Living in Byteland was good enough to begin with, but the good king decided to please his subjects and to introduce a national language. He gathered the best of wise men, and sent an expedition to faraway countries, so that they would find out all about how a language should be designed.
After some time, the wise men returned from the trip even wiser. They locked up for six months in the dining room, after which they said to the king: "there are a lot of different languages, but almost all of them have letters that are divided into vowels and consonants; in a word, vowels and consonants must be combined correctly."
There are very many rules, all of them have exceptions, but our language will be deprived of such defects! We propose to introduce a set of formal rules of combining vowels and consonants, and include in the language all the words that satisfy them.
The rules of composing words are:
- The letters are divided into vowels and consonants in some certain way;
- All words have a length of exactly n;
- There are m rules of the form (pos1, t1, pos2, t2). Each rule is: if the position pos1 has a letter of type t1, then the position pos2 has a letter of type t2.
You are given some string s of length n, it is not necessarily a correct word of the new language. Among all the words of the language that lexicographically not smaller than the string s, find the minimal one in lexicographic order.
The first line contains a single line consisting of letters 'V' (Vowel) and 'C' (Consonant), determining which letters are vowels and which letters are consonants. The length of this string l is the size of the alphabet of the new language (1 ≤ l ≤ 26). The first l letters of the English alphabet are used as the letters of the alphabet of the new language. If the i-th character of the string equals to 'V', then the corresponding letter is a vowel, otherwise it is a consonant.
The second line contains two integers n, m (1 ≤ n ≤ 200, 0 ≤ m ≤ 4n(n - 1)) — the number of letters in a single word and the number of rules, correspondingly.
Next m lines describe m rules of the language in the following format: pos1, t1, pos2, t2 (1 ≤ pos1, pos2 ≤ n,pos1 ≠ pos2, 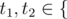 'V', 'C' }).
'V', 'C' }).
The last line contains string s of length n, consisting of the first l small letters of the English alphabet.
It is guaranteed that no two rules are the same.
Print a smallest word of a language that is lexicographically not smaller than s. If such words does not exist (for example, if the language has no words at all), print "-1" (without the quotes).
VC
2 1
1 V 2 C
aa
ab
VC
2 1
1 C 2 V
bb
-1
VCC
4 3
1 C 2 V
2 C 3 V
3 V 4 V
abac
acaa
In the first test word "aa" is not a word of the language, but word "ab" is.
In the second test out of all four possibilities only word "bb" is not a word of a language, but all other words are lexicographically less, so there is no answer.
In the third test, due to the last rule, "abac" doesn't belong to the language ("a" is a vowel, "c" is a consonant). The only word with prefix "ab" that meets the given rules is "abaa". But it is less than "abac", so the answer will be "acaa"
2-sat问题,具体见文章中转载自kuangbin博客的2-sat问题总结。
第一次遇到,不过上个月讲课的时候讲过,有点印象。
具体见代码注释
/************************************************************************* > File Name: code/cf/#315/E.cpp > Author: 111qqz > Email: rkz2013@126.com > Created Time: 2015年08月15日 星期六 13时48分36秒 ************************************************************************/ #include<iostream> #include<iomanip> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<map> #include<set> #include<queue> #include<vector> #include<stack> #define y0 abc111qqz #define y1 hust111qqz #define yn hez111qqz #define j1 cute111qqz #define tm crazy111qqz #define lr dying111qqz using namespace std; #define REP(i, n) for (int i=0;i<int(n);++i) typedef long long LL; typedef unsigned long long ULL; const int inf = 0x7fffffff; const int N=5E2+7; int flag[N],flag2[N]; int f[N][N]; int a[N]; char s[N]; int ans[N]; int len,n,m; char s1[13],s2[13]; int p1,p2,q1,q2,dq1,dq2; void add(int p,int q,int flag[]) { int dq = q * n + p;//找到元辅音状态为q,第p的点的下标 for (int i=1;i<=2*n;++i) { if (f[dq][i]==0) continue; flag[i]=1;//找到所有由dp出发的边指向的点,表示选了dp点一定要选的点。 } } bool check(int flag[]) { for (int i=1;i<=n;++i) if (flag[i]==1&&flag[i+n]==1) return false; //判断是否存在矛盾 //(选了j点后,既要选择某点k的元音,也要选择某点k的辅音) return true; } bool dfs(int pos,int x) { if (pos>n) return true;//如果能形成一个长度为n的单词,说明这种语言有word bool g[2]; g[0]=g[1]=false; for (int i=x;i<=len;++i)//从当前字母x往后枚举 { for (int j=1;j<=2*n;++j) flag2[j]=flag[j];//为了不影响原始数组,复制一个布尔数组出来。 add(pos,a[i],flag2);//找到所有选了pos点一定要选的点 if (check(flag2)&&(!g[a[i]])) { g[a[i]]=true; for (int j=1;j<=2*n;++j) flag[j]=flag2[j]; ans[pos]=i;//将第pos位置的字母变成i if (dfs(pos+1,1)) return true; else return false;//只要有一位找不到合适的字母形成单词,那么肯定就构不成单词。 } } return false; } int main() { scanf("%s",s); len=strlen(s); //0表示辅音,1表示原因,下同。 for (int i=1;i<=len;++i)//len 表示字母表中一共有的字母的个数 { if (s[i-1]=='V') { a[i] = 0; } else { a[i] = 1; } } memset(f,0,sizeof(f)); scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for (int i=1;i<=m;++i)//1..n表示元音的点,n+1..2*n 表示辅音的点 { scanf("%d",&p1); scanf("%s",s1); if (s1[0]=='V') q1=0;else q1=1; scanf("%d",&p2); scanf("%s",s2); if (s2[0]=='V') q2=0;else q2=1; dq1=q1*n+p1;dq2=q2*n+p2;//找到这组关系对应的点。 f[dq1][dq2]=1;//连一条由dq1指向dq2的边,表示如果选了dp1点,那么一定选dp2点 dq1=(1-q2)*n+p2;dq2=(1-q1)*n+p1;//找到逆否命题对应的点 // ("如果选1,一定选2"的逆否命题是,"如果不选2,一定不选1") f[dq1][dq2]=1; //在连一条边 } for (int i=1;i<=2*n;++i) f[i][i]=1; for (int k=1;k<=2*n;++k)//floyd ,把所有间接相连的边直接相连 { for (int i=1;i<=2*n;++i) for (int j=1;j<=2*n;++j) f[i][j]|=f[i][k]&f[k][j]; } scanf("%s",s+1); bool ok=false; for (int i=n;i>=0;--i) //倒着扫,每次只改变最后一位的字母,字母从小往大枚举 //这样就可以保证字典序最小。 { memset(flag,0,sizeof(flag)); for (int j=1;j<=i;++j) { add(j,a[s[j]-'a'+1],flag); ans[j]=s[j]-'a'+1; } if (!check(flag)) continue; if (dfs(i+1,s[i+1]-'a'+1+1)) { ok=true; break; } } if (!ok) printf("-1 "); else { for (int i=1;i<=n;++i) printf("%c",ans[i]+'a'-1); } return 0; }