一、非递归(从头开始反转)
1、保存头指针的下一个节点(第一个元素),同时将头指针指向NULL
2、从第一个元素节点开始while循环往后处理,将当前节点的下一个节点指向前一个节点
3、最后再将头指针指向反转后的第一个元素节点
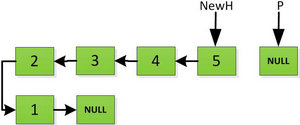
举个例子,反转如下链表:
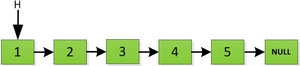
1、(NewH是反转后链表的头指针)
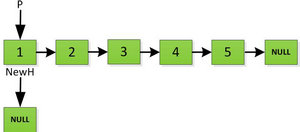
2、
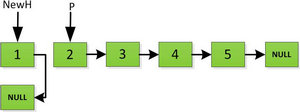
3、
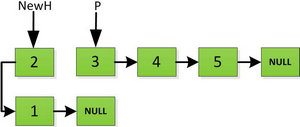
4、一直这样循环处理,直到最后一步
#include<iostream> #include<stdlib.h> using namespace std; struct node { int x; node* next;//指向结构体的一个指针 }; node *Head, *End; void add(int m) { node *temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));//强制类型转换+分配地址空间 //节点赋值,m是一个整数型的值,要把它变成结构体类型才能放进链表里 temp->x = m; temp->next = NULL; if (Head== NULL)//头指针为空,说明链表为空,那么temp即是头指针,也是尾指针 { Head = temp; End = temp; } else { //链表不为空的情况,让尾指针指向当前节点,同时尾指针后移,为下一次添加节点准备 End->next = temp; End = temp; //上面的是尾插,即在链表尾部加入节点 //如果在链表头部加入节点,让头指针指向当前节点,同时头指针前移就可以 //Head->next=temp; //Head=temp; } } void change() { node *now=Head->next;//保存头指针后的第一个节点 Head->next=NULL;//将头指针的下一个节点指向空 node *temp=NULL;//temp是反转后的第一个节点的指针 while(now!=NULL) { node *tp=now->next;//tp保存下一个节点 now->next=temp; temp=now; now=tp; } Head->next=temp; } int main() { Head = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); End = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); Head->next = NULL; End = Head; int n, m; cin>>n; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { cin>>m; add(m); } change(); node *temp=Head->next; while(temp!=NULL) { cout<<temp->x<<' '; temp=temp->next; } cout<<endl; return 0; }
二、递归(从尾开始反转)
1、通过now->next往下递归,直到最后一个节点
2、将最后一个节点指向前一个节点,同时将反转后的表头指针指向NULL,一直处理到最后
举个例子,同上链表
首先指针H迭代到底如下图所示,并且设置一个新的指针作为翻转后的链表的头(NewH)。由于整个链表翻转之后的头就是最后一个数,所以整个过程NewH指针一直指向存放5的地址空间。
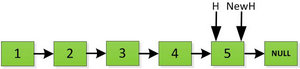
然后H指针逐层返回的时候依次做下图的处理,将H指向的地址赋值给H->next->next指针
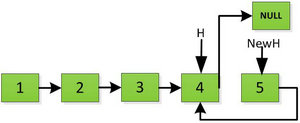
继续返回操作:
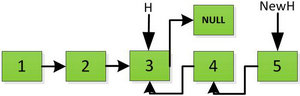
上图第一次如果没有将存放4空间的next指针赋值指向NULL,第二次H->next->next=H,就会将存放5的地址空间覆盖为3,这样链表一切都大乱了。接着逐层返回下去,直到对存放1的地址空间处理。
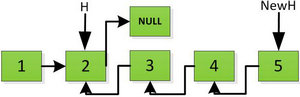
返回到头:
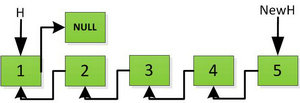
图片转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/FX677588/article/details/72357389
#include<iostream> #include<stdlib.h> using namespace std; struct node { int x; node* next;//指向结构体的一个指针 }; node *Head, *End; void add(int m) { node *temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));//强制类型转换+分配地址空间 //节点赋值,m是一个整数型的值,要把它变成结构体类型才能放进链表里 temp->x = m; temp->next = NULL; if (Head== NULL)//头指针为空,说明链表为空,那么temp即是头指针,也是尾指针 { Head = temp; End = temp; } else { //链表不为空的情况,让尾指针指向当前节点,同时尾指针后移,为下一次添加节点准备 End->next = temp; End = temp; //上面的是尾插,即在链表尾部加入节点 //如果在链表头部加入节点,让头指针指向当前节点,同时头指针前移就可以 //Head->next=temp; //Head=temp; } } node* find(node *now) { if(now==NULL||now->next==NULL) return now; else { node *pre=find(now->next);//先递归找now的后一个节点pre,直到pre->next为NULL(也就是说pre是倒数第二个节点) //然后从后面开始往前反转 now->next->next=now;//然后把pre的下一个节点指向now,这里就实现了反转 now->next=NULL;//把当前节点指向空 return pre;//pre是链表反转后的头指针 } } int main() { Head = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); End = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); Head->next = NULL; End = Head; int n, m; cin>>n; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { cin>>m; add(m); } node *temp=find(Head->next); while(temp!=NULL) { cout<<temp->x<<' '; temp=temp->next; } cout<<endl; return 0; }
三、翻转区间[n,m]位置上的链表
例如链表1->2->3->4->5->NULL
翻转[2,4]
翻转后为1->4->3->2->5->NULL
#include<iostream> #include<string.h> using namespace std; struct ListNode { int x; ListNode *next; }; ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) //head是无头指针链表,例如:1—>2->3->NULL { ListNode* res=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); res->next=head; ListNode *pre=res; //找到第m-1个结点 for(int i=1;i<m;++i) { pre=pre->next; } //找到第m个结点 ListNode* cur=pre->next,*pm=pre->next; //利用头插法进行反转 for(int i=m;i<=n;++i) { ListNode *temp=cur->next;//临时保存当前结点的下一个结点信息 cur->next=pre->next;//pre->next是第m个位置的结点,相当于翻转链表的头指针 pre->next=cur;//头指针后移 cur=temp; } //第m个节点指向n+1个结点 pm->next=cur; return res->next; } int main() { ListNode *head, *end; head = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode)); end = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode)); head->next = NULL; end = head; int t, n, m, x; cin >> t; cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) { cin >> x; ListNode* temp = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode)); temp->x = x; temp->next = NULL; end->next = temp; end = temp; } //cout<<head->x<<' '<<head->next->x<<endl; ListNode *temp = reverseBetween(head->next, n, m); while (temp!=NULL) { cout << temp->x << ' '; temp = temp->next; } cout << endl; return 0; }