Java提供一个线程调度器来监控程序中启动后进入就绪状态的所有线程。线程调 度器按照线程的优先级决定应调度哪个线程来执行。
线程的优先级用数字表示,范围从1到10
- Thread.MIN_PRIORITY = 1
- Thread.MAX_PRIORITY = 10
- Thread.NORM_PRIORITY = 5
使用下述方法获得或设置线程对象的优先级。
- int getPriority();
- void setPriority(int newPriority);
优先级的设定建议在start()调用前
注意:优先级低只是意味着获得调度的概率低。并不是绝对先调用优先级高后调 用优先级低的线程。
代码示例:
1 package com.sxt.state; 2 3 /** 4 * 线程的优先级1-10 5 * MAX_PRIORITY 5默认 6 * MIN_PRIORITY 1 7 * NORM_PRIORITY 10 8 * 优先级不代表绝对的先后顺序,代表概率 9 */ 10 public class PriorityTest { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); 14 15 MyPriority mp = new MyPriority(); 16 Thread t1 = new Thread(mp,"adidas"); 17 Thread t2 = new Thread(mp,"NIKE"); 18 Thread t3 = new Thread(mp,"回力"); 19 Thread t4 = new Thread(mp,"乔丹"); 20 Thread t5 = new Thread(mp,"李宁"); 21 Thread t6 = new Thread(mp,"双星"); 22 23 //在启动前这只优先级 24 t1.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); 25 t2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); 26 t3.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); 27 t4.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); 28 t5.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); 29 t6.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); 30 t1.start(); 31 t2.start(); 32 t3.start(); 33 t4.start(); 34 t5.start(); 35 t6.start(); 36 37 } 38 } 39 40 class MyPriority implements Runnable{ 41 42 @Override 43 public void run() { 44 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); 45 46 } 47 }
代码示例:
1 package com.sxt.state; 2 3 /** 4 * 守护线程:是为用户线程服务的;jvm停止不用等待守护线程执行完毕 5 * 默认:用户线程 jvm等待用户线程执行完毕才会停止 6 * 7 */ 8 public class DaemonTest { 9 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 God god = new God(); 12 You you = new You(); 13 Thread t = new Thread(god); 14 t.setDaemon(true);//将用户线程调整为守护 15 t.start(); 16 new Thread(you).start(); 17 } 18 } 19 20 class You implements Runnable{ 21 @Override 22 public void run() { 23 for (int i = 1; i <= 365*100; i++) { 24 System.out.println("happy life..."); 25 } 26 27 System.out.println("oooooo..."); 28 } 29 } 30 31 class God implements Runnable{ 32 33 @Override 34 public void run() { 35 for (;true;) { 36 System.out.println("bless you..."); 37 } 38 } 39 }
daemon:守护进程,后台程序
- 线程分为用户线程和守护线程;
- 虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕;
- 虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕;
- 如后台记录操作日志、监控内存使用等。
常用其他方法
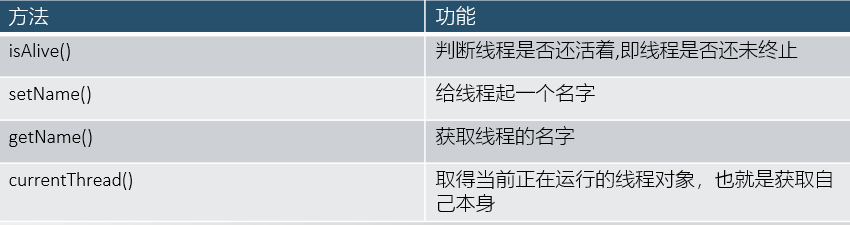
代码示例:
1 package com.sxt.state; 2 3 /** 4 * 其他方法 5 * isAlive:线程是否还活着 6 * Thread.currentThread():当前线程 7 * setName、getName:代理名称 8 */ 9 public class InfoTest { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 12 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().isAlive()); 13 //设置名称:真实角色+代理角色 14 MyInfo info = new MyInfo("战斗机"); 15 Thread t = new Thread(info); 16 t.setName("公鸡"); 17 t.start(); 18 Thread.sleep(1000); 19 System.out.println(t.isAlive()); 20 21 } 22 } 23 24 class MyInfo implements Runnable{ 25 26 private String name; 27 28 public MyInfo(String name) { 29 this.name = name; 30 } 31 32 @Override 33 public void run() { 34 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+name); 35 } 36 }