1、controllers
从IDEA初始化给的play2,x的模板中给的三个controllers:
AsyncController、HomeController、CountController
package controllers import play.api.mvc._ /** * This controller creates an `Action` that demonstrates how to write * simple asynchronous code in a controller. It uses a timer to * asynchronously delay sending a response for 1 second. * * @param cc standard controller components * @param actorSystem We need the `ActorSystem`'s `Scheduler` to * run code after a delay. * @param exec We need an `ExecutionContext` to execute our * asynchronous code. When rendering content, you should use Play's * default execution context, which is dependency injected. If you are * using blocking operations, such as database or network access, then you should * use a different custom execution context that has a thread pool configured for * a blocking API. */ @Singleton class AsyncController @Inject()(cc: ControllerComponents, actorSystem: ActorSystem)(implicit exec: ExecutionContext) extends AbstractController(cc) { /** * Creates an Action that returns a plain text message after a delay * of 1 second. * * The configuration in the `routes` file means that this method * will be called when the application receives a `GET` request with * a path of `/message`. */ def message = Action.async { getFutureMessage(1.second).map { msg => Ok(msg) } } private def getFutureMessage(delayTime: FiniteDuration): Future[String] = { val promise: Promise[String] = Promise[String]() actorSystem.scheduler.scheduleOnce(delayTime) { promise.success("Hi!") }(actorSystem.dispatcher) // run scheduled tasks using the actor system's dispatcher promise.future } }
package controllers import javax.inject._ import play.api.mvc._ /** * This controller demonstrates how to use dependency injection to * bind a component into a controller class. The class creates an * `Action` that shows an incrementing count to users. The [[Counter]] * object is injected by the Guice dependency injection system. */ @Singleton class CountController @Inject() (cc: ControllerComponents, counter: Counter) extends AbstractController(cc) { /** * Create an action that responds with the [[Counter]]'s current * count. The result is plain text. This `Action` is mapped to * `GET /count` requests by an entry in the `routes` config file. */ def count = Action { Ok(counter.nextCount().toString) } }
package controllers import javax.inject._ import play.api.mvc._ /** * This controller creates an `Action` to handle HTTP requests to the * application's home page. */ //@Singleton和@Inject()是DI(Dependency Injection,即依赖注入)注解。@Singleton注解告诉DI容器该类全局只能有一个实例, // @Inject()注解告诉DI容器,在该类初始化时注入右侧声明的参数cc。@extends关键字指明HomeController继承自AbstractController。 // AbstractController定义了一些常用方法,例如Action、Ok等等。 //常见Result类型 @Singleton class HomeController @Inject()(cc: ControllerComponents) extends AbstractController(cc) { /** * Create an Action to render an HTML page with a welcome message. * The configuration in the `routes` file means that this method * will be called when the application receives a `GET` request with * a path of `/`. */ def index = Action { Ok(views.html.index("Your new application is ready.")) } }
从这三个controller来明白需要相关的依赖注入和调用views包内的html的相关方法,并且还有相关的ActorSystem的存在,还有OK、Action就是常见的Result的类型等等。。。。
@Singleton和@Inject()
views.html.index
2、相关的控制器的改变
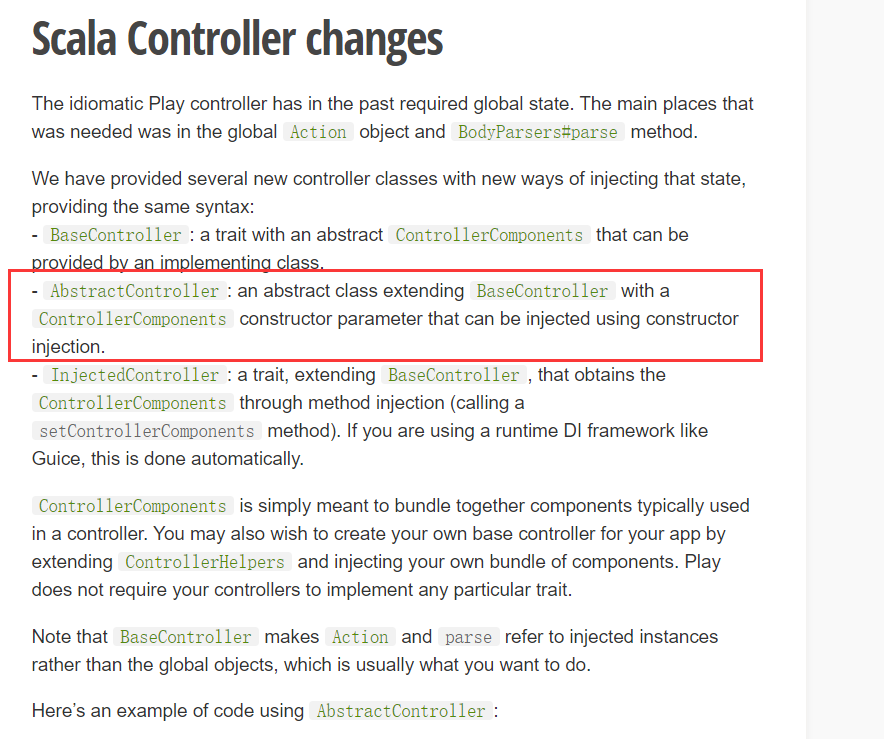
AbstractController和ControllerComponents相关的
3、html必须声明,即必须在html的第一行什么变量@(m:String)
! @7gagcp0dh - Internal server error, for (GET) [/] ->
play.sbt.PlayExceptions$CompilationException: Compilation error[Cannot write an instance of views.html.client.type to HTTP response. Try to define a Writeable[views.html.client.type]]
play.sbt.PlayExceptions$CompilationException: Compilation error[Cannot write an instance of views.html.client.type to HTTP response. Try to define a Writeable[views.html.client.type]]
controller调用了html的时候要views.html.sc("类似标题的的名字")