下载安装PyCharm
pycharm 专业版(PyCharm是一种Python IDE,带有一整套可以帮助用户在使用Python语言开发时提高其效率的工具,比如调试、语法高亮、Project管理、代码跳转、智能提示、自动完成、单元测试、版本控制。此外,该IDE提供了一些高级功能,以用于支持Django框架下的专业Web开发。)
注册之后可长期使用。
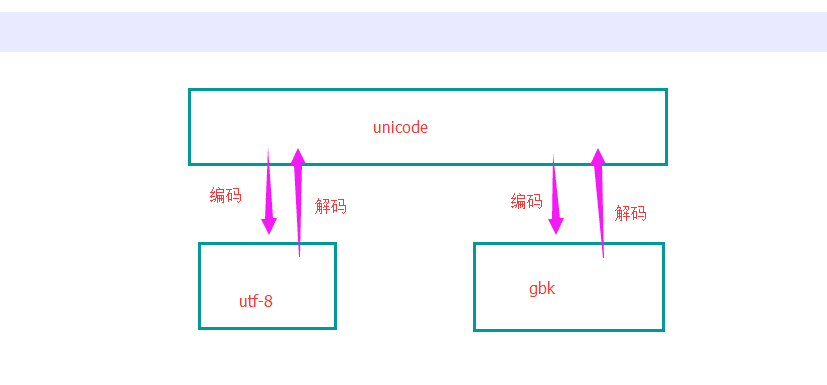
编码关系:
Python2.7
unicode是万国码,utf-8是对万国码的一个精简,gbk类似utf-8。unicode可以转换成utf-8,转换过程叫编码(动词),utf-8转换成unicode的过程叫解码,gbk和unicode之间的转换同理。如果utf-8变成gbk就需要先解码再编码。如图:
在写Python时,如果终端是gbk格式解码,而以utf-8格式输出,就会出现乱码。这时就需要把终端改成utf-8格式:
示例:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
1 temp = "测试" #utf-8
2 #解码,需要指定原来是什么编码
3 temp_unicode = temp.decode('utf-8')
4 #编码,需要指定要变成什么编码
5 temp_gbk = temp_unicode.encode('gbk')
6 print(temp_gbk)
Python3.5
py3是自动转换,通过utf-8转换成unicode,再转换成gbk。
并且py3,移除了Python的unicode类型。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
1 temp = "测试" #utf-8
2 temp_gbk = temp_unicode.encode('gbk')
3 print(temp_gbk)
-
运算符
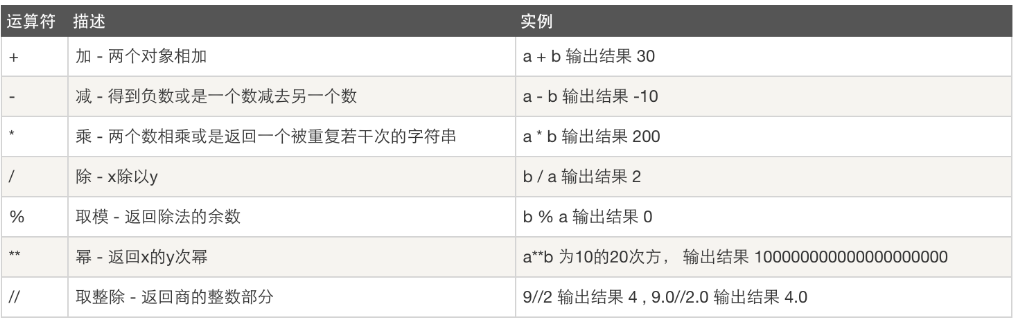
一、算数运算:
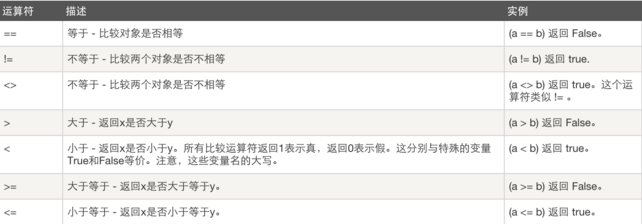
二、比较运算:
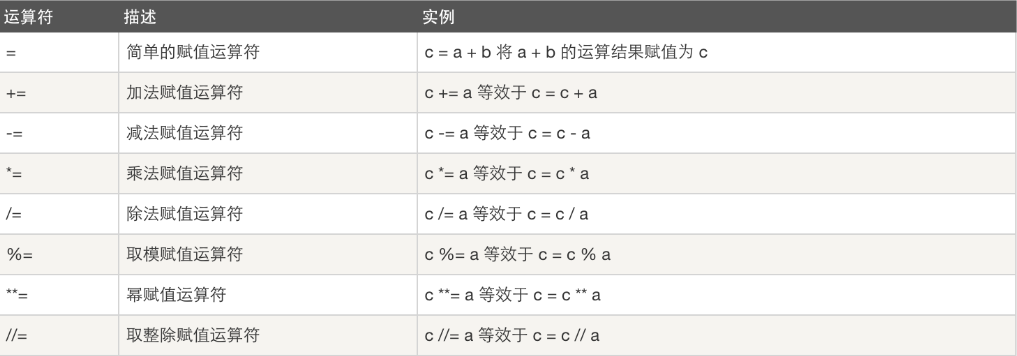
三、赋值运算:
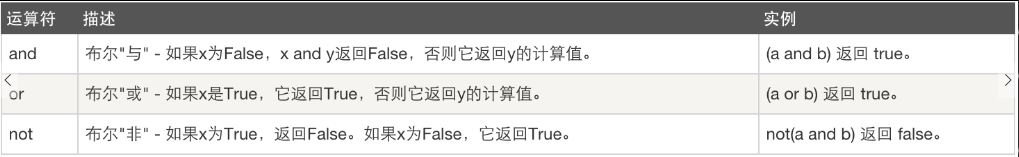
四、逻辑运算:
。
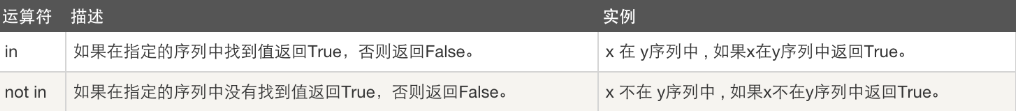
五、成员运算:
示例:一和二的粒度不一样
一:
s = "name age" ret = "age" in s print(ret) #打印结果:True s = "name age" ret = "ge" in s print(ret) #打印结果:True ########## s = "name age" ret = "lage" in s print(ret) #打印结果:False
二:
li = ["name","age","test"] ret = "age" in li print(ret) #打印结果:True ########## li = ["name","age","test"] ret = "ge" in li print(ret) #打印结果:False
-
基本数据类型
py2.7中9除以2等于4,要想实现等于4.5就需要引入模块了。此时PyCharm就派上用场了,方便引入模块。
一、数字
int(整型)
在32位机器上,整数的位数为32位,取值范围为-2**31~2**31-1,即-2147483648~2147483647
在64位系统上,整数的位数为64位,取值范围为-2**63~2**63-1,即-92233720368547758089223372036854775807

class int(object):
"""
int(x=0) -> int or long
int(x, base=10) -> int or long
Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero.
If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead.
If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or
Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The
literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace.
The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to
interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
4
"""
def bit_length(self):
""" 返回表示该数字的时占用的最少位数 """
"""
int.bit_length() -> int
Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary.
>>> bin(37)
'0b100101'
>>> (37).bit_length()
6
"""
return 0
def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 返回该复数的共轭复数 """
""" Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int. """
pass
def __abs__(self):
""" 返回绝对值 """
""" x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """
pass
def __add__(self, y):
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass
def __and__(self, y):
""" x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """
pass
def __cmp__(self, y):
""" 比较两个数大小 """
""" x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """
pass
def __coerce__(self, y):
""" 强制生成一个元组 """
""" x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """
pass
def __divmod__(self, y):
""" 相除,得到商和余数组成的元组 """
""" x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """
pass
def __div__(self, y):
""" x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """
pass
def __float__(self):
""" 转换为浮点类型 """
""" x.__float__() <==> float(x) """
pass
def __floordiv__(self, y):
""" x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """
pass
def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __getattribute__(self, name):
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 内部调用 __new__方法或创建对象时传入参数使用 """
pass
def __hash__(self):
"""如果对象object为哈希表类型,返回对象object的哈希值。哈希值为整数。在字典查找中,哈希值用于快速比较字典的键。两个数值如果相等,则哈希值也相等。"""
""" x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """
pass
def __hex__(self):
""" 返回当前数的 十六进制 表示 """
""" x.__hex__() <==> hex(x) """
pass
def __index__(self):
""" 用于切片,数字无意义 """
""" x[y:z] <==> x[y.__index__():z.__index__()] """
pass
def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__
""" 构造方法,执行 x = 123 或 x = int(10) 时,自动调用,暂时忽略 """
"""
int(x=0) -> int or long
int(x, base=10) -> int or long
Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero.
If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead.
If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or
Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The
literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace.
The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to
interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
4
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __int__(self):
""" 转换为整数 """
""" x.__int__() <==> int(x) """
pass
def __invert__(self):
""" x.__invert__() <==> ~x """
pass
def __long__(self):
""" 转换为长整数 """
""" x.__long__() <==> long(x) """
pass
def __lshift__(self, y):
""" x.__lshift__(y) <==> x<<y """
pass
def __mod__(self, y):
""" x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """
pass
def __mul__(self, y):
""" x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """
pass
def __neg__(self):
""" x.__neg__() <==> -x """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more):
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __nonzero__(self):
""" x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """
pass
def __oct__(self):
""" 返回改值的 八进制 表示 """
""" x.__oct__() <==> oct(x) """
pass
def __or__(self, y):
""" x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """
pass
def __pos__(self):
""" x.__pos__() <==> +x """
pass
def __pow__(self, y, z=None):
""" 幂,次方 """
""" x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
pass
def __radd__(self, y):
""" x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """
pass
def __rand__(self, y):
""" x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """
pass
def __rdivmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """
pass
def __rdiv__(self, y):
""" x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """
pass
def __repr__(self):
"""转化为解释器可读取的形式 """
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __str__(self):
"""转换为人阅读的形式,如果没有适于人阅读的解释形式的话,则返回解释器课阅读的形式"""
""" x.__str__() <==> str(x) """
pass
def __rfloordiv__(self, y):
""" x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """
pass
def __rlshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rlshift__(y) <==> y<<x """
pass
def __rmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """
pass
def __rmul__(self, y):
""" x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """
pass
def __ror__(self, y):
""" x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """
pass
def __rpow__(self, x, z=None):
""" y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
pass
def __rrshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rrshift__(y) <==> y>>x """
pass
def __rshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rshift__(y) <==> x>>y """
pass
def __rsub__(self, y):
""" x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """
pass
def __rtruediv__(self, y):
""" x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """
pass
def __rxor__(self, y):
""" x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """
pass
def __sub__(self, y):
""" x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """
pass
def __truediv__(self, y):
""" x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """
pass
def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs):
""" 返回数值被截取为整形的值,在整形中无意义 """
pass
def __xor__(self, y):
""" x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """
pass
denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 分母 = 1 """
"""the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 虚数,无意义 """
"""the imaginary part of a complex number"""
numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 分子 = 数字大小 """
"""the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 实属,无意义 """
"""the real part of a complex number"""
二、布尔值
真或假
1 或 0
非零即为真
三、字符串
字符串用单引号('')或者双引号("")来创建
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
name = "zouqian"
print(name)
字符串常用功能:
1.移除空白
2.分割
3.长度
4.索引
5.切片

"""
capitalize()
将字符串的首字母转换为大写
"""
name = " zou qian zouqian"
ret = name.capitalize()
print(ret)
"""
center(width, fillchar)
返回一个指定的宽度 width 居中的字符串,fillchar 为填充的字符,默认为空格
"""
ret = name.center(20,'*')
print(ret)
"""
count(str, beg= 0,end=len(string))
显示某字符在开始beg到结束end中间出现的次数
"""
ret = name.count('zo',0,15)
print(ret)
"""
decode(encoding='UTF-8',errors='strict')
解码
encode(encoding='UTF-8',errors='strict')
以 encoding 指定的编码格式编码字符串
temp = "测试"
#解码,需要指定原来是什么编码
temp_unicode = temp.decode('utf-8')
#编码,需要指定要编成什么编码
temp_gbk = temp_unicode.encode('gbk')
print(temp_gbk)
"""
"""
endswith(suffix, beg=0, end=len(string))
检查字符串是否以某字符串结尾如果是,返回 True,否则返回 False.
"""
ret = name.endswith('n')
print(ret)
"""
expandtabs(tabsize=8)
:表示tab键,默认为88个空格
"""
ret = name.expandtabs()
print(ret)
"""
find(str, beg=0 end=len(string))
检查“e”是否包含在指定范围内,如果是,会显示在第几位,如果不是就会提示-1
"""
ret = name.find('e')
print(ret)
"""
"""
isdigit()
是否是数字
"""
ret = name.isdigit()
print(ret)
"""
lstrip()
移除左侧空白
"""
ret = name.lstrip()
print(ret)
"""
rstrip()
移除右侧空白
"""
ret = name.rstrip()
print(ret)
“““
split
分割
”””
name = "hello,zouqian"
ret = name.split(",")
print(ret)
"""
strip([chars])
去除左右两边空格
"""
ret = name.strip()
print(ret)
"""
title()
标题格式
"""
ret = value.title()
print(ret)
四、列表
列表中每个位置都下标从0开始的数字
列表使用中括号:[]
创建列表:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
list = ['a','b','c']
基本操作:
1.索引
2.切片
3.追加
4.删除
5.长度
6.切片
7.循环
8.包含

"""
append 追加
"""
list = ['a','b','c']
list.append('d')
print(list)
"""
count 统计某个元素出现的次数
"""
list = [1,4,2,3,4,5,10,3,5,2,4,8,6]
ret = list.count(5)
print(ret)
"""
extend 在列表最后追加另一个列表中的所有元素
"""
list2 = [404,505,606]
list.extend(list2)
print(list)
"""
pop 移除列表中的一个元素(默认最后一个元素)
"""
num = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
num.pop()
print(num)
"""
remove 移除列表中某个值
"""
num = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
num.remove(6)
print(num)
"""
clear 清空列表
"""
五、元祖
元祖和列表是类似的,但是列表可以修改(增删改),元祖不能修改,只能查。
元祖使用小括号:()
基本操作:
1.索引
2.切片
3.循环
4.长度
5.包含
1 tuple 将列表转换为元祖
2 list = ['a', 'b', 'c']
3 temp = tuple(list)
4 print(temp)
六、字典(无序)
字典使用花括号:{}。字典的每个键值(key=>value)对用冒号(:)分割,每个对之间用逗号(,)分割
字典没办法切片,可以循环,默认只输出key,可以删除指定索引的键值对。
常用操作:
1.索引
2.新增
3.删除
4.键.值.键值对
5.循环
6.长度

class dict(object):
"""
dict() -> new empty dictionary
dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's
(key, value) pairs
dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via:
d = {}
for k, v in iterable:
d[k] = v
dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs
in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2)
"""
def clear(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 清除内容 """
""" D.clear() -> None. Remove all items from D. """
pass
def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 浅拷贝 """
""" D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D """
pass
@staticmethod # known case
def fromkeys(S, v=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
dict.fromkeys(S[,v]) -> New dict with keys from S and values equal to v.
v defaults to None.
"""
pass
def get(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 根据key获取值,d是默认值 """
""" D.get(k[,d]) -> D[k] if k in D, else d. d defaults to None. """
pass
def has_key(self, k): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 是否有key """
""" D.has_key(k) -> True if D has a key k, else False """
return False
def items(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 所有项的列表形式 """
""" D.items() -> list of D's (key, value) pairs, as 2-tuples """
return []
def iteritems(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 项可迭代 """
""" D.iteritems() -> an iterator over the (key, value) items of D """
pass
def iterkeys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" key可迭代 """
""" D.iterkeys() -> an iterator over the keys of D """
pass
def itervalues(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" value可迭代 """
""" D.itervalues() -> an iterator over the values of D """
pass
def keys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 所有的key列表 """
""" D.keys() -> list of D's keys """
return []
def pop(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 获取并在字典中移除 """
"""
D.pop(k[,d]) -> v, remove specified key and return the corresponding value.
If key is not found, d is returned if given, otherwise KeyError is raised
"""
pass
def popitem(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 获取并在字典中移除 """
"""
D.popitem() -> (k, v), remove and return some (key, value) pair as a
2-tuple; but raise KeyError if D is empty.
"""
pass
def setdefault(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 如果key不存在,则创建,如果存在,则返回已存在的值且不修改 """
""" D.setdefault(k[,d]) -> D.get(k,d), also set D[k]=d if k not in D """
pass
def update(self, E=None, **F): # known special case of dict.update
""" 更新
{'name':'alex', 'age': 18000}
[('name','sbsbsb'),]
"""
"""
D.update([E, ]**F) -> None. Update D from dict/iterable E and F.
If E present and has a .keys() method, does: for k in E: D[k] = E[k]
If E present and lacks .keys() method, does: for (k, v) in E: D[k] = v
In either case, this is followed by: for k in F: D[k] = F[k]
"""
pass
def values(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 所有的值 """
""" D.values() -> list of D's values """
return []
def viewitems(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 所有项,只是将内容保存至view对象中 """
""" D.viewitems() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's items """
pass
def viewkeys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.viewkeys() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's keys """
pass
def viewvalues(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.viewvalues() -> an object providing a view on D's values """
pass
def __cmp__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """
pass
def __contains__(self, k): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.__contains__(k) -> True if D has a key k, else False """
return False
def __delitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__delitem__(y) <==> del x[y] """
pass
def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
pass
def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
pass
def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
pass
def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
pass
def __init__(self, seq=None, **kwargs): # known special case of dict.__init__
"""
dict() -> new empty dictionary
dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's
(key, value) pairs
dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via:
d = {}
for k, v in iterable:
d[k] = v
dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs
in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2)
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """
pass
def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__len__() <==> len(x) """
pass
def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
pass
def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
pass
def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __setitem__(self, i, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__setitem__(i, y) <==> x[i]=y """
pass
def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.__sizeof__() -> size of D in memory, in bytes """
pass
__hash__ = None
-
其他
一、for循环
用户按照顺序循环可迭代对象中的内容
1 num = ["404","505","606"]
2 for item in num:
3 print(item)
二、enumerate
为可迭代的对象添加序号,自动生成一列,默认从0开始,自增一。
num = ["404","505","606"] for v in enumerate(num): print(v) #打印结果: (0, '404') (1, '505') (2, '606')
示例:
注:字符串转数字时:int(字符串)
li = ["电脑","鼠标垫","U盘","游艇"] for key,item in enumerate(li,1): print(key,item) inp = input("请选择商品:") inp_num = int(inp) print(li[inp_num-1])
通过输入商品取出索引:
li = ["电脑","鼠标垫","U盘","游艇"] print(li) inp = input("请输入商品:") ret = li.index(inp) print(ret) #打印结果: ['电脑', '鼠标垫', 'U盘', '游艇'] 请输入商品:电脑 0
三、range和xrange
Python2.7
range:是用来获取指定范围内的数(在内存中创建出来数,占内存)
xrange:只有通过for循环进行迭代的时候才创建(在内存中不创建)
Python3
只有range,等同于Python里面的xrange,通过for循环进行迭代时创建。
指定范围,生成指定的数字
1 print range(1, 10)
2 # 结果:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
3
4 print range(1, 10, 2)
5 # 结果:[1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
6
7 print range(30, 0, -2)
8 # 结果:[30, 28, 26, 24, 22, 20, 18, 16, 14, 12, 10, 8, 6, 4, 2]
只取索引:
li = ["电脑","鼠标垫","U盘","游艇"] len_li = len(li) for i in range(len_li): print(i) #打印结果: 0 1 2 3 ########## li = ["电脑","鼠标垫","U盘","游艇"] len_li = len(li) for i in range(len_li): print(i,li[i]) #打印结果: 0 电脑 1 鼠标垫 2 U盘 3 游艇
练习题
一、元素分类
有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90...],将所有大于 66 的值保存至字典的第一个key中,将小于 66 的值保存至第二个key的值中。

即: {'k1': 大于66的所有值, 'k2': 小于66的所有值}
li = [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90]
#创建一个空字典
dic = {
"k1":[],
"k2":[]
}
#循环li列表
for i in li:
if i <= 66: #筛选出<=66的元素
dic["k1"].append(i) #追加到k1对应的列表里面
else: #>66的元素
dic["k2"].append(i) #追加到k2对应的列表里面
print(dic) #打印出创建的字典
#打印结果:{'k2': [77, 88, 99, 90], 'k1': [11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66]}
二、查找
查找列表中元素,移除每个元素的空格,并查找以 a或A开头 并且以 c 结尾的所有元素。
li = ["alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain"]
tu = ("alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain")
dic = {'k1': "alex", 'k2': ' aric', "k3": "Alex", "k4": "Tony"}

for i in li: #i 表示每一个元素 new_i = i.strip() #if判断的顺序是从前到后。or,自己成功就行了。and,要继续往后找。 if (new_i.startswith("a") or new_i.startswith("A")) and new_i.endswith("c"): print(new_i) #打印结果:aric
三、输出商品列表,用户输入序号,显示用户选中的商品

li = ["手机", "电脑", '鼠标垫', '游艇'] for i, j in enumerate(li): print(i+1, j) num = input('num:') # 索引 num = int(num) len_li = len(li) if num > 0 and num <= len_li: goods = li[num - 1] print(goods) else: print("商品不存在") #打印结果: 1 手机 2 电脑 3 鼠标垫 4 游艇 num:1 手机 #打印结果: 1 手机 2 电脑 3 鼠标垫 4 游艇 num:5 商品不存在
四、购物车
功能要求:
要求用户输入总资产,例如:2000
显示商品列表,让用户根据序号选择商品,加入购物车
购买,如果商品总额大于总资产,提示账户余额不足,否则,购买成功。
附加:可充值、某商品移除购物车
goods = [
{"name": "电脑", "price": 1999},
{"name": "鼠标", "price": 10},
{"name": "游艇", "price": 20},
{"name": "美女", "price": 998},
]

#总资产 asset_all = 0 i1 = input("请输入总资产:") asset_all = int(i1) for i in goods: print(i["name"],i["price"]) car_dict = {} while True: i2 = input("请选择商品(Y/y结算):") if i2.lower() == "y": break #循环所有的商品,查找需要的商品 for item in goods: if item["name"] == i2: name = item["name"] if name in car_dict.keys():#判断购物车是否有该商品,有:num + 1 car_dict[name]["num"] = car_dict[name]["num"] +1 else: car_dict[name] = {"num":1,"single_price":item["price"]} print(car_dict) #循环购买后的购物车 all_price = 0 for k,v in car_dict.items(): n = v["single_price"] m = v["num"] all_sum = m * n all_price = all_price +all_sum if all_price > asset_all: print("余额不足") else: print("购买成功")
五、用户交互,显示省市县三级联动的选择
dic = {
"河北":{
"石家庄": ["鹿泉", "藁城", "元氏"],
"邯郸": ["永年", "涉县", "磁县"],
},
"河南":{
"郑州":["不知道","少林寺","嵩山"],
"开封":["包拯","展昭","威士忌"],
},
"山西":{
"太原":["xxx","哦哦哦","小店"],
"运城":["更不知道了","999","哈尔滨啤酒"],
}
}

for x in dic: print(x) i1 = input("请输入省份:") a = dic[i1] #循环输出所有的城市 for j in a: print(j) i2 = input("请输入城市:") b = dic[i1][i2] for z in b: print(z) #打印结果: 山西 河南 河北 请输入省份:河北 邯郸 石家庄 请输入城市:石家庄 鹿泉 藁城 元氏
