前不久,Flink社区发布了FLink 1.9版本,在其中包含了一个很重要的新特性,即state processor api,这个框架支持对checkpoint和savepoint进行操作,包括读取、变更、写入等等。
savepoint的可操作带来了很多的可能性:
- 作业迁移
1.跨类型作业,假如有一个storm作业,将状态缓存在外部系统,希望更好的利用flink的状态机制来增加作业的稳定和减少数据的延迟,但如果直接迁移,必然面临状态的丢失,这时,可以将外部系统的状态转换为flink作业的savepoint来启动。
2.同类型作业,假如有一个flink作业已经在运行,一个新的flink作业希望复用之前的某些状态,也可以将savepoint进行处理重新写入,进而使得新的flink作业可以在某个基础上运行。
- 作业升级
1.有UID升级,一般情况下,如果升级前的operator已经设置了uid,那么可以直接升级,但是如果希望在之前的状态数据上做些变更,这里就提供了一种接口。
2.无UID升级,在特殊情况下,一开始编写了没有UID的作业,后来改成了标准的有UID的作业,反而无法在之前的savepoint上启动了,这时也可以对savepoint同时做升级。
- 作业校验
1.异步校验,一般而言,flink作业的最终结果都会持久化输出,但在面临问题的时候,如何确定哪一级出现问题,state processor api也提供了一种可能,去检验state中的数据是否与预期的一致。
- 作业扩展
1.横向扩展,如果在flink作业一开始运行的时候,因为面对的数据量较小,设置了比较小的最大并行度,但在数据量增大的时候,却没办法从老的savepoint以一个比之前的最大并行度更大的并行度来启动作业,这时,也需要复写savepoint的同时更改最大并行度。
2.纵向扩展,在flink作业中新添加了一个operator,从savepoint启动的时候这个operator默认无状态,可以手动构造数据,使得这个operator的表现和其他operator保持一致。
可以对savepoint进行哪些操作?
- 读取savepoint
1.验证,读取出来的savepoint会转换为一个dataSet,随后可以以标准批处理的方式来验证你的业务预期;
2.source,也可以以savepoint作为数据源,来作为你另一个作业的输入。
- 写入savepoint
1.写入新的savepoint,可以写入一个全新的savepoint,这个savepoint是独立的存在,他可以有新的operator uid,新的operator state,以及新的max parallism等等。
2.复用原来的savepoint,可以在原来的savepoint的基础上加入新的operator的state,在新的savepoint被使用之前,老的savepoint不允许被删除。
那么究竟哪些state是可读的?有哪些接口了?
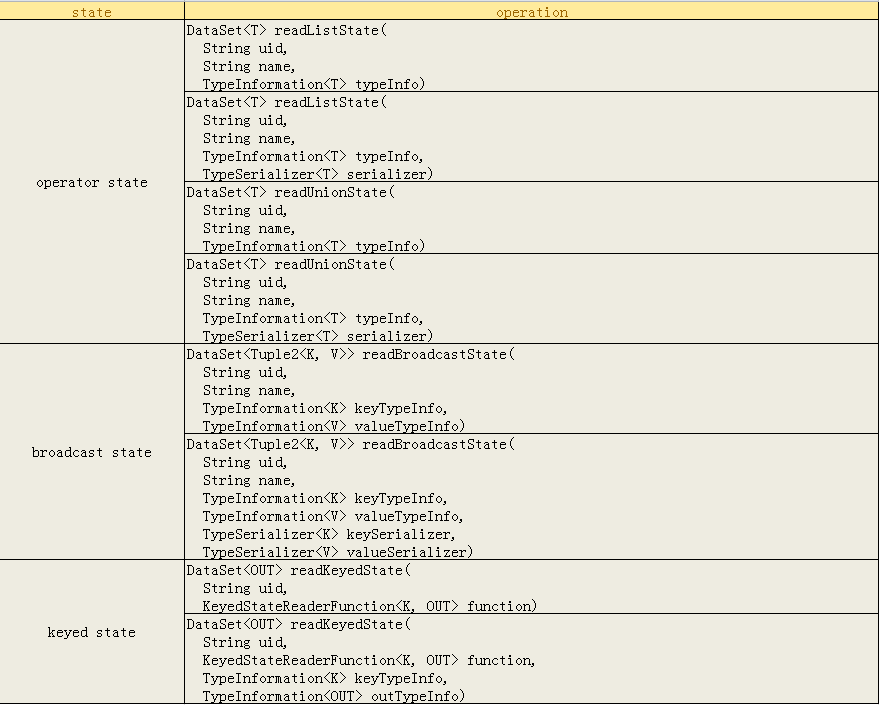
可以看到,主要提供对三种state的访问,operator state和broadcast state,其中broadcast state是一种特殊的operator state,因为他也支持自定义的serializer。
通关程序
目前在社区或者网上并没有完整的样例供大家参考,下面这个例子是完全在测试环境中跑通的,所有的flink相关组件的版本依赖都是1.9.0。
下面我们说明如何使用这个框架。
1.首先我们创建一个样例作业来生成savepoint
主类代码
1 final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); 2 env.enableCheckpointing(60*1000); 3 DataStream<Tuple2<Integer,Integer>> kafkaDataStream = 4 env.addSource(new SourceFunction<Tuple2<Integer,Integer>>() { 5 private boolean running = true; 6 private int key; 7 private int value; 8 private Random random = new Random(); 9 @Override 10 public void run(SourceContext<Tuple2<Integer,Integer>> sourceContext) throws Exception { 11 while (running){ 12 key = random.nextInt(5); 13 sourceContext.collect(new Tuple2<>(key,value++) ); 14 Thread.sleep(100); 15 } 16 } 17 18 @Override 19 public void cancel() { 20 running = false; 21 } 22 }).name("source").uid("source"); 23 24 25 kafkaDataStream 26 .keyBy(tuple -> tuple.f0) 27 .map(new StateTest.StateMap()).name("map").uid("map") 28 .print().name("print").uid("print");
在上面的代码中,只需要注意在自定义的source中,发送tuple2消息,而做savepoint的
关键在于状态,状态在StateMap这个类中,如下:
1 public static class StateMap extends RichMapFunction<Tuple2<Integer,Integer>,String> { 2 private transient ListState<Integer> listState; 3 4 @Override 5 public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception { 6 ListStateDescriptor<Integer> lsd = 7 new ListStateDescriptor<>("list",TypeInformation.of(Integer.class)); 8 listState = getRuntimeContext().getListState(lsd); 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public String map(Tuple2<Integer,Integer> value) throws Exception { 13 listState.add(value.f1); 14 return value.f0+"-"+value.f1; 15 } 16 17 @Override 18 public void close() throws Exception { 19 listState.clear(); 20 } 21 }
在上面的Map中,首先在open中声明了一个ListState,然后在消息处理的逻辑中,也很简单的只是把tuple2的值放进了listState中。然后提交作业,等作业运行一段时间之后,触发一个savepoint,
并记录savepoint的地址。至此,完成了state processor api验证工作的数据准备。
2.利用state processor api读取savepoint
这一步只是简单验证下savepoint是否能够被正确读取,代码如下:
1 public class ReadListState { 2 protected static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ReadListState.class); 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 5 final String operatorUid = "map"; 6 final String savepointPath = 7 "hdfs://xxx/savepoint-41b05d-d517cafb61ba"; 8 9 final String checkpointPath = "hdfs://xxx/checkpoints"; 10 11 // set up the batch execution environment 12 final ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); 13 14 RocksDBStateBackend db = new RocksDBStateBackend(checkpointPath); 15 DataSet<String> dataSet = Savepoint 16 .load(env, savepointPath, db) 17 .readKeyedState(operatorUid, new ReaderFunction()) 18 .flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<KeyedListState, String>() { 19 @Override 20 public void flatMap(KeyedListState keyedListState, Collector<String> collector) throws Exception { 21 keyedListState.value.forEach(new Consumer<Integer>() { 22 @Override 23 public void accept(Integer integer) { 24 collector.collect(keyedListState.key + "-" + integer); 25 } 26 }); 27 } 28 }); 29 30 dataSet.writeAsText("hdfs://xxx/test/savepoint/bravo"); 31 32 // execute program 33 env.execute("read the list state"); 34 } 35 36 static class KeyedListState { 37 Integer key; 38 List<Integer> value; 39 } 40 41 static class ReaderFunction extends KeyedStateReaderFunction<Integer, KeyedListState> { 42 private transient ListState<Integer> listState; 43 44 @Override 45 public void open(Configuration parameters) { 46 ListStateDescriptor<Integer> lsd = 47 new ListStateDescriptor<>("list", TypeInformation.of(Integer.class)); 48 listState = getRuntimeContext().getListState(lsd); 49 } 50 51 @Override 52 public void readKey( 53 Integer key, 54 Context ctx, 55 Collector<KeyedListState> out) throws Exception { 56 List<Integer> li = new ArrayList<>(); 57 listState.get().forEach(new Consumer<Integer>() { 58 @Override 59 public void accept(Integer integer) { 60 li.add(integer); 61 } 62 }); 63 64 KeyedListState kl = new KeyedListState(); 65 kl.key = key; 66 kl.value = li; 67 68 out.collect(kl); 69 } 70 } 71 }
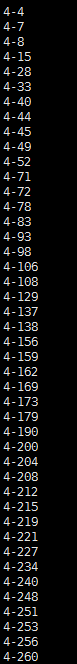
在读取了savepoint中的状态之后,成功将其转存为一个文件,文件的部分内容如下,每行的内容分别为key-value对:
3.利用state processor api重写savepoint
savepoint是对程序某个运行时点的状态的固化,方便程序在再次提交的时候进行接续,但有时候需要对savepoint中的状态进行改写,以方便从特定的状态来启动作业。
1 public class ReorganizeListState { 2 protected static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ReorganizeListState.class); 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 4 final String operatorUid = "map"; 5 final String savepointPath = 6 "hdfs://xxx/savepoint-41b05d-d517cafb61ba"; 7 8 final String checkpointPath = "hdfs://xxx/checkpoints"; 9 10 // set up the batch execution environment 11 final ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); 12 13 RocksDBStateBackend db = new RocksDBStateBackend(checkpointPath); 14 DataSet<KeyedListState> dataSet = Savepoint 15 .load(env,savepointPath,db) 16 .readKeyedState(operatorUid,new ReaderFunction()) 17 .flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<KeyedListState, KeyedListState>() { 18 @Override 19 public void flatMap(KeyedListState keyedListState, Collector<KeyedListState> collector) throws Exception { 20 KeyedListState newState = new KeyedListState(); 21 newState.value = keyedListState.value.stream() 22 .map( x -> x+10000).collect(Collectors.toList()); 23 newState.key = keyedListState.key; 24 collector.collect(newState); 25 } 26 }); 27 28 BootstrapTransformation<KeyedListState> transformation = OperatorTransformation 29 .bootstrapWith(dataSet) 30 .keyBy(acc -> acc.key) 31 .transform(new KeyedListStateBootstrapper()); 32 33 Savepoint.create(db,128) 34 .withOperator(operatorUid,transformation) 35 .write("hdfs://xxx/test/savepoint/"); 36 37 // execute program 38 env.execute("read the list state"); 39 } 40 41 static class KeyedListState{ 42 Integer key; 43 List<Integer> value; 44 } 45 46 static class ReaderFunction extends KeyedStateReaderFunction<Integer, KeyedListState> { 47 private transient ListState<Integer> listState; 48 49 @Override 50 public void open(Configuration parameters) { 51 ListStateDescriptor<Integer> lsd = 52 new ListStateDescriptor<>("list",TypeInformation.of(Integer.class)); 53 listState = getRuntimeContext().getListState(lsd); 54 } 55 56 @Override 57 public void readKey( 58 Integer key, 59 Context ctx, 60 Collector<KeyedListState> out) throws Exception { 61 List<Integer> li = new ArrayList<>(); 62 listState.get().forEach(new Consumer<Integer>() { 63 @Override 64 public void accept(Integer integer) { 65 li.add(integer); 66 } 67 }); 68 69 KeyedListState kl = new KeyedListState(); 70 kl.key = key; 71 kl.value = li; 72 73 out.collect(kl); 74 } 75 } 76 77 static class KeyedListStateBootstrapper extends KeyedStateBootstrapFunction<Integer, KeyedListState> { 78 private transient ListState<Integer> listState; 79 80 @Override 81 public void open(Configuration parameters) { 82 ListStateDescriptor<Integer> lsd = 83 new ListStateDescriptor<>("list",TypeInformation.of(Integer.class)); 84 listState = getRuntimeContext().getListState(lsd); 85 } 86 87 @Override 88 public void processElement(KeyedListState value, Context ctx) throws Exception { 89 listState.addAll(value.value); 90 } 91 } 92 }
这里的关键在于根据上一步读取出来dataSet,转换的过程中将其值全部累加10000,然后将这个dataSet作为输入来构建一个BootstrapTransformation,然后创建了一个空的savepoint,并把指定
operatorUid的状态写为一个savepoint,最终写入成功,得到了一个新的savepoint,这个新的savepoint包含的状态中的value相比原先的值发生了变化。
4.验证新生产的savepoint是否可用
由于验证用的state是ListState,换言之,是KeyedState,而KeyedState是属于Flink托管的state,意味着Flink自己掌握状态的保存和恢复的逻辑,所以为了验证作业是否正确从新的savepoint
中启动了,对之前的StateMap改写如下:
1 public static class StateMap extends RichMapFunction<Tuple2<Integer,Integer>,String> { 2 private transient ListState<Integer> listState; 3 4 @Override 5 public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception { 6 ListStateDescriptor<Integer> lsd = 7 new ListStateDescriptor<>("list",TypeInformation.of(Integer.class)); 8 listState = getRuntimeContext().getListState(lsd); 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public String map(Tuple2<Integer,Integer> value) throws Exception { 13 listState.add(value.f1); 14 log.info("get value:{}-{}",value.f0,value.f1); 15 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 16 listState.get().forEach(new Consumer<Integer>() { 17 @Override 18 public void accept(Integer integer) { 19 sb.append(integer).append(";"); 20 } 21 }); 22 log.info("***********************taskNameAndSubTask:{},restored value:{}" 23 ,getRuntimeContext().getTaskNameWithSubtasks(),sb.toString()); 24 return value.f0+"-"+value.f1; 25 } 26 27 @Override 28 public void close() throws Exception { 29 listState.clear(); 30 } 31 }
由于无法在state恢复之后立刻就拿到相应恢复的数据,这里之后在每次消息达到的时候输出下state中的内容,变通的看看是否恢复成功,结果如下:
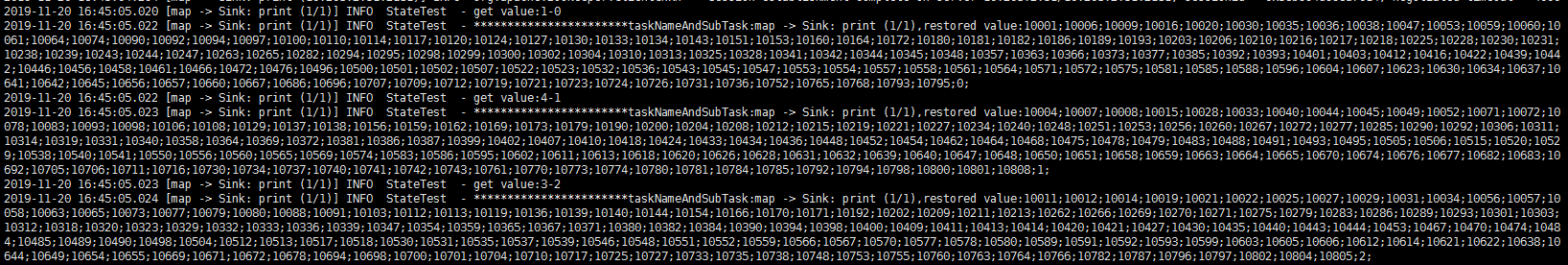
可以对比看下上图中key为4的输出,可以看到输出的值即为修改后的值,验证成功。
5.结语
上面我们以一个keyedState来对state processor api做了验证,但Flink的state分为KeyedState,OperatorState和BroadcastState,在state processor api中都提供相应的处理接口。
另外,对于keyedState,如果作业的并行度发生了变化会如何?如果Key发生了变化会如何?都需要进一步探究。
官方文档参见:
https://flink.apache.org/feature/2019/09/13/state-processor-api.html
https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.9/dev/libs/state_processor_api.html