线程的生命周期
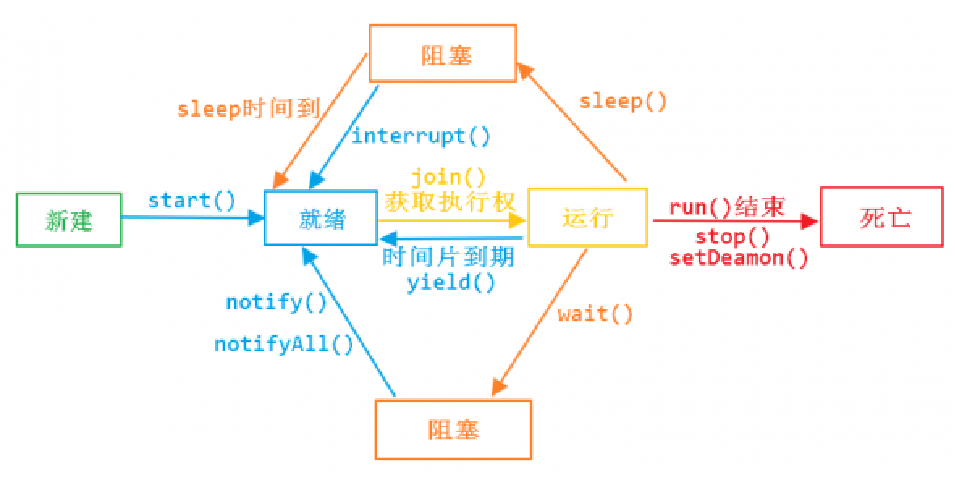
线程的启动
package com.thread.demo; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; public class ThreadByRunable { private static class ThreadByThread extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("我是继承Thread接口的线程"); } } private static class RunableThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("我是实现runable接口的线程"); } } /*实现callable线程,可以有返回值*/ private static class Callabled implements Callable<String> { @Override public String call() throws Exception { System.out.println("我是实现callable接口的线程,我的返回值类型是<String>"); return "CallableSuccess"; } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { ThreadByThread t = new ThreadByThread(); t.start(); RunableThread threadByRunable = new RunableThread(); new Thread(threadByRunable).start(); Thread t1 = new Thread(threadByRunable); t1.interrupt(); Callabled call = new Callabled(); FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(call); new Thread(futureTask).start(); System.out.println(futureTask.get()); } }
线程自然终止:自然执行完或抛出未处理异常
终止线程的方法
interrupt() 方法中断一个线程,并不是强行关闭这个线程,只是跟这个线程打个招呼,将线程的中断标志位置为true,线程是否中断,由线程本身决定。
isInterrupted() 判定当前线程是否处于中断状态。
static方法interrupted() 判定当前线程是否处于中断状态,同时中断标志位改为false。
java的线程是协作式的,不是抢占式,因此,想安全的中断一个线程,使用interrupt()只是告诉线程需要来中断了,但是,如果线程中对interrupt没有进行判定,没有使用isInterrupted(),那么该线程还是会一直运行,如下demo
package com.thread.demo; public class ThreadByThread { private static class UseThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { try { while(!interrupted()){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +"我是继承thread的线程"); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +"中断的状态是"+isInterrupted()); }finally{ System.out.println("over"); } } } private static class UseThread2 extends Thread { @Override public void run() { try { while(true){//此处没有对是否中断进行识别,那么当主方法中调用interrupt()时,该线程不会被中断 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +"我是继承thread的线程"); } }finally{ System.out.println("over"); } } } private static class RunableThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName(); while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { System.out.println(threadName+" is run!"); } System.out.println(threadName+" interrput flag is " +Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { UseThread useThread = new UseThread(); //设置为守护线程,默认为用户线程 useThread.setDaemon(true); useThread.start(); UseThread.sleep(5); useThread.interrupt(); UseThread2 useThread2 = new UseThread2(); //设置为守护线程,默认为用户线程 useThread2.setDaemon(true); useThread2.start(); UseThread2.sleep(5); useThread2.interrupt(); RunableThread threadByRunable = new RunableThread(); Thread t1 = new Thread(threadByRunable,"111"); t1.start(); Thread.sleep(20); t1.interrupt(); } }
当线程中catch到InterruptedException时,isInterrupt()会初始化为false
public class HasInterrputException { private static class UseThread extends Thread{ public UseThread(String name) { super(name); } @Override public void run() { String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName(); while(isInterrupted()) { try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println(threadName+" interrput flag is " +isInterrupted()); interrupt(); e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(threadName); } System.out.println(threadName+" interrput flag is " +isInterrupted()); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread endThread = new UseThread("HasInterrputEx"); endThread.start(); Thread.sleep(500); endThread.interrupt(); } }
守护线程:与主线程生命周期同步,finally不一定会执行,GC就是典型的守护线程
public class DaemonThread { private static class DaemonDemo extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { try { while (!isInterrupted()) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " I am extends Thread."); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " interrupt flag is " + isInterrupted()); } finally { System.out.println("...........finally"); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { DaemonDemo daemonDemo = new DaemonDemo(); // daemonDemo.setDaemon(true); daemonDemo.start(); Thread.sleep(10); daemonDemo.interrupt(); } }
main方法中的 setDaemon(true)放开,finally不会执行
线程间的共享
synchronized内置锁:
1.对象所锁:有synchronize没有static修饰词的方法
2.类锁:有synchronize有static修饰词的方法
自己的理解:对象锁,锁的是对象,必须要是同一个new 出来的对象,才会共享一个线程,排队执行方法;类锁,一种特殊的对象锁,锁的是类,所以不管new多少个类,但是共享的还是一个锁,所以都会共享一个线程,demo中主要根据main方法中的new出来的情况,看打印的顺序,同时打出来就是没有共享线程,一个一个的打出来就是共享了
public class SynClzAndInst { //使用类锁的线程 private static class SynClass extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("TestClass 开始运行了..."); synClass(); } } //使用对象锁的线程 private static class InstanceSyn implements Runnable{ private SynClzAndInst synClzAndInst; public InstanceSyn(SynClzAndInst synClzAndInst) { this.synClzAndInst = synClzAndInst; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println("InstanceSyn is running..."+synClzAndInst); synClzAndInst.instance(); } } //使用对象锁的线程 private static class Instance2Syn implements Runnable{ private SynClzAndInst synClzAndInst; public Instance2Syn(SynClzAndInst synClzAndInst) { this.synClzAndInst = synClzAndInst; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Instance2Syn is running..."+synClzAndInst); synClzAndInst.instance2(); } } //锁对象 private synchronized void instance(){ SleepTools.second(3); System.out.println("instance is going..."+this.toString()); SleepTools.second(3); System.out.println("instance ended "+this.toString()); } //锁对象 private synchronized void instance2(){ SleepTools.second(3); System.out.println("instance2 is going..."+this.toString()); SleepTools.second(3); System.out.println("instance2 ended "+this.toString()); } //类锁,实际是锁类的class对象 private static synchronized void synClass(){ SleepTools.second(1); System.out.println("synClass 在运行..."); SleepTools.second(1); System.out.println("synClass 运行完毕"); } public static void main(String[] args) { // //实例一个对象 // SynClzAndInst synClzAndInst = new SynClzAndInst(); // //把对象交给一个线程(runnable的启动) // Thread t1 = new Thread(new InstanceSyn(synClzAndInst)); // //实例另一个对象 // SynClzAndInst synClzAndInst2 = new SynClzAndInst(); //t2中放入的实例对象和t1不同,那就不是共享线程,是两个不同的锁,会同时打印 // Thread t2 = new Thread(new Instance2Syn(synClzAndInst2)); //如果t2中放入的对象和t1是同一个,那就是共享线程,是同一个对象锁,会排队打印 // Thread t2 = new Thread(new Instance2Syn(synClzAndInst)); // t1.start(); // t2.start(); //new 两个类(这个对象那中的内部类),虽然new出来是两个不同名的内部类,但是类锁却是同一个,所以会排队打印 SynClass synClass = new SynClass(); synClass.start(); SynClass synClass2 = new SynClass(); synClass2.start(); //线程休眠的工具方法 SleepTools.second(1); } }
SleepTools的代码
public class SleepTools { /** * 按秒休眠 * @param seconds 秒数 */ public static final void second(int seconds) { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } /** * 按毫秒数休眠 * @param seconds 毫秒 */ public static final void ms(int seconds) { try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(seconds); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } }
线程变量ThreadLocal
可以理解为是个map,类型 Map<Thread,Integer>

public class UseThreadLocal { //可以理解为 一个map,类型 Map<Thread,Integer> static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLaocl = new ThreadLocal<Integer>(){ @Override protected Integer initialValue() { return 1; } }; /** * 运行3个线程 */ public void StartThreadArray(){ Thread[] runs = new Thread[3]; for(int i=0;i<runs.length;i++){ runs[i]=new Thread(new TestThread(i)); } for(int i=0;i<runs.length;i++){ runs[i].start(); } } /** *类说明:测试线程,线程的工作是将ThreadLocal变量的值变化,并写回,看看线程之间是否会互相影响 */ public static class TestThread implements Runnable{ int id; public TestThread(int id){ this.id = id; } public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":start"); Integer s = threadLaocl.get();//获得变量的值 s = s+id; threadLaocl.set(s); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":" +threadLaocl.get()); //threadLaocl.remove(); } } public static void main(String[] args){ UseThreadLocal test = new UseThreadLocal(); test.StartThreadArray(); } }
等待和通知(wait()/notify(),notifyAll())
等待方:wait()
1、 获取对象的锁;
2、 循环里判断条件是否满足,不满足调用wait方法,
3、 条件满足执行业务逻辑
通知方来说:notify(),notifyAll()
1、 获取对象的锁;
2、 改变条件
3、 通知所有等待在对象的线程
尽量选用notifyAll()
一个烂大街的demo,打印1A2B3C...

public class AddNumAndWords { private static class demoThread1 extends Thread{ private AddNumAndWords add; public demoThread1(AddNumAndWords add) { this.add=add; } @Override public void run() { try { synchronized (add) { for(int i=0;i<26;i++){ System.out.print(i); add.notifyAll(); add.wait(); } } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } private static class demoThread2 extends Thread{ private AddNumAndWords add; public demoThread2(AddNumAndWords add) { this.add=add; } @Override public void run() { try { synchronized (add) { for(int i=0;i<26;i++){ add.wait(); char ss = (char) (65+i); System.out.print(String.valueOf(ss)); add.notifyAll(); } } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { AddNumAndWords add = new AddNumAndWords(); Thread t1 = new demoThread2(add); Thread t2 = new demoThread1(add); t1.start(); t2.start(); try { t1.join(); t2.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
