Vuex
官方文档:https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/
Vuex是一个专门为Vue.js应用程序开发的状态管理模式, 它采用集中式存储管理所有组件的公共状态, 并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化.
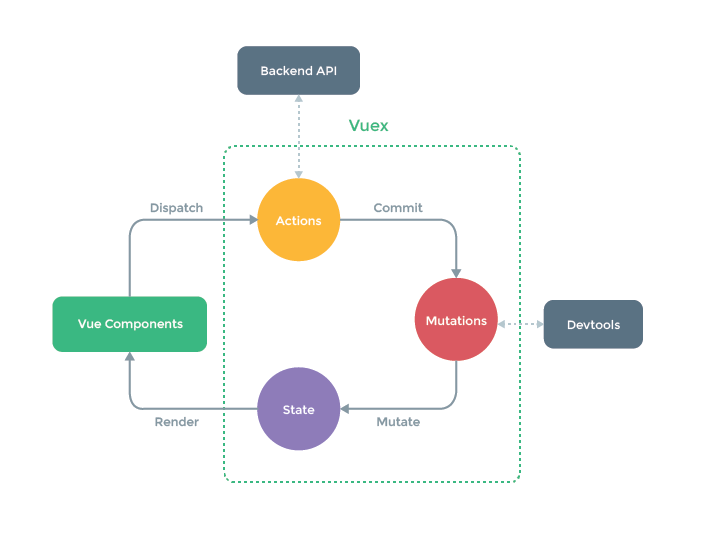
Vuex核心
- state:存放数据状态
- mutations:定义对state成员的同步操作
- getters :定义state成员的计算属性给外界
- actions:定义对state成员的异步操作,其实依赖mutations
- modules:模块化的状态管理
state就是Vuex中的公共的状态, 我是将state看作是所有组件的data, 用于保存所有组件的公共数据.
getters属性理解为所有组件的computed属性, 也就是计算属性. vuex的官方文档也是说到可以将getter理解为store的计算属性, getters的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算。mutaions理解为store中的methods, mutations对象中保存着更改数据的回调函数,该函数名官方规定叫type, 第一个参数是state, 第二参数是payload, 也就是自定义的参数.actions 类似于 mutations,不同在于:
-
actions提交的是mutations而不是直接变更状态 -
actions中可以包含异步操作,mutations中绝对不允许出现异步 -
actions中的回调函数的第一个参数是context, 是一个与store实例具有相同属性和方法的对象
Modules:应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割。
快速使用
1、初始化store下index.js中的内容
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' //挂载Vuex Vue.use(Vuex) export default new Vuex.Store({ //定义初始值 state: { count:0, }, getters:{ doubleCount(state){ return state.count * 2 } }, //定义同步的方法 mutations: { add(state){ state.count ++ }, decrese(state){ state.count -- }, }, //定义异步的方法 actions: { delayadd(context){ setTimeout(() => { context.commit('add') },1000); } }, modules: { } })
2、将store挂载到当前项目的Vue实例当中去
main.js
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' import router from './router' import store from './store' Vue.config.productionTip = false /* eslint-disable no-new */ new Vue({ el: '#app', router, store, //store:store 和router一样,将我们创建的Vuex实例挂载到这个vue实例中 render: h => h(App) })
3、在组件中使用Vuex
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>vuex count:{{ count }}</h1>
<h1>vuex doubleCount:{{ doubleCount }}</h1>
<button @click="add">add count</button>
<button @click="delayadd">delayaddadd count</button>
<button @click="decrese">decrese count</button>
</div>
</template>
<!--1.引入组件-->
<!--2.挂载组件-->
<!--3.在模板中使用-->
<script>
import { mapState,mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed:{
...mapState({
count : 'count',
}),
...mapGetters([
'doubleCount',
]),
},
methods:{
add(){
this.$store.commit('add')
},
decrese(){
this.$store.commit('decrese')
},
delayadd(){
this.$store.dispatch('delayadd')
},
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
总结
store定义初始值与计算方法
//定义初始值 state: { count:0, }, getters:{ doubleCount(state){ return state.count * 2 } },
store定义同步方法与异步方法
//定义同步的方法 mutations: { add(state){ state.count ++ }, decrese(state){ state.count -- }, }, //定义异步的方法 actions: { delayadd(context){ setTimeout(() => { context.commit('add') },1000); } },
在组件的Vue实例中引入store数据
import { mapState,mapGetters } from 'vuex'
computed:{
...mapState({
count : 'count',
}),
...mapGetters([
'doubleCount',
]),
},
在组件的模板中显示stote数据与计算属性
<h1>vuex count:{{ count }}</h1>
<h1>vuex doubleCount:{{ doubleCount }}</h1>
触发同步方法
<button @click="add">add count</button> <button @click="decrese">decrese count</button> methods:{ add(){ this.$store.commit('add') }, decrese(){ this.$store.commit('decrese') }, }
触发异步方法
<button @click="delayadd">delayaddadd count</button> methods:{ delayadd(){ this.$store.dispatch('delayadd') }, }