什么是策略模式
策略模式是对算法的包装,是把使用算法的责任和算法本身分割开来,委派给不同的对象管理,最终可以实现解决多重if判断问题。
1.环境(Context)角色:持有一个Strategy的引用。
2.抽象策略(Strategy)角色:这是一个抽象角色,通常由一个接口或抽象类实现。此角色给出所有的具体策略类所需的接口。
3.具体策略(ConcreteStrategy)角色:包装了相关的算法或行为。
定义策略接口->实现不同的策略类->利用多态或其他方式调用策略
为什么叫做策略模式
每个if判断都可以理解为就是一个策略。
策略模式优缺点
优点
算法可以自由切换(高层屏蔽算法,角色自由切换)
避免使用多重条件判断(如果算法过多就会出现很多种相同的判断,很难维护)
扩展性好(可自由添加取消算法 而不影响整个功能)
缺点
策略类数量增多(每一个策略类复用性很小,如果需要增加算法,就只能新增类)
所有的策略类都需要对外暴露(使用的人必须了解使用策略,这个就需要其它模式来补充,比如工厂模式、代理模式)
策略模式应用场景
聚合支付平台
比如搭建聚合支付平台的时候,这时候需要对接很多第三方支付接口,比如支付宝、微信支付、小米支付等。
通过传统if代码判断的,后期的维护性非常差!
Spring框架中使用的策略模式
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext Spring底层Resource接口采用策略模式
Spring 为 Resource 接口提供了如下实现类:
UrlResource:访问网络资源的实现类。
ClassPathResource:访问类加载路径里资源的实现类。
FileSystemResource:访问文件系统里资源的实现类。
ServletContextResource:访问相对于 ServletContext 路径里的资源的实现类:
InputStreamResource:访问输入流资源的实现类。
ByteArrayResource:访问字节数组资源的实现类。
1、new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("");
2.进入该构造函数。

3.
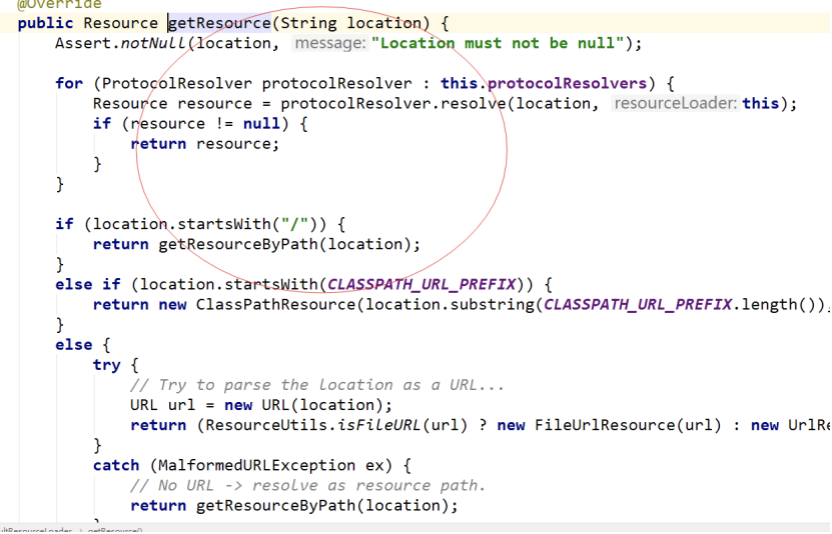
4.SpringBean初始化 SimpleInstantiationStrategy

SimpleInstantiationStrategy 简单初始化策略
CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy CGLIB初始化策略
策略模式架构图
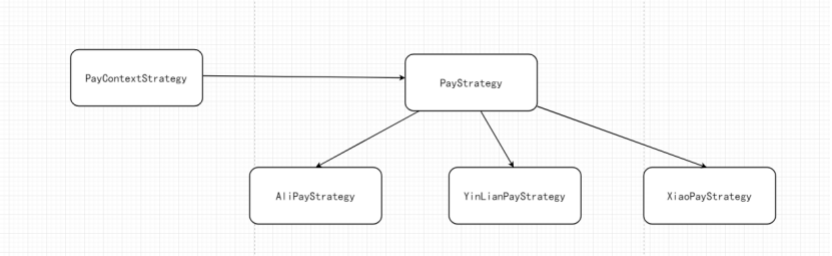
策略模式环境搭建
创建项目名称 springboot_ strategy
Maven依赖信息
1 <parent> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> 4 <version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version> 5 </parent> 6 <dependencies> 7 <!-- sprinboot web --> 8 <dependency> 9 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 10 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 11 </dependency> 12 <dependency> 13 <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> 14 <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> 15 <version>1.16.10</version> 16 </dependency> 17 <dependency> 18 <groupId>commons-lang</groupId> 19 <artifactId>commons-lang</artifactId> 20 <version>2.6</version> 21 </dependency> 22 <dependency> 23 <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> 24 <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> 25 <version>1.1.1</version> 26 </dependency> 27 <!-- mysql 依赖 --> 28 <dependency> 29 <groupId>mysql</groupId> 30 <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> 31 </dependency> 32 </dependencies>
PayStrategy(抽象角色)
1 public interface PayStrategy { 2 3 /** 4 * 共同算法实现骨架 5 * @return 6 */ 7 public String toPayHtml(); 8 }
ConcreteStrategy (具体实现角色)
1 @Component 2 public class AliPayStrategy implements PayStrategy { 3 public String toPayHtml() { 4 return "调用支付宝支付接口"; 5 } 6 }
1 @Component 2 public class XiaoMiPayStrategy implements PayStrategy { 3 public String toPayHtml() { 4 return "调用小米支付接口"; 5 } 6 }
PayContextService (上下文)
@RestController public class PayContextService { @Autowired private PaymentChannelMapper paymentChannelMapper; @Autowired private SpringUtils springUtils;
@RequestMapping("/toPayHtml") public String toPayHtml(String payCode){ // 1.验证参数 if(StringUtils.isEmpty(payCode)){ return "payCode不能为空!"; } // 2.使用PayCode查询 PaymentChannelEntity paymentChannel = paymentChannelMapper.getPaymentChannel(payCode); if(paymentChannel==null){ return "该渠道为空..."; } // 3.获取策略执行的beanid String strategyBeanId = paymentChannel.getStrategyBeanId(); // 4.使用strategyBeanId获取对应spring容器bean信息 PayStrategy payStrategy = springUtils.getBean(strategyBeanId, PayStrategy.class); // 5.执行具体策略算法 return payStrategy.toPayHtml(); } }
SpringUtils(工具类)
1 @Component 2 public class SpringUtils implements ApplicationContextAware { 3 4 private static ApplicationContext applicationContext; 5 6 @Override 7 public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { 8 this.applicationContext = applicationContext; 9 } 10 11 //获取applicationContext 12 public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() { 13 return applicationContext; 14 } 15 16 //通过name获取 Bean. 17 public static Object getBean(String name){ 18 return getApplicationContext().getBean(name); 19 } 20 21 //通过class获取Bean. 22 public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz){ 23 return getApplicationContext().getBean(clazz); 24 } 25 26 //通过name,以及Clazz返回指定的Bean 27 public static <T> T getBean(String name,Class<T> clazz){ 28 return getApplicationContext().getBean(name, clazz); 29 } 30 31 }
枚举类
1 public enum PayEnumStrategy { 2 3 /** 4 * 支付宝支付 5 */ 6 ALI_PAY("com.mayikt.strategy.impl.AliPayStrategy"), 7 /** 8 * 银联支付 9 */ 10 UNION_PAY("com.mayikt.strategy.impl.UnionPayStrategy"); 11 PayEnumStrategy(String className) { 12 this.setClassName(className); 13 } 14 15 public String getClassName() { 16 return className; 17 } 18 19 public void setClassName(String className) { 20 this.className = className; 21 } 22 23 /** 24 * class完整地址 25 */ 26 private String className; 27 28 }
StrategyFactory
1 public class StrategyFactory { 2 public static PayStrategy getPayStrategy(String strategyType) { 3 try { 4 // 1.获取枚举中className 5 String className = PayEnumStrategy.valueOf(strategyType).getClassName(); 6 // 2.使用java反射技术初始化类 7 return (PayStrategy) Class.forName(className).newInstance(); 8 } catch (Exception e) { 9 return null; 10 } 11 } 12 }
数据库访问层
相关SQL语句:
1 DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `payment_channel`; 2 CREATE TABLE `payment_channel` ( 3 `ID` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'ID', 4 `CHANNEL_NAME` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '渠道名称', 5 `CHANNEL_ID` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '渠道ID', 6 `strategy_bean_id` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '策略执行beanid', 7 PRIMARY KEY (`ID`,`CHANNEL_ID`) 8 ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='支付渠道 '; 9 10 -- ---------------------------- 11 -- Records of payment_channel 12 -- ---------------------------- 13 INSERT INTO `payment_channel` VALUES ('4', '支付宝渠道', 'ali_pay', 'aliPayStrategy'); 14 INSERT INTO `payment_channel` VALUES ('5', '小米支付渠道', 'xiaomi_pay', 'xiaoMiPayStrategy');
实体类
1 @Data 2 public class PaymentChannelEntity { 3 /** ID */ 4 private Integer id; 5 /** 渠道名称 */ 6 private String channelName; 7 /** 渠道ID */ 8 private String channelId; 9 /** 10 * 策略执行beanId 11 */ 12 private String strategyBeanId; 13 14 }
数据库访问层
1 public interface PaymentChannelMapper { 2 @Select(" " + 3 "SELECT id as id ,CHANNEL_NAME as CHANNELNAME ,CHANNEL_ID as CHANNELID,strategy_bean_id AS strategybeanid " + 4 "FROM payment_channel where CHANNEL_ID=#{payCode}") 5 public PaymentChannelEntity getPaymentChannel(String payCode); 6 }
优点:策略模式最终帮助我们解决在实际开发中多重if判断问题、提高扩展性、维护性增强、提高代码可读性。
缺点:后期维护不同策略类是非常多、定义类比较多、代码量增大。
优点大于缺点。