=" + score + '}'; } @Override public int compareTo(Student o) { if(this.score < o.score){ return -1; }else if(this.score == o.score){ return 0; }else { return 1; } } }
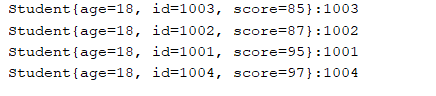
当然还想实现别的属性排序,只需要在comparaTo里面实现即可。