There are some beautiful girls in Arpa’s land as mentioned before.
Once Arpa came up with an obvious problem:
Given an array and a number x, count the number of pairs of indices i, j (1 ≤ i < j ≤ n) such that 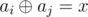 , where
, where  is bitwise xor operation (see notes for explanation).
is bitwise xor operation (see notes for explanation).

Immediately, Mehrdad discovered a terrible solution that nobody trusted. Now Arpa needs your help to implement the solution to that problem.
First line contains two integers n and x (1 ≤ n ≤ 105, 0 ≤ x ≤ 105) — the number of elements in the array and the integer x.
Second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 105) — the elements of the array.
Print a single integer: the answer to the problem.
2 3
1 2
1
6 1
5 1 2 3 4 1
2
In the first sample there is only one pair of i = 1 and j = 2. 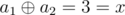 so the answer is 1.
so the answer is 1.
In the second sample the only two pairs are i = 3, j = 4 (since 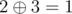 ) and i = 1, j = 5 (since
) and i = 1, j = 5 (since  ).
).
A bitwise xor takes two bit integers of equal length and performs the logical xor operation on each pair of corresponding bits. The result in each position is 1 if only the first bit is 1 or only the second bit is 1, but will be 0 if both are 0 or both are 1. You can read more about bitwise xor operation here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bitwise_operation#XOR.
题意:
n个数,问这n个数中有几对数异或运算后结果是x。
代码:
1 //c=a^b,a=c^b,b=a^c.用一个数组记录每个数出现的次数,每输入一个数将其与x异或运算得到的新数是否是前面输入过的, 2 //如果是,答案就加上该数出现的次数 3 #include<bitsstdc++.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 int a[100005],b[100005]; 6 int main() 7 { 8 int n,x; 9 memset(b,0,sizeof(b)); 10 long long ans=0; 11 scanf("%d%d",&n,&x); 12 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 13 { 14 scanf("%d",&a[i]); 15 int tem=a[i]^x; 16 if(tem>100000) continue;//不会出现大于100000的数 17 ans+=b[tem]; 18 b[a[i]]++; 19 } 20 printf("%lld ",ans); 21 return 0; 22 }
As you have noticed, there are lovely girls in Arpa’s land.
People in Arpa's land are numbered from 1 to n. Everyone has exactly one crush, i-th person's crush is person with the number crushi.

Someday Arpa shouted Owf loudly from the top of the palace and a funny game started in Arpa's land. The rules are as follows.
The game consists of rounds. Assume person x wants to start a round, he calls crushx and says: "Oww...wwf" (the letter w is repeated t times) and cuts off the phone immediately. If t > 1 then crushx calls crushcrushx and says: "Oww...wwf" (the letter w is repeated t - 1 times) and cuts off the phone immediately. The round continues until some person receives an "Owf" (t = 1). This person is called the Joon-Joon of the round. There can't be two rounds at the same time.
Mehrdad has an evil plan to make the game more funny, he wants to find smallest t (t ≥ 1) such that for each person x, if x starts some round and y becomes the Joon-Joon of the round, then by starting from y, x would become the Joon-Joon of the round. Find such t for Mehrdad if it's possible.
Some strange fact in Arpa's land is that someone can be himself's crush (i.e. crushi = i).
The first line of input contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100) — the number of people in Arpa's land.
The second line contains n integers, i-th of them is crushi (1 ≤ crushi ≤ n) — the number of i-th person's crush.
If there is no t satisfying the condition, print -1. Otherwise print such smallest t.
4
2 3 1 4
3
4
4 4 4 4
-1
4
2 1 4 3
1
In the first sample suppose t = 3.
If the first person starts some round:
The first person calls the second person and says "Owwwf", then the second person calls the third person and says "Owwf", then the third person calls the first person and says "Owf", so the first person becomes Joon-Joon of the round. So the condition is satisfied if x is 1.
The process is similar for the second and the third person.
If the fourth person starts some round:
The fourth person calls himself and says "Owwwf", then he calls himself again and says "Owwf", then he calls himself for another time and says "Owf", so the fourth person becomes Joon-Joon of the round. So the condition is satisfied when x is 4.
In the last example if the first person starts a round, then the second person becomes the Joon-Joon, and vice versa.
题意:
大小为n的数组a,a[i]表示从i点能一步到a[i]点,问有没有这样的一个最小的数t使得每一个a[i]满足从a[i]点走t步到a[j]点,从a[j]点走t步到达a[i]点。a[i]==i是允许的
代码:
1 //枚举起点,如果从该点出发向下找,回不到到改点即在改点后面的某几个点之间循环说明无答案,如果从该点出发经过x步之后 2 //又回到了改点说明改点合法,如果x是奇数说明循环的点就是改点,如果x是偶数说明循环的点是改点和x/2处的某一点 3 //找出每个点需要的循环步数取最小公倍数就是答案。 4 #include<bitsstdc++.h> 5 using namespace std; 6 int gcd(int x,int y) 7 { 8 if(y==0) return x; 9 return gcd(y,x%y); 10 } 11 int lcm(int x,int y) 12 { 13 return (x/gcd(x,y))*y; 14 } 15 int main() 16 { 17 int n,a[102],vis[102],ans=1; 18 scanf("%d",&n); 19 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 20 scanf("%d",&a[i]); 21 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 22 { 23 if(n==1&&a[1]!=1) //只有一个点的情况特殊考虑 24 {ans=-1;break;} 25 memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); 26 int x=i,tem=0; 27 while(!vis[x]) 28 { 29 vis[x]=1; 30 x=a[x]; 31 tem++; 32 } 33 if(x!=i) //如果从i点回到的是i后面的点就说明i点没有与之对应的点 34 {ans=-1;break;} 35 if(tem&1) ans=lcm(tem,ans); 36 else ans=lcm(tem/2,ans); 37 } 38 printf("%d ",ans); 39 return 0; 40 }