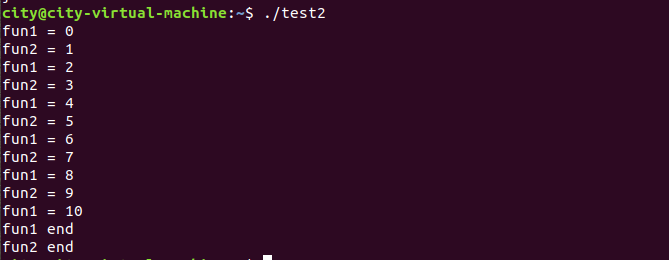
Linux下使用两个进程,交替控制输出1-10之间的数
#include<iostream> using namespace std; #include <unistd.h> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostream> #include <sys/types.h> #include <string.h> #include <string> #include<sys/types.h> #include<sys/wait.h> using namespace std; int fd1[2], fd2[2]; void fun1(){ char buf[105]; while(1){ memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); if(read(fd1[0], buf, sizeof(buf)) != -1){ int *a = (int *)buf; cout << "fun1 = " << *a << endl; int c = *a + 1; //将下一个要输出的值写入子进程的缓存区 memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); memcpy(buf, &c, sizeof(int)); write(fd2[1], buf, sizeof(int)); if(c >= 10){ cout << "fun1 end "; return;} } } } void fun2(){ char buf[105]; while(1){ memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); //读管道 if(read(fd2[0], buf, sizeof(buf)) != -1){ int *a = (int *)buf; //进程输出结束 if(*a > 10){ cout << "fun2 end "; return; } cout << "fun2 = " << *a << endl; int c = *a + 1; //清空缓存区,将下一个要输出的值写入主进程的缓存区 memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); memcpy(buf, &c, sizeof(int)); write(fd1[1], buf, sizeof(int)); } } } int main(){ //创建两个管道,主进程和子进程之间通过管道通信, //fd1[0]是子进程的读管道, fd1[1]是子进程的写管道 //fd2[0]是主进程的读管道,fd2[1]是主进程的写管道 pipe(fd1), pipe(fd2); int a = 0; //写进程 write(fd1[1], &a, sizeof(int)); //创建一个子进程 pid_t pid = fork(); //子进程输出 if(pid == 0){ fun2(); }else{ //主进程输出 fun1(); wait(&pid); } return 0; }