异常
在Java中使用Exception类来描述异常。

Throwable是Java 语言中所有错误或异常的超类,即祖宗类。
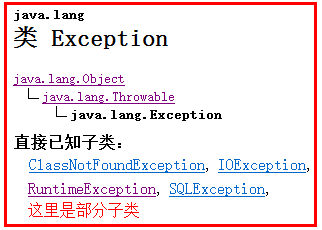

异常继承体系

Throwable -Error异常:错误--》无法处理,只能改代码 Exception异常 -RuntimeException以及子类:运行期异常,一旦发生只能修改代码 非RuntimeException:编译期异常,可以处理
异常与错误的区别
异常:指程序在编译、运行期间发生了某种异常(XxxException),我们可以对异常进行具体的处理。若不处理异常,程序将会结束运行。
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = new int[3]; System.out.println(arr[0]); System.out.println(arr[3]); // 该句运行时发生了数组索引越界异常ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException,由于没有处理异常,导致程序无法继续执行,程序结束。 System.out.println("over"); // 由于上面代码发生了异常,此句代码不会执行 }
错误:指程序在运行期间发生了某种错误(XxxError),Error错误通常没有具体的处理方式,程序将会结束运行。Error错误的发生往往都是系统级别的问题,都是jvm所在系统发生的,并反馈给jvm的。我们无法针对处理,只能修正代码。
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = new int[1024*1024*100]; //该句运行时发生了内存溢出错误OutOfMemoryError,开辟了过大的数组空间,导致JVM在分配数组空间时超出了JVM内存空间,直接发生错误。 }

抛出异常throw
使用格式:
throw new 异常类名(参数);
例如:
throw new NullPointerException("要访问的arr数组不存在"); throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("该索引在数组中不存在,已超出范围");
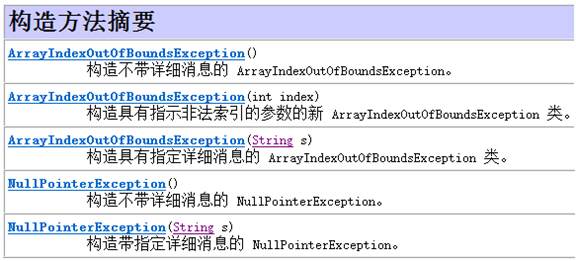
l 异常类ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException与NullPointerException的构造方法
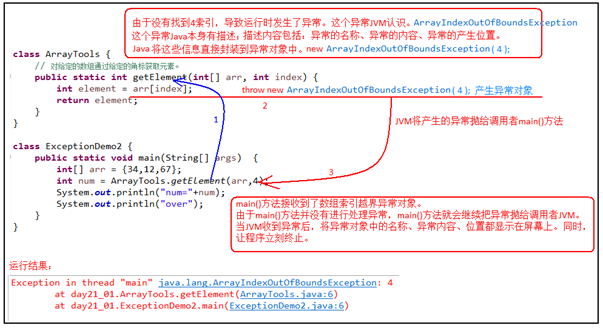
class ArrayTools{ //通过给定的数组,返回给定的索引对应的元素值。 public static int getElement(int[] arr,int index) { /* 若程序出了异常,JVM它会打包异常对象并抛出。但是它所提供的信息不够给力。想要更清晰,需要自己抛出异常信息。 下面判断条件如果满足,当执行完throw抛出异常对象后,方法已经无法继续运算。这时就会结束当前方法的执行,并将异常告知给调用者。这时就需要通过异常来解决。 */ if(arr==null){ throw new NullPointerException("arr指向的数组不存在"); } if(index<0 || index>=arr.length){ throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("错误的角标,"+index+"索引在数组中不存在"); } int element = arr[index]; return element; } }
class ExceptionDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {34,12,67}; //创建数组 int num = ArrayTools.getElement(null,2);// 调用方法,获取数组中指定索引处元素 //int num = ArrayTools.getElement(arr,5);// 调用方法,获取数组中指定索引处元素 System.out.println("num="+num);//打印获取到的元素值 } }
声明异常throws
声明异常格式:
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数) throws 异常类名1,异常类名2… { }
class Demo{ /* 如果定义功能时有问题发生需要报告给调用者。可以通过在方法上使用throws关键字进行声明。 */ public void show(int x)throws Exception { if(x>0){ throw new Exception(); } else { System.out.println("show run"); } } }
throws用于进行异常类的声明,若该方法可能有多种异常情况产生,那么在throws后面可以写多个异常类,用逗号隔开。
多个异常的情况,例如: public static int getElement(int[] arr,int index) throws NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException { if(arr==null){ throw new NullPointerException("arr指向的数组不存在"); } if(index<0 || index>=arr.length){ throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("错误的角标,"+index+"索引在数组中不存在"); } int element = arr[index]; return element; }
捕获异常try…catch…finally
捕获异常格式:
try { //需要被检测的语句。 } catch(异常类 变量) { //参数。 //异常的处理语句。 } finally { //一定会被执行的语句。 }
try:该代码块中编写可能产生异常的代码。
catch:用来进行某种异常的捕获,实现对捕获到的异常进行处理。
finally:有一些特定的代码无论异常是否发生,都需要执行。另外,因为异常会引发程序跳转,导致有些语句执行不到。而finally就是解决这个问题的,在finally代码块中存放的代码都是一定会被执行的。
class ExceptionDemo{ public static void main(String[] args){ //throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException try { int[] arr = new int[3]; System.out.println( arr[5] );// 会抛出ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 当产生异常时,必须有处理方式。要么捕获,要么声明。 } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { //括号中需要定义什么呢?try中抛出的是什么异常,在括号中就定义什么异常类型。 System.out.println("异常发生了"); } finally { arr = null; //把数组指向null,通过垃圾回收器,进行内存垃圾的清除 } System.out.println("程序运行结果"); } }
l try catch finally组合:检测异常,并传递给catch处理,并在finally中进行资源释放。
l try catch组合 : 对代码进行异常检测,并对检测的异常传递给catch处理。对异常进行捕获处理。
l 一个try 多个catch组合 : 对代码进行异常检测,并对检测的异常传递给catch处理。对每种异常信息进行不同的捕获处理。
注意:这种异常处理方式,要求多个catch中的异常不能相同,并且若catch中的多个异常之间有子父类异常的关系,那么子类异常要求在上面的catch处理,父类异常在下面的catch处理。
l try finally 组合: 对代码进行异常检测,检测到异常后因为没有catch,所以一样会被默认jvm抛出。异常是没有捕获处理的。但是功能所开启资源需要进行关闭,所有finally。只为关闭资源。
运行时期异常
l RuntimeException和他的所有子类异常,都属于运行时期异常。NullPointerException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException等都属于运行时期异常.
l 运行时期异常的特点:
方法中抛出运行时期异常,方法定义中无需throws声明,调用者也无需处理此异常
运行时期异常一旦发生,需要程序人员修改源代码.
异常在方法重写中细节
子类覆盖父类方法时,如果父类的方法声明异常,子类只能声明父类异常或者该异常的子类,或者不声明。
当父类方法声明多个异常时,子类覆盖时只能声明多个异常的子集
当被覆盖的方法没有异常声明时,子类覆盖时无法声明异常的。
package com.orcal.demo02; import java.sql.SQLException; public class Fu { public void f(){ } public void ff() throws SQLException{ } }
package com.orcal.demo02; import java.sql.SQLWarning; public class Zi extends Fu{ public void f(){//子类重写父类方法没有抛异常的方法时,重写后不能抛异常 try { ff();//调用了抛异常方法 } catch (SQLWarning e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } //重写抛异常方法,重写后可以不抛异常.如果抛,只能抛出父类异常或父类异常的子类 public void ff() throws SQLWarning{} }
异常中常用方法
l getMessage方法:返回该异常的详细信息字符串,即异常提示信息
l toString方法:返回该异常的名称与详细信息字符串
l printStackTrace:在控制台输出该异常的名称与详细信息字符串、异常出现的代码位置
package com.orcal.demo01; public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr={1,2,3}; try{ int n=get(arr); System.out.println(n); }catch(Exception ex){ System.out.println(ex.getMessage());//返回异常信息 //System.out.println(ex);//toString返回异常类名和异常信息 //ex.printStackTrace();//将异常类名。信息。位置以红字方式打印在控制台 }finally{//final.finlize.finally System.out.println("一定会被执行的语句"); } System.out.println("你好"); } public static int get(int[] arr) throws Exception{ if(arr.length<5){ throw new Exception("你的数组长度不够!"); } int num=arr[4]; return num; } }
自定义异常
NullPointerException异常类源代码:
public class NullPointerException extends RuntimeException { public NullPointerException() { super();//调用父类构造方法 } public NullPointerException(String s) { super(s);//调用父类具有异常信息的构造方法 } }
定义个自己的异常,即自定义异常。
格式:
Class 异常名 extends Exception{ //或继承RuntimeException
public 异常名(){
}
public 异常名(String s){
super(s);
}
}
class MyException extends Exception{ /* 为什么要定义构造函数,因为看到Java中的异常描述类中有提供对异常对象的初始化方法。 */ public MyException(){ super(); } public MyException(String message) { super(message);// 如果自定义异常需要异常信息,可以通过调用父类的带有字符串参数的构造函数即可。 } }
l 自定义异常继承RuntimeException
class MyException extends RuntimeException{ /* 为什么要定义构造函数,因为看到Java中的异常描述类中有提供对异常对象的初始化方法。 */ MyException(){ super(); } MyException(String message) { super(message);// 如果自定义异常需要异常信息,可以通过调用父类的带有字符串参数的构造函数即可。 } }