On a plane are n points (xi, yi) with integer coordinates between 0 and 106. The distance between the two points with numbers a and b is said to be the following value: 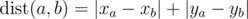 (the distance calculated by such formula is called Manhattan distance).
(the distance calculated by such formula is called Manhattan distance).
We call a hamiltonian path to be some permutation pi of numbers from 1 to n. We say that the length of this path is value 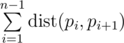 .
.
Find some hamiltonian path with a length of no more than 25 × 108. Note that you do not have to minimize the path length.
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 106).
The i + 1-th line contains the coordinates of the i-th point: xi and yi (0 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 106).
It is guaranteed that no two points coincide.
Print the permutation of numbers pi from 1 to n — the sought Hamiltonian path. The permutation must meet the inequality 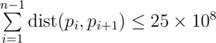 .
.
If there are multiple possible answers, print any of them.
It is guaranteed that the answer exists.
5
0 7
8 10
3 4
5 0
9 12
4 3 1 2 5
In the sample test the total distance is:
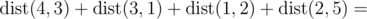
(|5 - 3| + |0 - 4|) + (|3 - 0| + |4 - 7|) + (|0 - 8| + |7 - 10|) + (|8 - 9| + |10 - 12|) = 2 + 4 + 3 + 3 + 8 + 3 + 1 + 2 = 26
初识分快.
引一段题解:
Let's split rectangle 106 × 106 by vertical lines into 1000 rectangles 103 × 106. Let's number them from left to right. We're going to pass through points rectangle by rectangle. Inside the rectangle we're going to pass the points in increasing order of y-coordinate if the number of rectangle is even and in decreasing if it's odd.
Let's calculate the maximum length of such a way. The coordinates are independent. By y-coordinate we're passing 1000 rectangles from0 to 106, 109 in total. By x-coordinate we're spending 1000 to get to the next point of current rectangle and 2000 to get to next rectangle. That means, 2 * 109 + 2000000 in total, which perfectly fits.
The complexity is O(n * log(n))
并不会做,看了题解写的,感觉好神奇...
然后加深了sort的cmp函数的理解...
原来还可以这么写.
有点开心,因为觉得解法有点美.
/************************************************************************* > File Name: code/cf/#319/E.cpp > Author: 111qqz > Email: rkz2013@126.com > Created Time: 2015年09月18日 星期五 20时55分10秒 ************************************************************************/ #include<iostream> #include<iomanip> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<map> #include<set> #include<queue> #include<vector> #include<stack> #include<cctype> #define y1 hust111qqz #define yn hez111qqz #define j1 cute111qqz #define ms(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a)) #define lr dying111qqz using namespace std; #define For(i, n) for (int i=0;i<int(n);++i) typedef long long LL; typedef double DB; const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int N=1E6+7; int n; int id[N],x[N],y[N]; bool cmp(int a,int b) //id[a] 和id[b]的大小比较定义 { if (x[a]<x[b]) return true; if (x[a]>x[b]) return false; if (x[a]%2==1) return y[a]<y[b]; else return y[a]>y[b]; //sort的cmp函数原来还可以这么写,长见识了. } int main() { #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); #endif scanf("%d",&n); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { scanf("%d %d",&x[i],&y[i]); x[i] /=1000; y[i] /=1000; id[i] = i; } sort(id,id+n,cmp); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { printf("%d ",id[i]+1); } #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE fclose(stdin); #endif return 0; }